* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Cyclic nucleotide–gated ion channel wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
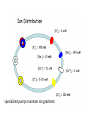
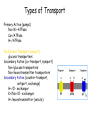
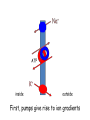
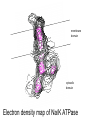
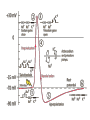
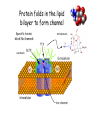
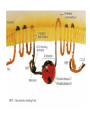
M1 Spring 2009 28 April9 00 AM Membrane Potential and Ion Channels Louis J De Felice, PhD Physiology and Biophysics specialized channels conduct ions specialized pumps maintain ion gradients Pumps are transporters Types of Transport Primary Active (pumps) Na+/K+-ATPase Ca+/ATPase H+/ATPase Facilitated Transport (uniport) glucose transporters Secondary Active (co-transport, symport) Na+/glucose transporters Na+/neurotransmitter transporters Secondary Active (counter-transport, antiport, exchange) H+/Cl- exchanger K+/Na+/Cl- exchanger H+/neurotransmitter (vesicle) membrane domain cytosolic domain Electron density map of Na/K ATPase The resting potential is a weighted sum of Nernst potentials for different channels Vrp = GK EK + GNa ENa + … GK + GNa + … = -60 mV GPA is a weighted sum GPA = 4 (3.0)+ 1 (4.0) 4+1 = 3.2 Protein folds in the lipid bilayer to form channel Specific toxins block Na channels saxatoxin tetrodatoxin Water in K channels How information integrates and propagates in the nervous system