* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solving Mania KCAS: 7.EE.4, 8.EE.7, A.SSE.1, A.CED.4, A.REI.1, A
Survey
Document related concepts
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
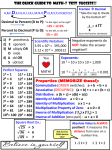
Solving Mania KCAS: 7.EE.4, 8.EE.7, A.SSE.1, A.CED.4, A.REI.1, A.REI.3 Operations with Integers 7.NS.1 The mathematical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Absolute Value is the distance from the ORIGIN on a number line. Absolute Value is NEVER NEGATIVE. Integers are the whole numbers and their additive inverses (opposites). 0, ±1, ±2, ±3, … ADDITION pos + pos = pos neg + neg = neg Pos + neg = ??? To add numbers with different signs, THINK of it like subt of abs values & take the sign of number with greater abs value. SUBTRACTION MULTIPLICATION pos * pos = pos neg * neg = pos pos * neg = neg neg * pos = neg DIVISION pos ÷ pos = pos neg ÷ neg = pos pos ÷ neg = neg neg ÷ pos = neg Use the definition of subtraction, and THEN follow addition rules Factor * Factor = Product Do integer quizzes using rules above, pictures, or common sense An equation is a mathematical sentence that contains an = (equal sign). It can be solved or graphed. There are absolute value equations like |x| = 7. There are literal equations that contain 2 or more variables (like formulas, y=2x+3, etc.). There are linear equations that graph as lines and are first degree (degree is exponent on variable). y=x There are quadratic equations that graph as parabolas (U-like smooth curves) and are second degree. y=x2 There are cubic equations that graph as “S-like” smooth curves and are third degree. y=x3 An inequality is a mathematical sentence that contains a < ≤ > ≥ ≠ < ≤ > ≥ (inequality symbol). It can be solved or graphed. < is read in words as “IS less than.” ≥ is read in words as “IS greater than or equal to.” ≠ is read in words as “IS NOT equal to.” In math, “less than” means subtract and “greater than” means add. 2 less than 3 means 3-2. 2 is less than 3 means 2 < 3. Terms: Separated by addition or subtraction signs NOT IN PARENTHESES. Like Terms: Sep by + or – signs not in ( ) AND their variables and the exponents on those variables match exactly. You can add and subtract like terms only. You can multiply anything. 3x2 + 4x2 = 7x2 3x2 * 4x2 = 12x4 3x2 + 4x3 cannot add because the two terms are NOT alike 3x2 * 4x3 = 12x5 Coefficient: a number that is multiplied by a variable. It is typically written in front of the variable. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8 steps to solve linear equations OR inequalities *******GOAL: isolate the variable for which you are solving!!!******* * Means step is OPTIONAL. * Use the definition of subtraction to change – to + - of the subtrahend. * Clear fractions by multiplying EACH TERM on both sides of the eqn/ineq by the LCD of ALL fractions. Clear decimals by multiplying EACH TERM on both sides of eqn/ineq by the proper power of 10 that would eliminate ALL decimals. Use the distributive property to clear parentheses. Combine Like Terms on the LEFT of the = or ineq. Combine Like Terms on the RIGHT side of the = or ineq. Get all terms containing the variable on only one side of the = or ineq by using the additive inverse property. Make sure to add the same thing to BOTH sides of the = or ineq. Use the additive inverse property to isolate the variable term (get rid of the constant term). Make sure to add the same thing to BOTH sides of the eqn or ineq. Use the multiplicative inverse property to isolate the variable. Make sure to multiply BOTH sides of the eqn or ineq by the same thing. ***REMEMBER that if you MULTIPLY or divide both sides of an INEQUALITY by a NEGATIVE number that you must reverse the direction of the inequality symbol!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! CHECK YOUR SOLUTION. Substitute your solution into the original eqn/ineq and see if it makes a true eqn/ineq. When solving linear equations, you can get the following “types” of results: I. X=4. This means you have one solution, and it is 4. II. -4 = 4 or 2=7 or 0=6, etc. If you get something untrue like this, there are NO SOLUTIONS to your equation. III. 4 = 4 or 2=2 or -6=-6, etc. If you get something always true like this, there are INFINITELY MANY solutions to your equation, and they are ALL REAL NUMBERS. That means any real number when substituted in for the variable will produce a true equation. WHEN SOLVING ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATIONS, YOUR GOAL IS TO ISOLATE THE ABS VALUE AND THEN MAKE AN “OR” STATEMENT. If |x|=7, then x=7 OR x=-7. If |x|=0, then x=0 If |x|=-3, then there are NO SOLUTIONS because abs val can’t yield a neg. When solving abs value inequalities, use the acronym GOLA. When solving literal equations, follow the 8 steps above.