* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
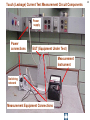
Download Touch (Leakage) Current Test
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Aluminium-conductor steel-reinforced cable wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
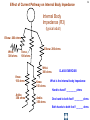
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
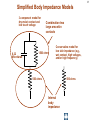
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
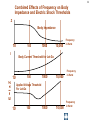
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
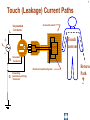
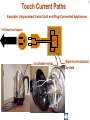
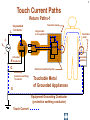
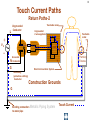
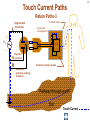
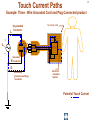
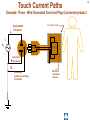
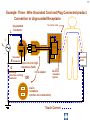
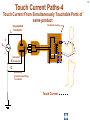
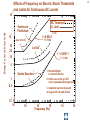
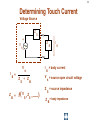
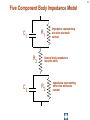
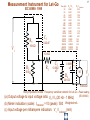
Hazard Based Safety Engineering - Touch (Leakage) Current 2 Touch (Leakage) Current Overall Session Objectives: 1. To understand the rationale for the Touch (leakage) Current Test, instrumentation, connections, test procedures and limits 2. To understand limitations of test and alternative approaches 3 Touch (Leakage) Current Topics • Definitions (UL 101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch current (electric shock) • Body impedance models and “safe” voltage limits • Touch (Leakage) Current Test –Touch current instruments (meters) –Measurement circuits and procedures –Limits 4 DEFINITIONS LEAKAGE CURRENT (UL101-2002): Electric current which flows through a person upon contact, between accessible parts of an appliance and (1) ground, or (2) other accessible parts of the appliance TOUCH CURRENT (IEC 60990): Electric current through a human body or an animal body when it touches one or more accessible parts of an installation or of equipment. 5 Touch (Leakage) Current Paths L Ungrounded Conductor Accessible metal Load + VS Load _ N Grounded Conductor Electrical insulation System G Touch current Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor Return Path ? Touch Current Paths 6 Example: Ungrounded 2 wire Cord and Plug-Connected Appliances Load To Electrical Supply Load touchable metal Electrical Insulation System 7 radio Can opener TV Toaster oven blender Examples of 2-wire Non-Grounded Appliances Coffee iron maker 8 Touch Current Paths Return Paths-1 L Ungrounded Conductor Ungrounded 2 wire appliance Touchable metal Load + Touchable metal VS Load _ Grounded appliance Grounded N Conductor G Electrical insulation System Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor G Touchable Metal of Grounded Appliances Equipment Grounding Conductor (protective earthing conductor) Touch Current 9 microwave Coffee maker radio TV blender range Can opener Toaster oven refrigerator dishwasher Examples of 2-wire Non-Grounded Appliances Examples of 3-wire Grounded Appliances iron 10 Touch Current Paths Return Paths-2 L Touchable metal Ungrounded Conductor Ungrounded 2 wire appliance Load + Touchable metal VS Load _ Plumbing Fixtures Grounded N Conductor G Electrical insulation System Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor Construction Grounds G Bonding connection to water pipe Metallic Piping System Touch Current 11 microwave Coffee maker radio TV blender Sink range Can opener Toaster oven refrigerator dishwasher Baseboard heating Examples of 2-wire Non-Grounded Appliances Examples of 3-wire Grounded Appliances Examples of Construction Grounds iron 12 Touch Current Paths Return Paths-3 L Ungrounded Conductor Touchable metal Ungrounded 2 wire appliance Load + VS Load _ Grounded N Conductor G Electrical insulation System Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor Pathway through earth Soil Touch Current 13 Touch Current Paths Example: Three - Wire Grounded Cord and Plug Connected product L Ungrounded Conductor Load + Touchable metal VS Load _ Grounded N Conductor G Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor Electrical insulation System Potential Touch Current Touch Current Paths Example: Three - Wire Grounded Cord and Plug Connected product L Ungrounded Conductor Load + Touchable metal VS Load _ Grounded N Conductor G Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor Electrical insulation System 14 15 Example: Three - Wire Grounded Cord and Plug Connected product Connection to Ungrounded Receptacle L Touchable metal Ungrounded Conductor + VS Load _ Grounded N Conductor G Grounded metal Open circuit or high impedance (fault) Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor 3 to 2 adapter OR Electrical insulation System 2-wire receptacle (normal- old construction) Touch Current 16 Touch Current Paths-4 Touch Current From Simultaneously Touchable Parts of same product L Ungrounded Conductor Load + touchable metal VS Load _ Grounded N Conductor G Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor Touch Current Z 17 Touch (Leakage) Current Topics • Definitions (UL 101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch (electric shock) current 18 Physiological Effects of Touch Current (sinusoidal, rms, 60 Hz) • Perception (microamperes to 0.5 mA) • Startle reaction (> 0.5 mA) • Muscle tetanization (inability to let go) (> 5 mA) • Ventricular fibrillation (> 50 mA) • Electrical burns (> 70 mA) V10-001 3 19 Effects of Frequency on Electric Shock Thresholds and Limits for Continuous AC current Body Current (rms mA) 10 IEC Threshold UL Limit Ventricular Fibrillation 10 2 I = 0.954 f 0.716 f > 70 Hz (see note 3) 35 20 2 Let-Go I ~ 0.0007 f 10 f > 1 kHz 5 1. threshold/limit = 2 mA at 0 Hz (dc) 1 Startle Reaction 1 2. In the case of let-go, IEC curve represents average value 0.5 3. respiratory arrest observed in dogs at 20, 30, and 40 mA -1 10 10 10 2 3 4 10 10 Frequency (Hz) 5 10 6 10 20 Other Touch Current Variables • Waveshape* • Duration* • Current Density • Pathway through body • (skin contact location) * See Special Situations for Touch Current Measurements V10-015 21 Touch (Leakage) Current Topics • Definitions (UL 101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch current (electric shock) • Body impedance models and “safe” voltage limits 22 Determining Touch Current Voltage Source Z S + V s_ V I B Z I s = Z S + Z B V Z = B f ( V S , Z S , .....) B = body current s = source open circuit voltage B Z B I S Z B = source impedance = body impedance 23 Five Component Body Impedance Model C R 1 1 R Internal body impedance (less the skin) 3 C 2 Impedance representing one skin-electrode contact R 2 Impedance representing other skin-electrode contact Effect of Current Pathway on Internal Body Impedance 24 Internal Body Impedance (R3) (typical adult) Elbow- 200 ohms Elbow- 200 ohms Wrist300 ohms Torso100 ohms Wrist300 ohms Knee150 ohms Knee150 ohms CLASS EXERCISE: What is the internal body impedance: Hand to hand? _________ohms Ankle350 ohms Ankle350 ohms One hand to both feet? ________ohms Both hands to both feet? ______ ohms 25 Simplified Body Impedance Models 3-component model for dry-moist contact and low touch voltage 0.22 Microfarad Combination two large area skin contacts 1500 ohms Conservative model for low skin impedance (e.g., wet contact, high voltages, and/or high frequency) 500 ohms 500 ohms Internal body impedance 26 Combined Effects of Frequency on Body Impedance and Electric Shock Thresholds Z Body Impedance 10 I 100 1000 10,000 Frequency in Hertz Body Current Threshold for Let-Go E=IxZ 10 100 1000 10,000 Frequency in Hertz Applied Voltage Threshold For Let-Go 10 100 1000 10,000 Frequency in Hertz Examples of "Safe" Voltage Criteria (Check the specific end-product standard) Let-go and fibrillation, dry locations (UL, NEC) 30 V AC rms (< 100 Hz) 60 V DC Let-go and fibrillation, wet locations, not including immersion (UL, NEC) 15 V AC rms (< 100 Hz) 30 V DC Immersion conditions Dry locations where startle reaction cannot be tolerated (UL) Generally no “safe” voltages 42.4 V peak (< 100 Hz) (including dc) IEC SELV circuits: normal conditions and single fault conditions for time > 0.2 sec 42.4 V peak (< 100 Hz) 60 V DC single fault conditions for time < 0.2 sec 71 V peak (< 100 Hz) 120 V DC 27 28 Electrical Insulation: Basic Equipment Safeguard Against Electric Shock Zs ZI + Vs Vs _ = source voltage Zs = source impedance Hazardous voltage and current source: IT ZB IS ZI = insulation impedance ZB = body impedance IS = available source current IT = Touch current VS exceeds “safe” voltage AND IS = VS / Zs exceeds “safe” available current 29 Basic Tests on Electrical Insulation Electrical insulation model Insulation Resistance Test Touch (Leakage) Current Test Dielectric Withstand Test (Hi-pot) 30 Touch (Leakage) Current Topics • Definitions (UL 101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch current (electric shock) • Body impedance models and “safe” voltage limits • Touch (Leakage) Current Test –Touch current instruments (meters) 31 Touch (Leakage) Current Test L Ungrounded Conductor Accessible metal MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT Load + VS Load _ N Grounded Conductor Electrical insulation System G Grounding (protective earthing) Conductor • applies when source exceeds “safe” voltage levels • represent body impedance as function of frequency • represent physiological effect as a function of frequency 32 Selection of Measurement Instrument Instrument Specifications SPECIFICATIONS FOR REACTION: (0.5 mA rms limit @ 60 Hz) ANSI C101- 1986 - Average Responding System (ARS) (Still specified in most UL standards) UL 101- 2002 (Replaced ANSI C101)(Specified in some UL end product standards and most harmonized UL standards) IEC 60990 – 1999 SPECIFICATIONS FOR LET-GO: (3.5 mA rms, 5 mA rms limits @ 60 Hz) IEC 60990 - 1999 SPECIFICATIONS FOR ELECTRICAL BURNS: UL101- 2002 IEC 60990 - 1999 (70 mA rms) 33 Measurement Instrument Specifications for Reaction Average Responding System (ARS) (ANSI C101- 1986) R1 Ammeter M (average responding) 1500 Ω C1 0.15 u F (a) Input impedance (Z) (intended to combine effect of frequency on body impedance and physiological response) (b) Meter type and location 34 Measurement Instrument Specifications for Reaction Average Responding System (ARS) (ANSI C101- 1986) IA = actual current to network I1 = indicated current to network ( = V1/R1 rms for sinusoid) IA II / IA = Z / R1 V1 I1 R1 1500 Ω C1 0.15 Z = R1par C1(0 - 100 kHz) VM M uF (a) Input impedance (Z) (combines effect of frequency on body (b) Meter type and location impedance and physiological response) (c) Meter indication (d) Circuit frequency response ( 0 to 100 kHz) Voltmeter (average responding) Indication (current) = 1.11 x VM (ave)/1500 = I 1 = V1 / R1 ( rms for sinusoid) Max 5% error @ indication of 0.75 mA 35 Simpson Model 229 (ANSI C101- 1986) Revised Measurement Instrument for ReactionV / I Freq (Hz) UL 101-1992, IEC 60990- 1999 20 1998 I1 50 1990 1 R1 1500 Ω V1 C1 0.22uF 60 100 200 500 1000 2000 5000 10000 20000 50000 100000 200000 500000 1000000 36 1 1986 1961 1857 1433 973 661 512 485 479 477 476 476 476 476 V1 / IIndicated V 3 / I1 500 499 498 495 480 405 284 162.9 68.3 34.4 17.21 6.89 3.45 1.722 0.680 0.345 2.00 2.00 1.99 1.98 1.93 1.77 1.71 2.03 3.75 7.06 13.9 34.6 69.1 138 346 691 10 K Ω R2 500 Ω R3 0.022 u F C2 M V3 Voltmeter Revised body impedance model Frequency sensitive network for reaction Rms reading (UL101) (a) Input impedance (UL 101): Z= V1 / I1 (20 Hz - 1 MHz) Peak reading (b) Transfer impedance (UL101): Z= V3 / I1 (IEC 60990) (c) Meter indication (IIndicated): = V3 / R2 = V3 / 500 (weighted mA -IEC 60990; (d) Input voltage per mA indication (IEC 60990): V1 / I Indicated (mA) MIU- ANSI C101) Measurement Instrument for Let-Go IEC 60990- 1999 R1 1500 Ω V1 C1 0.22 uF 37 V3 / V 1 Freq (Hz) 20 50 60 100 200 500 1000 2000 5000 10000 20000 50000 100000 200000 500000 1000000 V1 / IIndicated 0.250 0.251 0.251 0.253 0.261 0.298 0.348 0.377 0.280 0.164 0.0860 0.0349 0.0175 0.00874 0.00350 0.00175 2.00 1.99 1.99 1.98 1.92 1.68 1.44 1.33 1.79 3.04 5.81 14.3 28.6 57.2 143 286 10 K Ω R2 500 Ω R3 C2 0.0091 uF 0.0062 uF C3 R4 M V3 20 K Ω Voltmeter Body impedance model Frequency Frequency sensitive sensitive network network for for Let-Go reaction Peak reading (a) Output voltage to input voltage ratio: V3 / V1 (20 Hz - 1 MHz) (b) Meter indication (scale): IIndicated = V3 (peak) / 500 Weighted mA (c) Input voltage per milliampere indication: V1 / Iindicated (mA) (IEC 60990) 38 39 Touch (Leakage) Current Topics • Definitions (UL101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch current (electric shock) • Body impedance models and “safe” voltage limits • Touch (Leakage) Current Test –Touch current instruments (meters) –Measurement circuits and procedures Touch (Leakage) Current Test Measurement Circuit Components Power supply Power connections EUT (Equipment Under Test) Measurement Instrument Switching network Measurement Equipment Connections 40 41 Measurement Circuit for 120 Volt Equipment Switching Network UL101 L Polarity reversing switch EQUIPMENT UNDER TEST (EUT) S2 Power Supply A MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT B Load 120 V N A S1 B GND OPEN INSULATING TABLE Grounded conductor switch Connection to grounded supply conductor Applicable EUT Plug Configurations G G N 15 amp non-polarized 15 amp polarized 2-pole, 2-wire N N 15 amp 20 amp 2-pole, 3-wire 42 Optional transformer Measurement Circuit for 120 Volt Equipment IEC 60990 L EQUIPMENT UNDER TEST (EUT) S2 A 120 V supply MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT B Load 120 V N S1 G S3 A B < 1% line voltage For 3-wire applications Applicable EUT Plug Configurations G G 15 amp 20 amp N 15 amp non-polarized 15 amp polarized 2-pole, 2-wire 2-pole, 3-wire 43 Measurement circuit for 2- pole 208 or 230-240 Volt equipment suitable for use on 230-240 volt to ground circuit (U.S.Commercial / Industrial) (European 230/400 v residential) L Polarity reversing switch EQUIPMENT UNDER TEST (EUT) S2 Power Supply A MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT B 208 or 230-240 V Load A S1 L N B GND OPEN INSULATING TABLE Line Switch Connection to grounded supply conductor Applicable U.S. EUT Plug Configurations 15 amp 20 amp 2-pole, 2-wire G G 15 amp 20 amp 2-pole, 3-wire Measurement circuit for 2- pole 208 and 240 volt equipment for connection only to 120 volts to ground circuits (120/208, 120/240) (U.S.Residential) Power Supply Polarity reversing switch L EQUIPMENT UNDER TEST (EUT) S2 A 120 V B N 208 or 240 V Load 120 V L A S1 B GND OPEN Line Switch INSULATING TABLE Connection to grounded supply conductor Applicable U.S. EUT Plug Configurations 15 amp 20 amp 2-pole, 2-wire G G 15 amp 20 amp 2-pole, 3-wire MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT 44 Measurement circuit for single phase, 3- pole, 208 or 240 Volt Equipment (e.g., electric ranges, clothes dryers) Polarity reversing switch L Power Supply S2 A 120 V 208 or 240 V GND OPEN EQUIPMENT UNDER TEST (EUT) MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT B N Load 120 V S1 A B L INSULATING TABLE Line and Neutral Switch Connection to grounded supply conductor Applicable U.S. EUT Plug Configurations G N G N N 20 amp 30 amp 3-pole, 3-wire N G N 15 amp 20 amp 3-pole, 4-wire 30 amp 45 46 Touch (Leakage) Current Topics • Definitions (UL 101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch current (electric shock) • Body impedance models and “safe” voltage limits • Touch (Leakage) Current Test –Touch current instruments (meters) –Measurement circuits and procedures –Limits 47 Touch (Leakage) Current Test Limits UL 101- 2002 Recommendations Type of appliance Indication in MIU Two-wire cord- and plugconnected appliance 0.50 MIU Three-wire (including grounding conductor) cord- and plug- connected portable appliance 0.50 MIU Three-wire (including grounding conductor) cord- and plug- connected stationary or fixed appliance 0.75 MIU All 70 mA rms (electric burn) 48 SUMMARY • Definitions (UL 101, IEC 60990) • Touch current paths • Physiological effects of touch current (electric shock) • Body impedance models and “safe” voltage limits • Touch (Leakage) Current Test –Touch current instruments (meters) –Measurement circuits and procedures –Limits 49 Questions and Answers 50 - END -