* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vir Hep 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
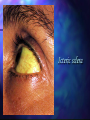
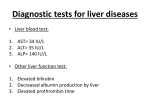
Viral Hepatitis Clinics, diagnostics, treatment and prophylaxis Asymptomatic form: the specific markers of infectious agent and proper immunological changes are exposed only Sub-clinical form: immunologic, biochemical and histological changes, however exposed clinical signs of illness are absent Non-jaundice form: appears different clinical symptoms of illness except jaundice Jaundice form: appears jaundice, which is the main sign of hepatitis Fulminant (malignant) form: extremely severe Duration of hepatitis: Acute – till 3 months; Prolonged – from 3 to 6 months; Chronic – more than 6 months. Periods of viral hepatitis, with jaundice: 1. Pre jaundice (initial , prodromal); 2. Jaundice or climax of disease; 3. Period of recovery. Pathologic syndromes of liver affection Cytolytic – ↑ ALT, LDG, Cu; ↓ albumins, protrombin Mesenchimal-inflammation – ↑ α-, γ globulins, tymol-test Cholestasis – ↑ bilirubin, bile acids, cholesterine, GGTP, alkaline phosphatase Variants of initial period: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Asteno-vegetative: general weakness, fatigue, headache, insomnia, and change in behavior; Dyspeptic: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea; Catarrhal: influenza, feeling of scratching in throat, hyperemia of conjunctiva and mucus of soft palate, dry cough, increase of body temperature; Artharalgic: characterized by pain in joints without local inflammatory changes; Mixed Criteria for severity of viral hepatitis: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Stage of intoxication; Intensity of jaundice; Liver sizes (mild – enlarged from 1 to 2 cm on right mid-clavicle line, moderate – from 3 to 5 cm, severe – 6 and more or vice versa decreases); Level of bilirubin (respectively 85 micmol/l, 86 – 170 micmol/l and >170 micmol/l); Complications; Index of albumin transport function. Clinical peculiarities of viral hepatitis A: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Short incubation period (3 – 6 weeks); Acute beginning; Mostly catarrhal syndrome in prodromal period; Short prodromal period (5 – 7 days); Quick appearance of jaundice (within some days); Improvement of self feelings with appearance of jaundice; Mild forms are predominant, severe forms occurs rarely; Jaundice period persist not more than 1-2 weeks. Clinical peculiarities if viral hepatitis B: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Long incubation period (more than 45 days, maximum – 6 months); Progressive beginning of disease; Often arthralgic syndrome in prodromal period (20 – 30 %); Prurience of skin and urticaria in prodromal period; Prodromal period often persist more than 2 weeks; Progressive appearance of jaundice, sometimes 2 weeks and more; Self feelings do not improve with appearance of jaundice; Prolonged and severe jaundice period, less than during hepatitis A; 9. Often exacerbations, remissions and complications (reason may be hepatitis D infection); 10. Presence of expressed asthenic syndrome during all clinical periods of disease, prolonged post hepatic asthenia, sometime years and more; 11. Possible transformation into chronic hepatitis (in 5 – 15% cases) and then into liver cirrhosis (in 15 – 30% patients of chronic hepatitis); 12. Hepatitis B often run on background of concomitant diseases. 8. Rashes in case of viral hepatitis Icteric sclera Skin jaundice Skin jaundice Criteria for without jaundice form of viral hepatitis : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Concrete epidemiological data (contact with patient or parenteral manipulations, which according to time are similar to maximum incubation period); Typical prodromal period; Presence of hepatic splenomegaly syndrome; Brick color of urine (lot of urobilin); High activity of serum ALT; Positive data of specific investigation (presence of infectious agent’s markers). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Signs of cholestatic form of viral hepatitis: Developed pruritis of skin; Mild intoxication or absent; Green or grey-green shade of jaundice; Liver has normal sizes or little enlarged; Activity of secretary enzymes is elevated in blood (alkaline phosphates, gammaglutamiltranspeptidase), quantity of β-lipoproteins, cholesterol and salts of bile acids; Don’t present urobilin in urine and stercobilin in stools; Little elevation or normal activity of liver cell’s enzymes; Prolonged duration – 3-5 months and more. Precursors of liver coma: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Quick increase of jaundice and intoxication; Memory disturbances; Inversion of sleep; Complaints about pain in liver region; Liver smell from mouth; Elevation in body temperature; Tremors; Appearance of hemorrhagic syndrome; Tachycardia; Decreasing of liver sizes; Bilirubin-enzymes dissociation; Elevation of nitrogen products concentration in blood; Decreasing of prothrombin index <50%; Appearance of tyrosine and lucien in urine; Periods of acute hepatic encephalopathy: 1. 2. 3. 4. Pre-coma 1, 2. Initial period of precoma (period of precursors); Finishing period of precoma (partial disorders of consciousness); Coma 1, 2. Superficial coma (loss of verbal contact with kept reactions on painful irritations); Deep coma (disappear pain reaction). Diagnostic Preliminary diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on epidemiological anamnesis finding of the development of the disease, clinical picture, duration of incubation period character of prejaundice period presence of typical subjective and objective signs with account of the patients age Diagnostic Routine blood test – lymphocytosis, anemia and leucopenia, ESR is slightly decreased In urine - urobilin and bile pigments In blood serum - bilirubinemia (direct fraction) increasing activity of ALT, ACT, testifying about the presence of cytolytic processes in the liver Diagnostic Revealing of specific antigens and antibodies to antigens in the blood Discovery of antibodies of class IgM testifies about acute disease Discovery antibodies of other classes of immunoglobulins testifies about chronic course of viral hepatitis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Differential diagnosis Influenza Food born toxic infections Acute appendicitis Leptospirosis Infection mononucleosis Pseudo-tuberculosis Malaria Toxic hepatitis Pregnancy toxicosis Hemolytic jaundice Sub-hepatic mechanical jaundice Pigmented hepatosis ( syndrome ZhielberMailengrkht, Krigler-Nayar, Dabin-Jhonsen and Rotor) Treatment Bed regime Diet № 5 Polyvitamines (A, B, E) Desensitizing drugs: calcium gluconate, Diazolin, Diprazin or Tavegil Ferment drugs: Festal, Digestal, Enzystal, Panzinorm, Pancurmen, Allochol, Cholenzym. Treatment Plentiful drink In Vein - 5 % solution of glucose, saline solutions, Ringer’s solution, Trisault, Quartasault, 20 % solution of Sorbit (or. Sorbitoli), donor Albumin Enterosorbents of different brands: Carbaphosfer, Carbosilan, Sillard P, Enterosgel, Polyphepan Drugs for improving of metabolism in hepatocytes: ascorbinic acid, Thiamin chlorid, pyridoxine hydrochloride, cocarboxylase, potassy Orotat, Riboxin, Citochrom C, Lipamid, Calcy Pangamat Treatment: Etiotropic: antiviral preparations (lamivudin); natural interferon (velferon, human leukocytes interferon, leukinferon); recombinant interferon (intron A, roferon, reaferon, laferon); inductors of endogenous interferon stimulators (cycloferon, amikain). Pathogenetic: disintoxication therapy; entero-sorbents, immunomodulators methods; glucocorticoids; hepatoprotectors (bioflavonoids, analogue of amino acids, essential phospholipids); Symptomatic: regulators of motor function; enzymes preparations; cholekinetics; choleretics; herbal therapy; vitamin therapy. Prophylaxis Hepatitis А и Е Medical observation in epidemic spot during 35 days; laboratory examination of contact persons (blood analyses of bilirubin level, alaninaminotrasferase activity, bile pigments in urine) Children under 10 and pregnant women - injection of human immunoglobuline, for others - amizon, mephenamine acid; Current and final desinfection; Sanitary control measures; Active immunization – HAV-Vax; Parenteral hepatitis (В, С, D) Use of disposable medical instruments, thorough sterilisation of nonexpendable instruments Clinical and laboratory examination of blood and organ donors; Specific prophylaxis - vaccination against B hepatitis HB-Vax, Ingerix-B