* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neanderthals in Tibet
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
HLA A1-B8-DR3-DQ2 wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
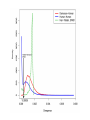
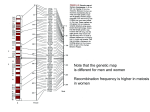
Neanderthals in Tibet Neanderthals (with)in Tibetan people The EPAS1 gene encodes a half of a transcription factor involved in the induction of genes regulated by oxygen, which is induced as oxygen levels fall (hypoxia). From Wikipedia Hypothesis? Adaptation to high altitudes in Tibetans is explained by neanderthal/denisovan introgression. How would you demonstrate this hypothesis? Filter Genotype data Calculate Fst Simulations, selection on a de-novo mutation and on standing variation Search haplotypes in 1000 genomes database Haplotype network. D and S* statistics under models of no gene flow Genome-wide FST versus maximal allele frequency difference FST calculated for each SNP between Tibetan and Han populations. Haplotype pattern in a region defined by SNPs that are at high frequency in Tibetans and at low frequency in Han Chinese. A haplotype network based on the number of pairwise differences between the 40 most common haplotypes. Genealogical structure in a model with gene flow from Denisovans to Tibet