* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - Spring Branch ISD
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
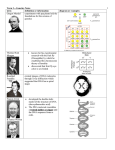
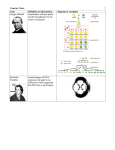
Name_________________________________ Period_________ Genetics Class Notes Reproduction Reproduction is common to all living things. When organisms reproduce they make more of their own kind. Offspring are the products of reproduction. Every organism requires a set of genetic instructions for specifying its traits or characteristics. What is a trait? Trait A characteristic that a parent organism passes on to its offspring through genetic material Examples: Eye Color Hair Color Leaf Shape BIG IDEA: When organisms reproduce, many traits or characteristics are passed to the new organism. Heredity Heredity is the passage of genetic instructions from one generation of organisms to the next generation. Genetics is the study or science of heredity. Class Notes Page 1 What is DNA? DNA Structure discovered by Watson and Crick 1.Nucleic Acid 2.Macromolecule: C, N, H, O, P 3. Organic Double Helix Shaped (Twisted Ladder shape) Sides of Ladder Sugars and Phosphates 1. Located in the cell’s nucleus 2. Packaged in Chromosomes Rungs of Ladder Nitrogen bases ; Bases connected to Sugar molecules DNA language is built on the alphabet of A, T, C, G. The sequence or order of these nitrogen bases forms the genetic code. BIG IDEA DNA stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation to the next. Class Notes Page 2 What is a chromosome? DNA is packaged into bundles called chromosomes. What is the relationship between traits, genes, chromosomes, and alleles? A gene is a section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. Alleles are different forms of a gene that provide the code for specific inherited traits. Examples:hair color, eye color, leaf shape The code in the DNA of the gene determines the type of allele (ex: shortness or tallness) that will be present in the gene. Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, noticed that genes always come in pairs. Every organism that reproduces sexually receives two genes for each trait. They receive one gene from the mother and one gene from the father for a specific trait. BIG IDEAS An organism receives two genes for each trait, one from each parent. One of the genes may be stronger; the trait of the stronger gene shows up and is called the dominant gene. The trait of the weaker gene is “hidden” or does not show up and is called the recessive gene. Dad Mom DominantUpper case RecessiveLower Case Brown Blue Brown Class Notes Page 3 What is the language of genetics? A capital letter is used to represent a dominant allele. A lower case letter is used to represent a recessive allele. Example: In the color of pea plant flowers, purple is the dominant allele and white is the recessive allele. Dominant_Purple (P) Genetics Term Recessive__White (p)_ Example: Flower Color Genotype Definition the genetic makeup of an organism; the type of genes Phenotype the external or physical appearance of an organism White Purple Homozygous an organism with two identical alleles for a trait PP and pp an organism with both a dominant and a recessive allele for a trait Heterozygous Pp, PP, pp Pp How do you predict heredity? A Punnett square is a chart used to predict the genetic outcomes of offspring. The letters on the outside of the square represent the alleles of the parents. The letters on the inside of the square represent the possible combinations of alleles among the offspring. Parent Parent Offspring Class Notes Page 4 L l L l LL Ll Ll ll 3/4 1/4 75 25 25 50 25 Tall LL Short w w W W Ww Ww Ww Ww 4/4 0 ll 100 0 0 100 0 Long Ll Ww Class Notes Page 5 What are the characteristics of Asexual Reproduction? Number of Parents Inheritance of Genetic Material Offspring Advantage/Disadvantage One parent One set of genetic material is passed to offspring Identical to the parents Advantage: Produces a large number of offspring rapidly Disadvantage: Offspring are not genetically diverse Binary Fission: Single celled organisms (prokaryote) Reproduces by dividing in half Vegetative Propagation: Processes Plant asexual reproduction Examples Produce runners Bulbs Potato eyes Budding: Eukaryote New organism grows directly out of parent’s body Class Notes Page 6 What are the characteristics of Sexual Reproduction? Number of Parents Inheritance of Genetic Material Offspring Two parents Two sets of genetic material are passed to the offspring Offspring inherits traits from both parents Advantage: Offspring are genetically diverse; diversity helps organisms survive when their environment changes Advantage/Disadvantage Disadvantage: Cannot reproduce quickly Process Organisms Male sperm cell unites with female egg cell Most animals Seed plants Class Notes Page 7 There are two X’s Female male There is an X and a Y X Y X X X XX XX Y XY XY Class Notes Page 8