* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Failure
Survey
Document related concepts
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
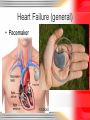
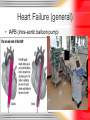
Lori Baker, RN BSN Cardiovascular Disorders HEART FAILURE TERMS • Cardiac Output – Heart rate x stroke volume – That is, amount of volume with each beat multiplied by the number of beats – 5L/min • Compensatory mechanisms Compensatory Mechanisms • Sympathetic nervous system detects low cardiac output • HR speeds up – Epinephrine and norepinephrine • Raises CO – Increases oxygen needs of heart Compensatory Mechanisms • Increase to heart means decrease to kidneys • Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system – ADH released to conserve water – UOP decreases – Fluid retention develops – Adds to heart failure problem – Cycle continues Increased Workload = … • Enlarged chambers • Increased muscle mass • Increased oxygen demand What Start’s It? • • • • • • CAD MI Cardiomyopathy Valve problems HTN Ischemia Left-Sided Heart Failure • Major cause – HTN – Due to peripheral vascular resistance (PVR) – HTN also causes hypertrophy Left-Sided Heart Failure • Other causative factors – Restriction of blood flow from LV • Aortic stenosis • Coarctation of aorta – Impairment of myocardial contractility • MI • Cardiomyopathy – Backward blood flow • MR Left-Sided Heart Failure • S/S – Pulmonary • • • • • • • • Dyspnea Orthopnea Increased pulmonary pressures Crackles/rales Tachycardia Chest pain AMS Pulmonary edema Right-Sided Heart Failure • Major cause – left-sided heart failure • Other causative factors – Increased pulmonary pressures (from chronic or acute lung disease) • Cor pulmonale – Restriction of blood flow from the RV • Pulmonary stenosis – Abnormal flow of blood from LA to RA • Atrial septal defect (ASD) Right-Sided Heart Failure • S/S – Systemic • JVD • Peripheral edema • Organomegaly – Hepatomegaly – Splenomegaly • Nocturia Heart Failure (general) • Diagnostic Tests – CXR – congestion, cardiomegaly – ABG’s – EKG • Ischemia • A-fib – Hemodynamic monitoring – ECHO – Cardiac cath – Renal and liver studies Heart Failure (general) • Treatment – Goal is to increase cardiac output – Oxygen – Mechanical ventilation – Semi-or high-Fowler’s – Bed/chair rest initially – VS – UOP – Daily weight Heart Failure (general) • Meds – ACE inhibitors • Captopril (Capoten) – Diuretics • Furosemide (Lasix) – Beta-blockers • Metoprolol (Lopressor) • Meds – Inotropes • Digoxin (Lanoxin) – Aldosterone antagonist • Aldactone – Vasodilators • Nitroglycerin Heart Failure (general) • Pacemaker Heart Failure (general) • IAPB (intra-aortic balloon pump) Heart Failure (general) • VAD (ventricular assist devises) Heart Failure (general) • Cardiomyoplasty Questions ???????????