* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10
Survey
Document related concepts
Greeks (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Private equity wikipedia , lookup
Security interest wikipedia , lookup
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Asset-backed commercial paper program wikipedia , lookup
Stock valuation wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Business valuation wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Mergers and acquisitions wikipedia , lookup
Capital gains tax in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Corporate finance wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
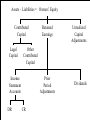
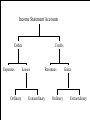
Chapter 10: The Balance Sheet Linking the balance sheet and income statement Evolving definitions Asset valuation Liabilities and owners’ equities Hybrid securities Derivatives Balance sheet classification issues Two Types of Relationships between Balance Sheet & Income Statement Articulated The two statements are mathematically linked Net income is equal to the change in owners’ equity for a period, assuming no capital transactions or prior period adjustments Nonarticulated The two statements are independently defined The relationship between the balance sheet and the income statement is severed Assets – Liabilities = Owners’ Equity Contributed Capital Legal Capital Unrealized Capital Adjustments Other Contributed Capital Income Statement Accounts DR Retained Earnings Prior Period Adjustments CR Dividends Income Statement Accounts Debits Expenses Ordinary Credits Losses Revenues Extraordinary Ordinary Gains Extraordinary Accounting Classification System Rather simple Complex transactions do not always fit neatly into one of the categories Surprisingly, current accounting classification system is virtually unchanged since Pacioli’s time Articulated System Alternatives Revenue-Expense approach Concerned with the definition, recognition, and measurement of income Result is that balance sheet contains assets, liabilities and ambiguous debits and credits called deferred charges and deferred credits Asset-Liability approach SFAC No. 6 defines comprehensive income as the change in the firm’s net assets from nonowner sources Focuses on the measurement of net assets Definitions: Assets Something represented by a debit balance that is or would be properly carried forward upon a closing of books of account according to the rules or principles of accounting ... Economic resources of an enterprise that are recognized and measured in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Assets also include certain deferred charges... Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a particular entity as a result of past transactions or events. Asset Definition Trend Definitions of assets have evolved from a narrow legal orientation to a broader concept of economic resources. As the definition has broadened, the boundary around what is and what is not an asset has become hazy and ambiguous. Executory Contracts: Assets? a contract unperformed by both parties. A long-standing problem in accounting has been the question of how to account (if at all) for mutually unperformed executory contracts. traditional accounting view is that no recognition is required in financial statements because a binding exchange has not yet occurred. The contract is prospective. Recognition and Measurement Assets and liabilities generally are initially recorded on the basis of events in which the enterprise acquires resources from other entities or incurs obligations to other entities. The assets and liabilities are measured by the exchange prices at which the transfers take place. Assets Initially recognized when the transaction transferring control occurs At this point in time, a potential exists for future economic benefits Measured at the market value (exchange price) of the consideration exchanged or sacrificed to acquire the assets and place them in operating condition. called historical acquisition cost however, an asset should not be recorded in an amount greater than its cash equivalent purchase price. Asset Valuation: A Lack of Additivity original acquisition cost (historical cost) historical cost less cumulative charges to income (book value) replacement cost selling prices net realizable value net realizable value less normal markups Summary of Asset Measurement Receivables Approximate net realizible value Investments...APB 115 Amortized historical cost or fair value Investments...APB 18 Unique accounting attribute (equity accounting) Inventories Cost, replacement cost, NRV or NRV less mark-up Summary of Asset Measurement Self-constructed assets Full-asbsorption for inventory; capitalize interest for noninventory Assets subject to depreciation or depletion Unique accounting attribute (book value) Nonmonetary exchanges Of similar assets Book value of old asset plus cash Intangible assets Unique accounting attribute (book value) Summary of Asset Measurement Deferred charges Unique accounting attribute (book value) Restructured receivables ...modification of terms Newly restructured future cash inflows discounted at original rate Impaired assets Fair value if less than carrying value, assuming... Definition: Liabilities ... not only items which constitute liabilities in the popular sense of debts or obligations ...but also credit balances to be accounted for which do not involve a debtor and creditor relation economic obligations of an enterprise recognized and measured in conformity with GAAP probable future sacrifices of economic benefits Definition: Owners’ Equity (OE) The owners’ residual interest in the net assets of the firm Two types of owners’ equity transactions Capital Income-related Definition: Hybrid Securities Redeemable preferred stock Trust preferred stock Company sells preferred stock to subsidiary Subsidiary sells bonds to parent Parent takes interest tax deduction and eliminates debt in consolidation process Securitizations involves the sale by a firm (called the transferor) of an asset or group of assets to another firm (called the transferee) is to keep debt off of its balance sheet Definition: Derivatives Financial instruments whose value is based upon other financial instruments, stock indexes or interest rates, or interest rate indexes Two types Forward-based derivatives Options-based derivatives Types of Derivatives Forward-based derivatives arise between two parties where one party will realize a gain and the other party will realize a loss due to a change in value of the factor underlying the instrument. Option holders pay a specific “up front” price that gives them the right to buy (“call”) or sell (“put”) a specific quantity at a specific price of a standard commodity or a financial or equity instrument. Balance Sheet Classification Issues Current-noncurrent approach gives only a crude indication of a firm’s liquidity There are five distinctly different types of accounting liabilities: contractual, constructive, equitable, contingent, and deferred charges Chapter 10: The Balance Sheet Linking the balance sheet and income statement Evolving definitions Asset valuation Liabilities and owners’ equities Hybrid securities Derivatives Balance sheet classification issues