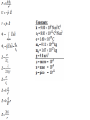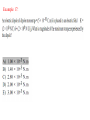* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.22.Problems
Survey
Document related concepts
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrodynamic tether wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electron paramagnetic resonance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
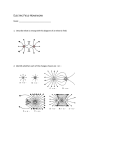
CH22.Problems Electric Fields JH Example 3: Example 4: Example 5: Example 14: Example 17: Q1 and Q2 cancels due to opposite forces because of direction Q3 and Q4 cancels due to opposite signs and matching charge to square of distance factor: 52. An electron enters a region of uniform electric field with an initial velocity of 40 km/s in the same direction as the electric field, which has magnitude E = 50 N/C. (a) What is the speed of the electron 1.5 ns after entering this region? (b) How far does the electron travel during the 1.5 ns interval? Answer: a) 27 km/s, b) 5.0×10^-5 m = 50 micro-m