* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Mitsubishi AWC wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Sagnac effect wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
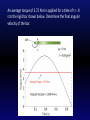
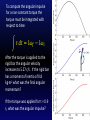
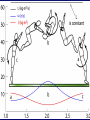
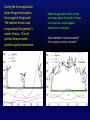
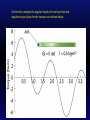
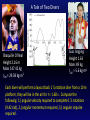
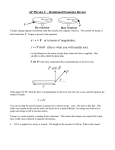
KINE 3301 Biomechanics of Human Movement Angular Impulse Chapter 13 𝜏 𝑡 = 𝐼𝜔𝑓 − 𝐼𝜔𝑖 𝜏 𝑑𝑡 = 𝐼𝜔𝑓 − 𝐼𝜔𝑖 Linear and Angular Momentum • Recall from chapter 8 that linear momentum was defined as mass x velocity. 𝑝 = 𝑚𝑣 • Angular momentum is defined as moment of inertia x angular velocity 𝐿 = 𝐼𝜔 • Angular momentum is a vector , the direction of the vector is defined by the right hand rule. • The units for angular momentum are kg∙m2/s • Angular momentum describes the quantity of rotation that a body possesses. Computing Angular Momentum The diver shown below is rotating with an angular velocity (𝜔) of −4.2 r/s and a moment of inertia (I) of 5 kg∙m2, compute the magnitude of the divers angular momentum. Angular Impulse – Angular Momentum Relationship • The angular impulse – angular momentum relationship is derived from Newton’s law of angular acceleration: Στ = Ι𝛼 𝜔𝑓− 𝜔𝑖 Στ = Ι 𝑡 𝜔𝑓− 𝜔𝑖 𝛼= 𝑡 Στ(t) = I𝜔𝑓 − 𝐼𝜔𝑖 Angular Impulse = change in angular momentum If you apply a torque over time (angular impulse), it changes the angular momentum of an object. An angular impulse is required to make an object spin or stop an object from spinning An average torque of 3.72 N∙m is applied for a time of t = .9 s to the rigid bar shown below. Determine the final angular velocity of the bar. A constant torque of 4.55 N∙m is applied to a rigid bar with a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg∙m2 and an initial angular velocity of 0.0 r/s, determine the final angular velocity. What was the angular impulse that was applied? To compute the angular impulse for a non-constant torque the torque must be integrated with respect to time: 𝜏 𝑑𝑡 = 𝐼𝜔𝑓 − 𝐼𝜔𝑖 After the torque is applied to the rigid bar the angular velocity increases to 5.27 r/s. If the rigid bar has a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg∙m2 what was the final angular momentum? If the torque was applied for t = 0.9 s, what was the angular impulse? Principle of Conservation of Angular Momentum When gravity is the only force acting on a system the angular momentum is constant. During the force application phase the gymnast applies forces against the ground. The reaction forces cause torque about the gymnast’s center of mass. The net positive torque creates positive angular momentum. When the gymnast is in the air the net torque about the center of mass is zero and as a result angular momentum is constant. Is the moment of inertia constant? Is the angular velocity constant? Use Excel to compute the angular impulse for each positive and negative torque phase for the torque curve shown below. A Tale of Two Divers Shaquille O’Neal Height 2.16 m Mass 147.42 kg ICM = 29.58 kg∙m2 Guo Jingjing Height 1.63 Mass 49 kg ICM = 5.6 kg∙m2 Each diver will perform a layout back 1 ½ rotation dive from a 10 m platform, they will be in the air for t = 1.68 s. Compute the following: 1.) angular velocity required to complete 1 ½ rotations (9.42 rad), 2.) angular momentum required, 3.) angular impulse required.