* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modeling Of Single-Phase To Three-Phase Drive
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
Modeling Of Single-Phase To Three-Phase Drive System Using
Two Parallel Single-Phase Rectifiers
Radha Krishna1, Amar kiran2
1, 2
(Department of EEE, GIET, JNTU University, Kakinada)
Abstract: This paper proposes a single-phase to three-phase drive system composed of two parallel single-phase rectifiers,
a three-phase inverter, and an induction motor. The proposed topology permits to reduce the rectifier switch currents, the
harmonic distortion at the input converter side, and presents improvements on the fault tolerance characteristics. Even with
the increase in the number of switches, the total energy loss of the proposed system may be lower than that of a conventional
one. The model of the system is derived, and it is shown that the reduction of circulating current is an important objective in
the system design. A suitable control strategy, including the pulse width modulation technique(PWM), is developed.
Experimental results are presented as well.
Index Terms—Ac-dc-ac power converter, drive system, parallel Converter, Fault Identification System(FIS).
I. INTRODUCTION
Several solutions have been proposed when the objective is to supply a three-phase motor from single-phase ac
mains [1]-[4]. It is quite common to have only a single phase power grid in residential, commercial, manufacturing, and
mainly in rural areas, while the adjustable speed drives may request a three-phase power grid. Single-phase to three-phase
ac–dc–ac conversion usually employs a full-bridge topology, which implies in ten power switches. This converter is denoted
here as conventional topology.
Parallel converters have been used to improve the power capability, reliability, efficiency, and redundancy. Parallel
converter techniques can be employed to improve the performance of active power filters [5]-[6], uninterruptible power
supplies (UPS) [7], fault tolerance of doubly fed induction generators, and three-phase drives [8]. Usually the operation of
converters in parallel requires a transformer for isolation. However, weight, size, and cost associated with the transformer
may make such a solution undesirable [9]. When an isolation transformer is not used, the reduction of circulating currents
among different converter stages is an important objective in the system design [10]-[12].
In this paper, a single-phase to three-phase drive system composed of two parallel single-phase rectifiers and a
three-phase inverter is proposed. The proposed system is conceived to operate where the single-phase utility grid is the
unique option available. Compared to the conventional topology, the proposed system permits: to reduce the rectifier switch
currents; the total harmonic distortion (THD) of the grid current with same switching frequency or the switching frequency
with same THD of the grid current; and to increase the fault tolerance characteristics. In addition, the losses of the proposed
system may be lower than that of the conventional counterpart. The aforementioned benefits justify the initial investment of
the proposed system, due to the increase of number of switches.
II. METHODS TO CONNECT SINGLE PHASE TO THREE PHASE DRIVE SYSTEMS
2.1 Static Phase Converter:
Static Phase Converters operate by charging and discharging capacitors to temporarily produce a 3rd phase of
power for only a matter of seconds during startup of electric motors, then it will drop out forcing the motor to continue to run
on just 1 phase and only part of its windings. Due to their technology, Static Phase Converters do not properly power any
class of 3 phase machinery or equipment. They will not in any way power 3 phase welders, 3 phase battery chargers, 3
phase lasers, or any type of machinery with 3 phase circuitry. Static Phase Converters also will not start delta wound 3 phase
motors.
2.2 Rotary phase converter:
A rotary phase converter, abbreviated RPC, is an electrical machine that produces three-phase electric power from
single-phase electric power. This allows three phase loads to run using generator or utility-supplied single-phase electric
power. A rotary phase converter may be built as a motor-generator set. These have the advantage that in isolating the
generated three-phase power from the single phase supply and balancing the three-phase output. However, due to weight,
cost, and efficiency concerns, most RPCs are not built this way. Rotary Phase Converters Provide Reliable, Balanced, and
Efficient Three Phase Power. Quick and Effective Three Phase Electricity.
All converters can be mainly categorized into two groups: one is cascade type and another is unified type [2]. In
cascade type, the PWM converter for power factor correction and the PWM inverter for speed control are connected in series
with large DC-Link capacitor and two static power converters are operated and controlled in separate. In this type, specific
number of switches, to compose the converter and inverter, are required. Therefore, the required number of switches cannot
be reduced significantly. On the other hand, in the unified type, conventional concepts of PWM converter and inverter are
merged together and same converter handles the functions of PWM converter (power factor correction) and PWM
inverter(motor control) at the same time. As an added advantage, the input inductor, which is commonly used in the PWM
www.ijmer.com
3899 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
converter for power factor correction, can be eliminated and replaced by the existing motor inductor. Therefore, this new
concept can significantly reduce the number of components, compared to any conventional cascade type topologies.
III. SYSTEM MODEL
The Conventional system single-phase to three phase system and the Proposed system single phase to three phase
systems are labeled as fig 1 and fig 2 respectively as shown below:
Fig 1 Conventional single-phase to three-phase system
Fig 2 Proposed single-phase to three-phase drive system
The system is composed of grid, input inductors (𝐿𝑎 , 𝐿′𝑎 , 𝐿𝑏 , 𝐿′𝑏 ). Rectifiers (A and B), capacitor bank at the dc-link,
inverter, and induction machine. Rectifiers A and B are constituted of switches
and
and
and
respectively. The inverter is constituted of switches
and
.
From Fig. 2, the following equations can be derived for the front-end rectifier
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
Wherep = d/dt and symbols like r and l represent the resistances and inductances of the input inductors
The circulating current
can be defined from
.
.
(6)
www.ijmer.com
3900 | Page
Introducing
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
and adding (3) and (4), relations (1)–(4) Become
(7)
(8)
(9)
Where
(10)
(11)
(12)
B), and
Relations (7)–(9) and (5) constitute the front-end rectifier dynamic model. Therefore, (rectifier A), (rectifier
(rectifiers A and B) are used to regulate currents
respectively. Reference currents and are chosen
equal to
and the reference circulating current is chosen equal to 0.
In order to both facilitate the control and share equally current, voltage, and power between the rectifiers, the four
inductors should be equal, i.e.,
and
. In this case, the model (7)–(9) can be
simplified to the model given by
+
=
(13)
=
(14)
=
Additionally, the equations for
=
(15)
,
and
can be written as
=
(16)
=
+
(17)
=
(18)
In this ideal case (four identical inductors), the circulating current can be reduced to zero imposing.
=0.
When
=0 (
(19)
) the system model (7)–(9) is reduced to
2( +
2( +
)
(20)
)
(21)
IV. PWM STRATERGY
The PWM strategy for the rectifier will be presented. The rectifier pole voltages
the conduction states of the power switches, i.e.,
= (2 -1) , for j=a1 to b2
(22)
Where is the total dc-link voltage. Considering that
controllers.
,
and
and
depend on
denote the reference voltages determined by the current
(23)
(24)
(25)
www.ijmer.com
3901 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
The gating signals are directly calculated from the reference pole voltages
and
. However, (23)–
(25) are not sufficient to determine the four pole voltages uniquely from , and . Introducing an auxiliary variable =
, that equation plus the three equations (23)–(25) constitute a four independent equations system with four variables (
and
). Solving this system of equations, we obtain
=
(26)
=
(27)
(28)
(29)
From these equations, it can be seen that, besides , and , the pole voltages depend on also of . The limit values of the
variable can be calculated by taking into account the maximum
and minimum –
value of the pole voltages.
(30)
(31)
Where
is the reference dc-link voltages,
ϑ= {
written as
= maxϑ and
= minϑ, with
}.Introducing a parameter μ (0 ≤ μ ≤ 1), the variable can be
(32)
When μ = 0, μ = 0.5, and μ = 1 the auxiliary variable Has the following values =
, =
=(
+
)/2and =
, respectively. When =
or
a converter leg operates with zero switching frequency. The
gating signals are obtained by comparing pole voltages with one (
), two ( and ) or more high-frequency triangular
carrier signals. In the case of double-carrier approach, the phase shift of the two triangular carrier signals ( and ) is
.The parameter μ changes the place of the voltage pulses related to and . When =
(μ = 0) or =
(μ = 1)
are selected, the pulses are placed in the begin or in the end of the half period (Ts ) of the triangular carrier signal On the
other hand, when =
the pulsesare centered in the half period of the carrier signal
The change of the position of the voltage pulses leads also to the change in the distribution of the zero instantaneous voltages
(i.e., = 0 and = 0).With μ = 0 or μ = 1 the zero instantaneous voltages are placed at the beginning or at the endof the
switching period, respectively, while with μ = 0.5, they are distributed equally at the beginning and at the end of the half
period. This is similar to the distribution of the zero-voltage vector in the three-phase inverter.
V. CONTROL STRATERGY
The control block diagram of Fig 2 highlighting the control of the rectifier to control the dc-link voltage and to
guarantee the grid power factor close to one. Additionally, the circulating current in the rectifier of the proposed system
needs to be controlled is shown below:
Fig 3 Control block diagram
In this way, the dc-link voltage is adjusted to its reference value using the controller
Which is standard
Fuzzy logic controllers. This controller provides the amplitude of the referencegrid current To control power factor and
harmonics in the grid side, the instantaneous reference current must be synchronized with voltage , as given in the
voltage-oriented control (VOC) for three-phase system This is obtained via blocks Ge- , based on a PLL scheme. The
reference currents and are obtained by making = =
.Which means that each rectifier receives half of the grid
www.ijmer.com
3902 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
current. The control of the rectifier currents is implemented using the controllers indicated by blocks and . These
controllers can be implemented using linear or nonlinear techniques.
The homopolar current is measured ( ) and compared to itsreference ( = 0). The error is the input of Fuzzy
controller ,that determines the voltage . The calculation of voltage isgiven from (30) to (32) as a function of μ,
selected.The motor there phase voltages are suppliedfrom the inverter (VSI). Block VSI-Ctr indicates the inverterand its
control. The control system is composed of the PWMcommand and a torque/flux control strategy.
VI. FAULT COMPENSATION
The proposed system presents redundancy of the rectifier converter, which can be useful in fault-tolerant systems.
The proposed system can provide compensation for open-circuit and short-circuit failures occurring in the rectifier or
inverter converter devices. The fault compensation is achieved by reconfiguring the power converter topology with the help
of isolating devices (fast active fuses— , j = 1, . . . , 7) and connecting devices (back to back connected SCRs—t1 , t2 , t3 ),
as observed in Fig. 10(a)and discussed. These devices are used to redefine the post-fault converter topology, which allows
continuous operation of the drive after isolation of the faulty power switches in the converter. Fig. 7.8.1(b) presents the block
diagram of the fault diagnosis system. In this figure, the block fault identification system (FIS) detects and locates the faulty
switches, defining the leg to be isolated. This control system is based on the analysis of the pole voltage error.
The
fault detection and identification is carried out in four steps:
1. Measurement of pole voltages ( ).
2. Computation of the voltage error
by comparison of reference voltages and
measurements
affected in Step (1).
3. Determination as to whether these errors correspond or not to a faulty condition; this can be implemented by the
hysteresis detector.
4. Identification of the faulty switches by using .
Fig.4 (a) Proposed configuration highlighting devices of fault-tolerant system.
(b) Block diagram of the fault diagnosis system.
Fig.5 Possibilities of configurations in terms of fault occurrence. (a) Prefault system.
(b) Post-fault system with fault at the rectifier B. (c) Post-fault system with fault at the
rectifier A.(d) Post-fault system with fault at the inverter.
www.ijmer.com
3903 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
This way, four possibilities of configurations have been considered in terms of faults:
1) pre-fault (―healthy‖) operation
2) post-fault operation with fault at the rectifierB
3) post-fault operation with fault at the rectifierA
4) post-fault operation with fault at the inverter
Table 1 Efficiency of the proposed system normalized in terms conventional one
)
Frequency/Inductor
S-Ca µ=0.5
D-Ca µ=0.5
D-Ca µ=0
-1.60%
-1.47%
-0.41%
10kHz( = )
10kHz( = /2)
3.12%
3.25%
4.36%
5kHz( = )
-0.74%
-0.27%
1.72%
When the fault occurrence is detected and identified by the control system, the proposed system is reconfigured and
becomes similar to that in Fig.1.For instance, if a fault in any switch of rectifier A has been detected by the control system,
the hole rectifier needs to be isolated. This isolation procedure depends on the kind of fault detected. If an open-circuit
failure is detected, the control system will open all switches of the rectifier A. On the other hand ,if a short circuit is detected,
the control system will turn on all switches related to rectifier A, and in this case, the fuses will open, and consequently, the
rectifier will be isolated, as discussed. Considering now a fault in one leg of inverter, in this case the SCR related with this
leg in turned on and the leg b1 is isolated, so that the leg b2 of rectifier B will operate as the leg of inverter.
VII.
MATLAB SIMULINK MODELS
The simulink models of the Proposed converter system, its control strategy and fault diagnosis is also carried out.
Fig 6 Simulink diagram of single phase to three phase drive system using two parallel single phase rectifiers
Fig 7 Sub-system
www.ijmer.com
3904 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
Fig 8 Vector control
Fig 9 Fault Identification at Rectifier B
VIII.
RESULTS
(a)
(b)
www.ijmer.com
3905 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
(c)
(d )
(e)
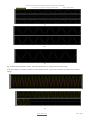
Fig. 10 Shows the waveforms of steady state three phase motor: (a) voltage and current of the grid,
(b) dc-link voltage, (c) currents of rectifier A and circulating current, (d) currents of rectifiers A and B, and (e) load line
voltage.
(a)
(b)
www.ijmer.com
3906 | Page
International Journal of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER)
www.ijmer.com
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3899-3907
ISSN: 2249-6645
(C)
Fig 11 Experimental results when fault occurs at rectifier B. (a) Grid voltage and grid current
(b) Currents of rectifiers A and B (c) Capacitor voltage (d) Currents of rectifier A
IX. CONCLUSION
A single phase to three phase drive system using two parallel converters, three phase inverter and induction motor
are proposed. The comparison between conventional and proposed system has been carried out and experimental results are
also shown.
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
P. Enjeti and A. Rahman, ―A new single phase to three phase converter with active input current shaping for low cost AC motor
drives,‖ IEEETrans. Ind. Appl., vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 806–813, Jul./Aug. 1993.
B.K. Lee, B. Fahimi, and M. Ehsani, ―Overviewof reduced parts converter topologies for AC motor drives,‖ in Proc. IEEE PESC,
2001, pp. 2019–2024.
C. B. Jacobina, M. B. de R. Correa,A.M. N. Lima, and E. R. C. da Silva, ―AC motor drive systems with a reduced switch count
converter,‖ IEEETrans. Ind. Appl., vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 1333–1342, Sep./Oct. 2003.
C. B. Jacobina, E. C. dos Santos Jr., E. R. C. da Silva, M. B. R. Correa,A. M. N. Lima, and T. M. Oliveira, ―Reduced switch count
multiple three-phaseac machine drive systems,‖ IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 23,no. 2, pp. 966–976, Mar. 2008.
D.-C. Lee and Y.-S. Kim, ―Control of single-phase-to-three-phase AC/DC/AC PWM converters for induction motor drives,‖ IEEE
Trans.Ind. Electron., vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 797–804, Apr. 2007.
[6] L. Woo-Cheol, L. Taeck-Kie, and H. Dong-Seok, ―A threephase parallel active power filter operating with PCC voltage compensation with consideration for an unbalanced load,‖ IEEE Trans.
Power Electron., vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 807–814, Sep. 2002.
L. Asiminoaei, E. Aeloiza, P. N. Enjeti, F. Blaabjerg, and G. Danfoss, ―Shunt active-power-filter topology based on parallel
interleaved inverters,‖ IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 1175–1189, Mar. 2008.
M. Ashari, W. L. Keerthipala, and C. V. Nayar, ―A single phase parallel connected uninterruptible power supply/demand side
management system,‖ IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 97–102, Mar. 2000.
J.-K. Park, J.-M. Kwon, E.-H. Kim, and B.-H. Kwon, ―High-performance transformer less online UPS,‖ IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron.,
vol. 55, no. 8, pp. 2943–2953, Aug. 2008.
Z. Ye, D. Boroyevich, J.-Y. Choi, and F. C. Lee, ―Control of circulating current in two parallel three-phase boost rectifiers,‖ IEEE
Trans. PowerElectron., vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 609–615, Sep. 2002.
S. K. Mazumder, ―Continuous and discrete variable-structure controls for parallel three-phase boost rectifier,‖ IEEE Trans. Ind.
Electron., vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 340–354, Apr. 2005.
Z. Ye, P. Jain, and P. Sen, ―Circulating current minimization in high frequency AC power distribution architecture with multiple
inverter modules operated in parallel,‖ IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 54, no. 5,. pp. 2673–2687, Oct. 2007.
J. Holtz, ―Pulse width modulation for electronic power conversion,‖ Proc.IEEE, vol. 82, no. 8, pp. 1194–1214, Aug. 1994.
M. P. Kazmierkowski and L. Malesani, ―Current control techniques for three-phase voltage-source PWM converters: A survey,‖
IEEE Trans. Ind.Electron., vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 691–703, Oct. 1998.
[15] B. A. Welchko, T. A. Lipo, T. M. Jahns, and S. E.
Schulz, ―Fault tolerant three-phase AC motor drive topologies: A comparison of features, cost, and limitations,‖ IEEE Trans. Power
Electron., vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 1108–1116, Jul. 2004.
www.ijmer.com
3907 | Page