* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functions Structural Plan
Survey
Document related concepts
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Freediving blackout wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Human vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Biofluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Common raven physiology wikipedia , lookup
Acute respiratory distress syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Circulatory system wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Insect physiology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
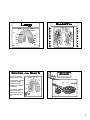
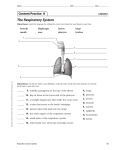
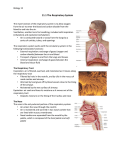
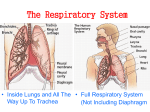
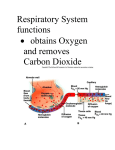
Respiratory System Biology Content Standards 4. Anatomy and Physiology Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the By: Mrs. Bailey Functions • Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body’ ’s cells • Filters, warms and humidifies the air we breathe organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. 4.3 Explain how the system (nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, alveoli) provides exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. 4.8 Recognize that the body’’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. Describe the basic function of a physiological feedback loop. Structural Plan Upper Respiratory Tract • .ose, pharynx, and larynx • Influences sound production (speech) Lower Respiratory Tract • Makes the sense of smell possible • Trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs • Plays a role in regulation of pH in the body 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Pharynx Nose Functions • Passageway for air traveling to and from the lungs • Filters air • Aids speech • Makes possible the sense of smell Larynx Location Lies between the root of the tongue and the upper end of the trachea Function • Helps in the removal of dust particles and in the warming and humidification of inspired air • Protects against entering of solids and liquids - epiglottis • Serves as the organ of voice production • Also known as the throat. • Serves as a common pathway for the respiratory and digestive tracts. • Affects speech production. Lower Respiratory Tract Trachea Structure • Extends from the larynx to the chest cavity • C-shaped rings of cartilage give it stability and prevent collapsing. Function Part of the open passageway through which air travels into the lungs 2 Lungs Bronchial Tree Structure of the Bronchi Alveoli • 2 primary bronchi divide from the trachea • Each primary bronchi branch into smaller, secondary bronchi and again into smaller bronchioles • Bronchioles subdivide into alveolar ducts, which end in clusters of alveoli called alveolar sacs. 3 Structure/Function of the Alveoli Pulmonary Ventilation - technical term for breathing • Very effective in exchange of CO2 and O2 because each has extremely thin walls and is in contact with blood capillaries. • The barrier in which gases are exchanged between alveolar air and the blood is respiratory membrane. HOMEOSTASIS Pressure gradients allow for respiration. These gradients are established by changes in the size of the chest cavity. HOMEOSTATIC CONTROL MECHANISMS The relatively constant states maintained by the body Examples: SE.SOR detects some physiological parameter constantly when significant changes occur 1. Thermoregulation 2. Regulation of blood O2/CO2 level 3. Glucoregulation I.TEGRATOR EFFECTOR sums up information from sensors “target” ” whose activity is changed in order to bring the factor back into its normal range 4. Osmoregulation 4 Biology Content Standards 4. Anatomy and Physiology Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. 4.3 Explain how the system (nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, alveoli) provides exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. 4.8 Recognize that the body’’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. Describe the basic function of a physiological feedback loop. 5