* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH - Chemwiki
Survey
Document related concepts
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Sulfuric acid wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
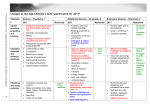
3/18/2015 Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH - Chemwiki Sign In Forgot Password Register ashwenchan username •••••••• password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki BioWiki Periodic Table of the Elements GeoWiki Reference Tables StatWiki Physical Constants PhysWiki MathWiki SolarWiki Units & Conversions Lab Techniques ChemWiki: The Dynamic Chemistry E-textbook > Physical Chemistry > Acids and Bases > Ionization Constants > Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH The quantity pH, or "power of hydrogen," is a numerical representation of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It can be used to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions [H+] or hydronium ions [H3O+] in an aqueous solution. Solutions with low pH are the most acidic, and solutions with high pH are most basic. Definitions Although pH is formally defined in terms of activities, it is often estimated using free proton or hydronium concentration: or Ka, the acid ionization constant, is the equilibrium constant for chemical reactions involving weak acids in aqueous solution. The numerical value of Ka is used to predict the extent of acid dissociation. A large Ka value indicates a stronger acid (more of the acid dissociates) and small Ka value indicates a weaker acid (less of the acid dissociates). For a chemical equation of the form , the equation for Ka is the following: HA is the undissociated acid and A- is the conjugate base of the acid. (H2O, a pure liquid, has an activity equal to one, and is therefore ignored in the equilibrium constant equation.) Solving for K a When given the pH value of a solution, solving for Ka requires the following steps: 1. Set up an ICE table for the chemical reaction. 2. Solve for the concentration of H3O+ (denoted x) using the equation for pH: 3. Use the concentration of H3O+ to solve for the concentrations of the other products and reactants. 4. Plug all concentrations into the equation for Ka and solve. Example 1 Calculate the Ka value of a 0.2 M aqueous solution of propionic acid, CH3CH2CO2H, with a pH of 4.88. SOLUTION ICE TABLE http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Physical_Chemistry/Acids_and_Bases/Ionization_Constants/Calculating_A_Ka_Value_From_A_Measured_Ph 1/2 3/18/2015 Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH - Chemwiki ICE Initial Concentration Change in Concentration Equilibrium Concentration According to the definition of pH, 0.2 M -x M (0.2 - x) M 0M +x M xM 0M +x M xM Thus, Related Articles The Determination of pKa of Multiprotic, Weak Acids The pKa of a Weak Acid as a Function of Temperature and Ionic Strength Graphical Correlation Between pH Values, Molarities and Dissociation Constants of Weak Acids References 1. Petrucci,et al. General Chemistry:Principles & Modern Applications; Ninth Edition, Pearson/Prentice Hall; Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07. Contributors Paige Norberg, Gabriela Mastro (UCD) © Copyright 2015 Chemwiki Powered by MindTouch ® Unless otherwise noted, content in the UC Davis ChemWiki is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License. Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at [email protected]. Questions and concerns can be directed toward Prof. Delmar Larsen ([email protected]), Founder and Director. Terms of Use http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Physical_Chemistry/Acids_and_Bases/Ionization_Constants/Calculating_A_Ka_Value_From_A_Measured_Ph 2/2