* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme kinetics wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
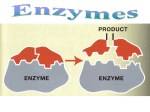
KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. A catalyst lowers activation energy. • Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. – decrease activation energy – increase reaction rate • Activation energy usually comes from an increase in temp – Slow process • Catalyst: substance that decreases the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction – Speeds up reaction • Enzymes reduce energy needed (activation energy) to start a chemical reaction Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. • Enzymes are catalysts in living things. – Enzymes are needed for almost all processes. – Most enzymes are proteins. Controlled Settings • Human body ~98.6°F – Can’t raise body temp to start reactions. • Internal reactions would be too slow to sustain life without a catalyst • Ex: Saliva – Breaks down starch 1,000,000x faster with amylase • Disruptions in homeostasis can prevent enzymes from functioning. – Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions. – Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds. – An enzyme’s function depends on its structure. • An enzyme’s structure allows only certain reactants to bind to the enzyme. – substrates – active site substrates (reactants) enzyme Substrates bind to an enzyme at certain places called active sites. • The lock‐and‐key model helps illustrate how enzymes function. – substrates brought together – bonds in substrates weakened Substrates bind to an enzyme at certain places called active sites. The enzyme brings substrates together and weakens their bonds. The catalyzed reaction forms a product that is released from the enzyme. Exothermic Reaction Endothermic Reaction Catalyzed Reactions