* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Hubble Space Telescope
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Orion Nebula wikipedia , lookup
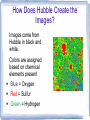
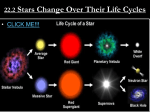
The Hubble Space Telescope Getting to know The Hubble •Named for Edwin Hubble (astronomer) •Launched in 1990 •Changed our view and understanding of the Universe. Hubble Facts Hubble orbits 400 mi above the Earth Orbits the Earth every 97 minute Weighs 12 tons Size of a school bus Carrie Murray NASA Top Stars, 2010 How Does Hubble Create the Images? Images come from Hubble in black and white. Colors are assigned based on chemical elements present Blue = Oxygen Red = Sulfur Green = Hydrogen One image takes almost a year to create. An image is made up of 48 separate images. The Hubble Space Telescope has helped us understand how stars are born, age, and ultimately die! Eagle Nebula 500 light years away 3 gigantic pillars of gas and dust Towers 4 light years tall Shows the early stages of a star Known as the pillars of creation Fun Fact Our Solar System could fit inside any one of the forming stars! Wow!!! Orion Nebula 1,000 light years away Next phase in star development Tiny dark spots are flattened disks of gases and dust from recently hatched “eggs” Orion Nebula The bright orange spot in the center gathers dust and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become PLANETS Helix Nebula (Death of a star) Layers of the star expand leaving behind a hot white ball of oxygen and carbon becoming a white dwarf Supernova Bigger Star Shorter the life More violent death Known as supernova Every star is balanced by the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure of heat by nuclear fusion. Once a star runs out of fuel the pressure needed for balance is gone. Gravity causes the star to cave in and BOOM an explosion destroying the star and everything around it. Crab Nebula (The Aftermath) Expanding wreckage of a supernova that happened in 1054 A.D. Explosion recorded by Chinese astronomers Still expanding 3 million miles per hour Black Hole Created by stars 4x larger than our star Collapsed into a single point smaller than the head of pin A hunk of matter that is so small and gravitational pull is so strong light can't escape Astronomers noticed that stars closer to the center of a galaxy zoom at very high speeds. Most stars move around at slow speeds. Stars being thrown around by something that is massive, but compact... A BLACK HOLE Carrie Murray NASA Top Stars, 2010 Carrie Murray NASA Top Stars, 2010 Power Point Credits Images from: www.hubblesite.org Information from: Naked Science “Hubble's Amazing Universe” viewed on National Geographic Channel Carrie Murray NASA Top Stars, 2010