* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dewey - Blumberg Lab
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
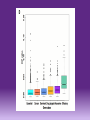
Distribution and clinical impact of functional variants in 50,726 whole-exome sequences from the DiscovEHR Study Dewey et al. Presented By: Natasha Granneman & Christina Tran Background • What is Precision Medicine? • Considers a person’s environment, lifestyle, and genes when looking for course treatment • Theoretically, treatment should be catered to one person • Goals of Precision Medicine • Expand cancer treatments • Use a cohort study to learn more about health and disease Background Background • In 2014, DiscovEHR initiative started by Regeneron Genetics Center and Geisinger Health Systems (GHS) • Cohort in this study came from consenting GHS patients who gave blood and DNA samples as well as clinical phenotypes and records • 50, 726 participants • 87 clinical examinations, 658 lab tests, and 7 procedures per participant Goals of DiscovEHR • Find genes that affect a large number of diseases and similar traits between them • Use these factors to uncover new scientific knowledge • Possible drug targets • Analyzing genetic variants to scale the use of precision medicine Method • Genome wide array genotyping via Omni Express exome platform • Sequenced coding regions of 18,852 genes in 50, 726 participants using Illumina Sequencing • 20x read depth at > 85% of targeted bases in 96% of samples • Average of 80% mean read depth in targeted bases Bead MicroArray Technology Exome Capture Method • Once sequenced, uploaded to DNAnexus to analyze • Aligned the sequences from Illumina to a reference • GRCh37.p13 Method • Used various computer programs to: • Align exomes to the reference • Loss of functions variants • Zygosity • Build pedigrees • Compared exome sequences to phenotypes derived from electronic health records • Lipid levels • Clinically actionable genetic variants Results • Found previously unidentified associations between pLOFs in various genes and phenotypes from EHR • 4.2 million SNV’s and indels (176,000 predicted LOFs) • 76 clinically actionable genes • 3.5% of participants had possible pathogenic variants • PCSK9 was the most significant finding • Normally degrades LDL receptor blood LDL levels increase • pLOF in gene results in lower LDL levels • Similar to drugs that target the gene (alirocumab and evolocumab) Conclusion from Study • There needs to be large scale sequencing used in health care system • Allow us to fill gaps in our knowledge regarding role of genetic variation in health, disease, genomics, and medical care • Represents a “powerful platform” for human genetics research • DiscovEHR is merely a “blueprint” for precision medicine and target gene discovery Limitations Our Conclusions • Precision medicine using this is a great initiative, but might be too big to accomplish • Doubtful that this can be used to treat more terminal diseases such as cancer • Saw no links to cardiac illnesses in sample even though cardiac illnesses were in the majority • Big pharm companies might not find precision medicine as profitable as it costs too much per person References/Additional Reading • Dewey, F.E, et al. Distribution and clinical impact of functional variants in 50,726 wholeexome sequences from the DiscovEHR Study. Science, 354: 1549. • https://www.illumina.com/techniques/sequencing.html • https://www.nih.gov/research-training/allofus-research-program • Additional Reading • Precision Medicine – Personalized, Problematic, and Promising • http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsb1503104 • A New Initiative on Precision Medicine • https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5101938/