* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry - U
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
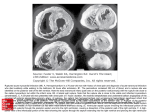
Pathology Lecture 28 Ischemic Heart Disease 1) Know the risk factors for atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. Risk factors for both include: advanced age, sex with males>females (↑postmenopausal women), cigarette smoking, hyperlipidemia especially hypercholesterolemia (dietary or genetic), hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and genetics (i.e. a positive family history or familial hypercholesterolemia). Other risk factors may include lack of exercise, stressful lifestyle with "Type a" personality, and obesity. 2) Describe the sequence of events in the formation of an occlusive coronary thrombus and the myocardial response. a) Sudden change in the morphology of atheromatous plaque, i.e. disruption manifest as intraplaque hemorrhage, erosion or ulceration, or rupture/fissure. b) Exposed to subendothelial collagen and necrotic plaque contents, platelets undergo adhesion, aggregation, activation, and release of potent aggregators including thromboxane A2, serotonin, and platelet factors 3 and 4. c) Vasospasm is stimulated by platelet aggregation and the release of mediators. d) Other mediators activate the extrinsic pathway of quite elation adding to the bulk of the thrombus. e) Within minutes, the thrombus evolves to completely occluded the lumen of the coronary vessel. Myocardial response: cessation of aerobic glycolysis and initiation of anaerobic glycolysis leading to inadequate energy production. Myocardial necrosis begins around 30 minutes after coronary occlusion, and therefore, reperfusion should occur within the first 20 minutes if possible to reverse any damage. 3) List the gross and microscopic appearances of acute, organizing and healed myocardial infarcts. Type of MI Acute MI Gross 1/2-4 hr – none. 4-12 hr – occasionally dark mottling. 12-24 hr – dark mottling. Organizing MI 1-3 days – mottling with yellow-tan infarct center. 3-7 days – hyperemic border; Central yellow-tan softening. Healed MI 7-10 days – maximally yellow-tan and soft, with depressed red-tan margins. 10-14 days – red-gray depressed infarct borders. 2-8wk – gray-white scar, progressive from border towards core of infarct. >2 mo - scarring complete. Microscopic Usually none; variable waviness of border fibers Beginning coagulation necrosis; edema; hemorrhage Ongoing coagulation necrosis; pyknosis of nuclei; myocyte hypereosinophilia; marginal contraction band necrosis; beginning neutrophilic infiltrate. Coagulation necrosis, with loss of nuclei and striations; interstitial infiltrate of neutrophils. Beginning disintegration of dead myofibers, with dying neutrophils; early phagocytosis of dead cells by macrophages at infarct border. Well-developed phagocytosis of dead cells; early formation of fibrovascular granulation tissue at margins. Well-established granulation tissue with new blood vessels and collagen deposition. Increased collagen deposition, with decreased cellularity. Dense collagenous scar. 4) List and give the pertinent details of the consequences and the complications of myocardial infarcts. a) Contractile Dysfunction (Cardiogenic Shock) – some degree of left ventricular failure with hypotension, which may progress to pulmonary edema. 10-15% of patients, generally large infarct (40%), with a 70% mortality rate accounting for 2/3 of in-hospital deaths. b) Arrhythmias - conduction disturbances including sinus bradycardia, heart block (asystole), tachycardia, ventricular premature contractions or ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation. c) Myocardial Rupture - weakening from necrotic and inflamed myocardium results in rupture of the ventricular free wall (most common), intraventricular septum (left to right shunt produced), and papillary muscle rupture (least common) usually the posteriormedial muscle resulting in acute mitral valve regurgitation. Generally occurs in first week with 1-5% incidence. d) Ventricular Aneurysms or Mural Thrombi – resulting from stasis of blood in the area of hypo-contractibility. Systemic embolization of Meryl thrombus can results in obstruction of arteries in the brain, kidneys, bowel, etc. 5) Describe the concept of chronic ischemic heart disease. Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease (CIHD) describes patients who develop progressive heart failure as a consequence of ischemic myocardial damage. In most instances, there's been a prior MI and sometimes previous coronary arterial bypass graft surgery or other interventions. Usually presents as insidious onset of CHF. 6) Define and give the pathophysiology of sudden cardiac death. Sudden cardiac death implies that death at that time was unexpected and that it occurred within one hour of the onset of symptoms (if symptoms exist). Most are caused by CAD and are the result of fatal dysrrhythmias. The majority of successfully resuscitated patients do not show subsequent clinical evidence of acute MI. Pathophysiology: critical coronary atherosclerosis involving two or three of the major epicardial arteries. Acute MI in less than 1/3.