* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Notes G.6 Isosceles, Equilateral Triangles Mrs. Grieser
Survey
Document related concepts
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
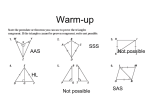
Geometry Notes G.6 Isosceles, Equilateral Triangles Mrs. Grieser Name: _____________________________________________ Date: ______________ Block: ________ Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles Base Angles Theorem If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite them are congruent. Converse of Base Angles Theorem If two angles of a triangle are congruent, the sides opposite them are congruent. Corollary to the Base Angles Theorem If a triangle is equilateral, then it is equiangular. Corollary to the Converse of the Base Angles Theorem If a triangle is equiangular, then it is equilateral. Examples a) Given RT ST . Name two congruent angles. b) Find AB and AC in the triangle at right. c) In the diagram find: 1) WY 2) mWXY d) mDEF 90 . Find values of x and y. e) 1) What post. can be used to prove that ABC AED ? f) Find the values of x and y. 2) Explain why ACD is equiangular. 3) Show that ABD AEC . Each angle in an equiangular triangle measures _______ Geometry Notes G.6 Isosceles, Equilateral Triangles g) Find the values of x and y. h) Given: BD bisects ADC ; DB AC Prove: ADC is isosceles Statements Reasons 1)________________ 1) Given 2) _______________ 2) Definition of < bisector 3) 3 4 3) ____________________ 4) DB DB 4) ____________________ 5) ______________ 5) ASA 6) ______________ 6) CPCTC 7) ADC is isosceles 7) _____________________ Mrs. Grieser Page 2