* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
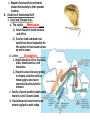
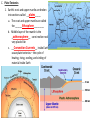
I. Plate Tectonics A. ___Continental Drift______ 1. Many early scientists have noticed that the Earth’s continents seemed to fit together. 2. ___Alfred Wegener____- proposed the theory of continental drift a. _Permian Period_ - about 225 million years ago 1.) all the continents formed a supercontinent called Pangaea 2.) ____Panthalassa____ was the major ocean b. __Triassic Period____ - Pangaea was split in two 1.) _____Laurasia_____ in the north (North America, Eurasia) and Gondwanaland in the south ( India, Africa, and South America) 2.) Panthalassa broken in two, one part becomes the ____Tethys Sea______ pg. 77 c. Wegner theorized that continents moved horizontally to their present location. B. Evidence of Continental Drift 1. Fossil and Climate Clues a. The reptile ___Mesosaurus____ 1.) fossils found in South America and Africa 2.) lived on land and water but would have been impossible for this animal to have swam across an entire ocean b. A fern _____Glossopteris________ 1.) fossils found in Africa, Australia, India, South America, and Antarctica 2.) found in areas that vary greatly in climate, scientists believe these regions once were connected and had similar climates c. Fossils of warm weather plants were found in Arctic Ocean Islands d. Glacial deposits have been found where no glaciers exist today 2. Sea-floor Spreading a. ___Mid-Ocean Ridge____1. using sound waves, scientists discovered a system of underwater mountain ranges in many oceans 2. The peaks of some of these mountains can form an island b. 1960’s scientist, _Harry Hess_, suggested a theory of ___sea-floor spreading___ 1. Magma gets forced upward through cracks in the ocean floor 2. As new material comes up it pushes sections of the sea floor away from the ridge. 3. The magma solidifies and creates new sea floor c. Evidence for Sea-floor Spreading 1. Youngest rocks are located at the midocean ridge 2. Reversals of Earth’s magnetic field are recorded by rocks in strips parallel to ridges Harry Hess C. Plate Tectonics 1. Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections called __plates_____ a. The crust and upper mantle are called the ______lithosphere_________ b. Middle layer of the mantle is the _asthenosphere__ - semi-molten rock, very plastic-like c. __Convection Currents__ inside Earth cause plate tectonics – the cycle of heating, rising, cooling, and sinking of material inside Earth 2. Plate Boundaries a. Divergent Boundary - two plates move away from one another; ex. Sea-floor spreading b. Convergent Boundary -two plates move toward each other, there are three types: 1.) subduction zone- dense ocean plate sinks under light continental plate ex: deep sea trench, volcanic mountain chains 2.) two ocean plates collide ex: deep sea trench, volcanic island chain 3.) two continental plates collide ex: mountains, earthquakes common c. Transform Fault Boundary two plates slide past each other; they can move in opposite directions or in the same direction