* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mod 64 SocPsych
Survey
Document related concepts
Milgram experiment wikipedia , lookup
Solomon Asch wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
In-group favoritism wikipedia , lookup
Stanford prison experiment wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Self-serving bias wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
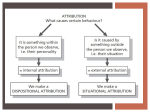
Social Psychology Unit 12 Attributions Attribution Theory • Attribution = explanation • Attribution Theory • Explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person’s disposition • Dispositional – factors within the person (personality) • Situational – factors outside the person (luck) Fundamental Attribution Error (FAE) • Tendency to use a dispositional explanation without considering the situational factors • “That guy cut me off because he is a jerk” – not that his wife could be in labor • video Attribution Bias • Actor-Observer Bias • Tendency to explain the behavior of others with dispositional attributes BUT use situational attitributes to explain our own behavior • Two people in comparison • Samantha watches her classmate stumble while giving a speech – “She’s a bad speech giver” BUT when Samantha stumbles in her own speech it was because she was distracted by a noise in the hallway. Self-Serving Bias • Tendency to attribute our successes to dispositional factors and our failures to situational factors. • Only your own behavior and makes you look good. • Jordan believes he aced the math test because he is smart but failed the history test because the teacher did not explain the material very well. Self-Effacing Bias • Tendency to attribute failures to dispositional factors and our successes to situational factors • Modesty False Consensus Effect • Tendency for an individual to overestimate how many others act and think the way they do. • You speed because because everyone else is speeding. Individualist vs. Collectivist • Individualist societies • U.S. and Western Europe • Self-serving bias and fundamental attribution error • Collectivist societies • Eastern Asia, Western Africa • Self-effacing bias Attitudes • Change • Central Route to Persuasion • People focus on factual information, logical arguments, and a thoughtful analysis of details • Peripheral Route to Persuasion • People focus on emotional appeals and incidental cues • Foot-in-the-door Phenomenon • Complying with small request then leads to going along with a larger request • video Social Influence • Study how other individuals’ thoughts and actions shape our own beliefs, feelings, and behaviors Cognitive Dissonance • Only occurs within an individual • Tension is created when one holds two conflicting beliefs or if one’s beliefs and actions do not match • Smoking • Attitude or behavior change results because one is motivated to reduce the tension • Leon Festinger -Festinger’s $1 or $20 Study • Video Song • Philip Zimbardo Stanford Prison Experiment • Stanford ‘72 • Power of social roles and impact of situation • Mock prison • 2 wk experiment called off in 6 days • Highly unethical • video Conformity • Adoption of attitudes and behaviors shared by a particular group of people • Asch Line Study • Group size • Unanimity • Asch Experiment Obedience • Altering one’s behavior in response to a demand from an authority figure • Stanley Milgram • Shock Study • With demand from authority figure, 65% of participants obey • Video