* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How the universe began
Survey
Document related concepts
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
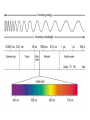
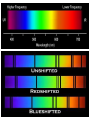
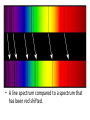
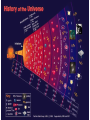
How the universe began 1.2 unit 1 theme 1 My wider world Learning objectives • What happens to the observed wave length and frequency of a moving wave source? • What do we mean by the ‘red shift’ in light observed from most distant galaxies? • What evidence do we have that the universe is expanding and how does this support the Big Bang theory? Wave lengths and wave source • Hubble used telescopes to measure the light from stars and galaxies • Light from stars is a blend of different colours • Different colours of light have different blends of colours present • Spectroscopy - shows different colours of light as lines on a coloured spectrum • A line spectrum compared to a spectrum that has been red shifted. Doppler effect • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/scien ce/aqa/origins/redshiftrev2.shtml • H:\My Documents\My Videos\The Doppler Effect.flv • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/scien ce/aqa/origins/redshiftrev2.shtml • http://www.animations.physics.unsw.edu.au/jw/ doppler.htm#example • http://www.animations.physics.unsw.edu.au/jw/ doppler.htm#source Doppler effect • Imagine a train travelling past you very fast • As it gets closer the noise it makes goes to a higher pitch • As it moves away the pitch falls • This is the Doppler effect Doppler effect • Wave source moving towards us is squashed • Wave source moving away from us is stretched. How can we tell that the stars are moving • When a star or galaxy moves away from us it’s light appears redder than expected because its wavelength is stretched. • Hubble’s results proved that galaxies move away from us. • The galaxies further away have a bigger red shift because they are moving away faster than closer galaxies How could Hubble tell that galaxies further away were moving faster than closer galaxies? The universe is expanding • Galaxies in all directions are moving away from the earth • Does this make the Earth the centre of the universe? • Scientists don’t think this is true • Blow up a balloon with spots all over it – all the spots get further away from each other The universe was once smaller • So small – all matter and energy squashed in one tiny place • Cosmic egg • The big bang theory • Hugh explosion 14 billion years ago • Scientists can detect cosmic backgound radiation coming from all directions – this is called the ‘echo of the big bang’ Did you know? • The researchers who discovered the cosmic background radiation were investigating something completely different • They thought the noise was caused by pigeon droppings in the receiver of the telescope Key points • The universe began as a huge explosion called the Big Bang • The red-shift is evidence that the universe is still expanding • The cosmic background radiation is evidence that the big bang took place • The wave length and frequency of a moving light source changes • http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/space/universe /questions_and_ideas/big_bang#p00fz68w • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/sc ience/add_ocr_pre_2011/wave_model/lighta ndsoundact.shtml