* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2A. Two similar inductive coils with negligible resistance are wound
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
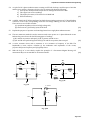
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Reg. No. : MANIPAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, MANIPAL (A Constituent Institute of Manipal University, Manipal) FIRST SEMESTER B.E. DEGREE END SEMESTER EXAMINATION (REVISED CREDIT SYSTEM: 2007) 16 November 2009 BASIC ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (ELE 101) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 50 Note : Answer any FIVE full questions. Missing data, if any, may be suitably assumed. 1A. Define and explain the significance of the term “temperature coefficient of resistance”. The field winding of a motor has a resistance of 500 Ω at 150C. By how much will the resistance increase if the motor attains a temperature of 450C, when it is running? The winding is made of copper and its temperature coefficient of resistance at 00C is 0.00428/0C. (03) 1B. Determine the resistance between the points A and B using star‐delta transformation in Fig Q1B (04) 1C. In the circuit shown in Fig. Q1C, find the current through all resistors by mesh current analysis. (03) 2A. Two similar inductive coils with negligible resistance are wound on the same core. When excited by a 200V, 50Hz source, the first coil takes 5.2A and the emf induced in the second coil is 50V. Find the self inductance of the two coils, mutual inductance between the two coils and the coupling coefficient. (04) 2B. For the network shown in Fig Q2B the switch is in position 1 at t = 0 and is moved to position 2 at t = 10 ms. Determine iL(t) for 0 ≤ t ≤ ∞ and sketch the current variation with respect to time. (03) 2C. A mild steel ring having a cross sectional area of 400 mm2 and a mean circumference of 400 mm has a coil of 200 turns wound uniformly around it. Relative permeability of mild steel is 300. It is required to produce a flux of 800x10‐6 wb in the ring. Determine a) Reluctance of the ring b) Excitation current required. (03) 3A. Analytically derive the phasor relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductor. Hence show that average power consumed by the inductor is zero. Draw the waveform showing voltage, current and power. (03) 3B. A single phase circuit comprises of two lagging loads, which are connected in series and dissipate 800W and 1000W respectively. Two voltmeters connected across each load read 100V and 200V respectively. If the current flowing through the circuit is 10A, determine (i) Applied voltage (ii) power factor of the combination. (04) 3C. An inductive load takes 60A of a single phase a. c. supply of 230 volt, 50 Hz at a p. f. of 0. 6 lagging. Calculate the value of capacitance to be connected across the load to raise the power facter of the combined circuit to 0.9 lagging. Also calculate the active, reactive and apparent powers after power factor improvement. (03) 4A. A symmetrical 3 phase, RYB sequence, 3 wire, 400V, 50 Hz supply feeds an unbalanced star connected load. The branch impedances of the load are Z R= (8.66+j5) Ω, ZY = (7.07‐j7.07) Ω and ZB=(10+j17.32) Ω. Calculate the three line currents by converting star connected load to equivalent delta connected load. Hence determine the voltages across the original star connected impedances. Take VRY as reference. (06) 4B. With a neat sketch, explain the operation of a Star‐Delta starter used with 3 phase induction motor. (04) Page 1 of 2 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering 5A. A 6 pole 50 Hz 3‐phase induction motor running on full load develops a useful torque of 160 Nm and the rotor emf has a frequency of 120 cycles per minute. Calculate the following: i) Gross power developed if the torque loss in windage and friction is 12Nm. ii) The copper loss in rotor windings iii) The input to the motor, if the stator loss is 800W and iv) Full load efficiency (05) 5B. A 30KVA, 2400/120 V, 50Hz transformer has high voltage winding resistance of 4.5 Ω and leakage reactance of 10 Ω. The corresponding values on low voltage winding are 0.01 Ω and 0.025 Ω. The iron losses are 1.5 KW. Calculate (a) equivalent impedance referred to high voltage side, (b) total losses at (i) full load (ii) 60% of full load. (03) 5C. Explain the purpose of capacitor and centrifugal switch in a single phase induction motor. (02) 6A. The two wattmeter method is used to measure total active power in a 3 phase balanced circuit. Indicate the power factors for the following types of readings: (i) W1 and W2 are positive and equal, (ii) W1 is positive and W2 is zero (iii) W1 and W2 are equal and opposite and (iv) W1 and W2 are positive, but not equal (02) 6B. A series resonant circuit with a resistance is 4 Ω resonates at frequency of 2.9 KHz. The bandwidth is 3x103 rad/sec. Calculate (i) the inductance and capacitance of the circuit, (ii) lower half power frequency and (iii) Quality factor. (04) 6C. With the help of a neat sketch, explain the principle of a Permanent Magnet Moving Coil instrument. Why it is not suitable for AC measurements? (04) A 6Ω 4Ω 3Ω 5Ω 2Vx Vx + 4Ω 3Ω 5Ω 2Ω 5V 4Ω 3A 6V 2Ω Fig. Q 1C B Fig. Q 1B t = 10 ms 1 2 10 Ω 15 Ω 10 V 0.1 H Fig. Q 2B Page 2 of 2