* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ohms Law - Abel Electronics
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
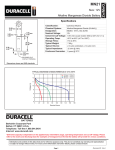
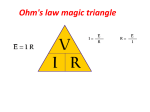
Electronics Calculations Using Ohm’s Law Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference or voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. The mathematical equation that describes this relationship is: I=V/R Ohm's Law is commonly used in calculations dealing with electronic circuits. Ohm's Law is straight forward, but when you're trying to solve for one variable or another, it is easy to get them confused. The Table below is some common calculations using Ohm's Law. In these calculations: • • • • V= Voltage ( In Volts ) I= Current ( In Amps ) R=Resistance ( In Ohms ) P=Power ( In Watts ) Unknown Value Formula Voltage V=IR Current I=V/R Resistance R=V/I Power P=VI, P=V²/R or P=I²R Volt-Amp to Amp Conversion To convert volt-amps to amps take the volt amp rating and divide it by the voltage of the unit. For example you have a 24 volt 50VA power supply the amp rating would be 2.08 V/VA=A For informational use only. Although information is in compliance with industry standards, Abel Electronics cannot be responsible for any errors or misprints with the data above.