* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquake Waves - davis.k12.ut.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
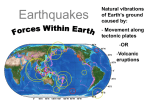
Seismic Waves Seismic Waves (notes) • Wave shape: Transverse and longitudinal • Wave type: Mechanical • Medium: The Earth • Structure: • Composed of two parts: a longitudinal P-wave and a transverse S-wave. The Fault In Our Earth (notes) • Earthquakes are produced by the Earth moving along faults • Faults are areas where two volumes of rock have been shifted relative to each other • Faults are produced by the movement of the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface Piqiang Fault, China Wasatch Fault (not notes) • We have a fault line running through our area called the Wasatch Fault • Because we are close to a lake, another concern is something called “liquefaction”, which is when loose, sandy soil behaves like a liquid when shaken • After class if interested I have a map up front of Davis County’s fault lines Faults =/= Plate Boundaries (not notes) • A plate boundary is where two major tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface meet • Faults are only minor “stretches” or “slips” that are a result of these larger plates moving P-Waves (notes) • P-wave stands for “primary wave” because it is faster and reaches us first • P-waves are longitudinal waves S-Waves (notes) • S-wave stands for “secondary wave” because it is slower and reaches us after the P-wave • S-waves are transverse waves Locating Earthquakes (not notes) • Because P-waves and S-waves travel at different speeds, we can use the difference in time to estimate the distance of an earthquake Close near source P-Wave S-Wave Separated far from source The further away an earthquake is the more separation between the arrival time of the P-waves and S-waves. Think of it like timing the distance of lightning by counting the difference between the arrival of light and sound.