* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Genetics
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
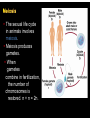
§ An organism produces gametes (sex cells) to maintain the same number of chromosomes from generation to generation. § Human gametes contain 23 chromosomes. § A cell with n chromosomes is called a haploid cell. § A cell that contains 2n chromosomes is called a diploid cell. § The sexual life cycle in animals involves meiosis. § Meiosis produces gametes. § When gametes combine in fertilization, the number of chromosomes is restored. n + n = 2n. § Asexual reproduction § The organism inherits all of its chromosomes from a single parent. § The new individual is genetically identical to its parent. § Sexual reproduction § Beneficial genes multiply faster over time. Mendelian Genetics How Genetics Began The passing of traits to the next generation is called inheritance, or heredity. § Gregor Mendel performed crosspollination in pea plants. § Mendel followed various traits in the pea plants he bred. Gregor Mendel: 100 Greatest Discoveries Mendelian Genetics Mendelian Genetics § Mendel studied seven different traits. § Seed or pea § Seed pod shape color § Stem length § Seed pod color § Flower position § Seed shape or texture § Flower color Review Scientific Method: Independent Variable Dependent Variable Constants Mendelian Genetics Genes in Pairs § Allele § An alternative form of a single gene passed from generation to generation § We use letters of the alphabet to represent alleles § Recessive (lowercase letter) § Dominant (uppercase letter) Mendelian Genetics Dominance § An organism with two of the same alleles for a particular trait is homozygous. Both alleles are either dominant or recessive. § An organism with two different alleles for a particular trait is heterozygous. One allele is dominant, and one allele is recessive. Mendelian Genetics Genotype and Phenotype § An organism’s allele pairs are called its genotype. § The observable characteristic or outward expression of an allele pair is called the phenotype. Make a Bunny! and Bioethics in Genetic Testing! Which symbol is used to represent the number of chromosomes in a gamete? A. # B. x C. r D. n Which person is known as the father of genetics? A. Felix Mendelssohn B. Gregor Mendel C. Bill Nye D. Albert Einstein Which term refers to the outward physical expression of an allele pair? A. gamete B. hybrid C. phenotype D. genotype What are the segments of DNA that control the production of proteins? A. chromatids B. chromosomes C. genes D. traits What type of organisms can only reproduce asexually? A. bacteria (prokaryote) B. protists (unicellular eukaryote) C. plants (eukaryote) D. animals (eukaryote) What is the name for different forms of a single gene that are passed from generation to generation? A. alleles B. genotypes C. phenotypes D. traits Which pair of alleles is heterozygous? A. RR B. Rr C. rr D. yR Homozygous Dominant Heterozygous Homozygous Recessive What is this process called? A. fertilization B. gamete formation C. inheritance D. reproduction