* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Level Guide Chapter 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
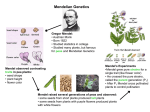
Name ___________________________ Date _______ Period ________ Level I Guide: Chapter 9 Level I Directions: Read each statement carefully. Using your textbook, decide if the statement is true or false. Determine if the statement is true or false and place that in the first blank and the page number in the second blank. Correct all statements that are false so that you have statements so that you have true statements to help you study for your test. True False Page ___________ ___________ 1. ___________ 2. ___________ A trait is a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring. A set of traits that is passed on from parents to offspring Is called heredity. Mendel saw that traits that appeared in the parent generation did not show up in the first generation, but did show up in the second generation. Mendel chose pea plants for his experiment because they were his favorite vegetable. ___________ ___________ 3. ___________ ___________ 4. ___________ ___________ 5. ___________ ___________ 6. ___________ ___________ 7. ___________ ___________ 8. ___________ ___________ 9. ___________ ___________ 10. A phenotype is the form of the trait that we see. ___________ ___________ 11. The genotype of an organism shows the genes if contains. ___________ ___________ 12. ___________ ___________ 13. A lowercase letter represents the dominant allele and an uppercase letter represents the recessive allele. Individual units called genes determine an organism’s traits. ___________ ___________ 14. A gene is a piece of DNA on the chromosomes that carries hereditary information. ___________ ___________ 15. A punnett square can be used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring. When true-breeding plants self-pollinate they produce offspring with the same form of the trait as the parent plant. Mendel used cross-pollination to find out what would happen if he crossed two plants with different forms of a trait. When Mendel used ratios to compare the number of white flowers to the number of purple flowers produced in the second generation, he found that the ratio of purple flowers to every white flower was 4:1. Mendel found that for every trait of a gene there must be two forms of the same gene called alleles. A recessive allele covers up the appearance of the dominant allele when it is present. Name ___________________________ Date _______ Period ________ ___________ ___________ 16. Probability is the chance that an event will occur. ___________ ___________ 17. ___________ ___________ 18. A female has two X chromosomes in her body cells, while a male has two Y chromosomes in his body cells The chances of having a boy or a girl are 50:50. Level II Directions: Using your prior knowledge and what you have learned from this section, to complete the assignment below. You are Gregor Mendel! Write a short letter explaining your work with pea plants to a friend or colleague. BE SURE TO INCLUDE how you actually carry out your experiments as well as what you have discovered through your work.