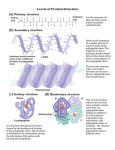
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download REVIEW PowerPoint - Ch. 1-5
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
1. Which of these is not a property of all living organisms? a. organization b. acquisition of materials and energy c. care for their offspring d. reproduction e. responding to the environment 1. Which of these is not a property of all living organisms? a. organization b. acquisition of materials and energy c. care for their offspring d. reproduction e. responding to the environment 3. The level of organization that includes cells of similar structure and function would be a. b. c. d. An organ A tissue An organ system An organism 3. The level of organization that includes cells of similar structure and function would be a. b. c. d. An organ A tissue An organ system An organism 4. The color, temperature, and foul odor of the flowers of the titan arum are examples of a. obtaining materials b. adaptations c. organizations d. homeostasis 4. The color, temperature, and foul odor of the flowers of the titan arum are examples of a. obtaining materials b. adaptations c. organizations d. homeostasis • 5. which of the following is an example of adaptation? a. In a very wet year, some plants grow unusually tall stalks and large leaves b. Over millions of years, the eyes of cave salamanders lose their function c. An escaped dog joins a pack of wild dogs and begins interbreeding with them d. A harsh winter kills many birds within a population, especially the smallest ones • 5. which of the following is an example of adaptation? a. In a very wet year, some plants grow unusually tall stalks and large leaves b. Over millions of years, the eyes of cave salamanders lose their function c. An escaped dog joins a pack of wild dogs and begins interbreeding with them d. A harsh winter kills many birds within a population, especially the smallest ones • 6. energy is brought into ecosystems by which of the following? a. fungi and other decomposers b. cows and other organisms that graze on grass c. meat-eating animals d. organisms that photosynthesize, such as plants e. all of these are correct • 6. energy is brought into ecosystems by which of the following? a. fungi and other decomposers b. cows and other organisms that graze on grass c. meat-eating animals d. organisms that photosynthesize, such as plants e. all of these are correct 7. we use the scientific method every day. Suppose one morning that your car does not start. Which of the following is a testable hypothesis stemming from this observation? a. b. c. d. e. I’m going to be late My battery is dead Check to see if I left the lights on Kick the tires I will add a quart of oil 7. we use the scientific method every day. Suppose one morning that your car does not start. Which of the following is a testable hypothesis stemming from this observation? a. b. c. d. e. I’m going to be late My battery is dead Check to see if I left the lights on Kick the tires I will add a quart of oil 8. which of the following statements is a hypothesis? a. Will increasing my cat’s food increase her weight? b. Increasing my cat’s food consumption will result in a 25% increase in her weight c. I will feed my cat more food d. My cat has gained weight; therefore, she is eating more food 8. which of the following statements is a hypothesis? a. Will increasing my cat’s food increase her weight? b. Increasing my cat’s food consumption will result in a 25% increase in her weight c. I will feed my cat more food d. My cat has gained weight; therefore, she is eating more food 9. After formulating a hypothesis, a scientist a. b. c. d. Proves the hypothesis Tests the hypothesis Decides how to best avoid having a control Makes sure environmental conditions are just right e. Formulates a scientific theory 9. After formulating a hypothesis, a scientist a. b. c. d. Proves the hypothesis Tests the hypothesis Decides how to best avoid having a control Makes sure environmental conditions are just right e. Formulates a scientific theory 10. The experimental variable in the bluebird experiment was the a. b. c. d. e. Use of a model male bluebird Observations of the experimenter Various behavior of the males Identification of what bluebirds to study All of these are correct 10. The experimental variable in the bluebird experiment was the a. b. c. d. e. Use of a model male bluebird Observations of the experimenter Various behavior of the males Identification of what bluebirds to study All of these are correct 12. Which of the following are agents of natural selection? a. Changes in the environment b. Competition among individuals for food and water c. Predation by another species d. Competition among members of a population for prime nesting sites e. All of these are correct 12. Which of the following are agents of natural selection? a. Changes in the environment b. Competition among individuals for food and water c. Predation by another species d. Competition among members of a population for prime nesting sites e. All of these are correct 13. Which of the following is an example of natural selection? a. In a very wet year, some plants grow unusually tall stalks and large leaves b. After unusually cold winters, squirrels with an extra layer of fat have more offspring c. Squirrels may have long or short tails d. Dogs with longer legs are able to run faster than dogs with shorter legs 13. Which of the following is an example of natural selection? a. In a very wet year, some plants grow unusually tall stalks and large leaves b. After unusually cold winters, squirrels with an extra layer of fat have more offspring c. Squirrels may have long or short tails d. Dogs with longer legs are able to run faster than dogs with shorter legs 14. Which of the following statements regarding evolution is false? a. Adaptation may be physical or behavioral b. Natural selection always results in organisms becoming more adapted to the environment c. A trait selected for may suddenly become selected against when the environment changes d. Some traits are neither selected for nor against 14. Which of the following statements regarding evolution is false? a. Adaptation may be physical or behavioral b. Natural selection always results in organisms becoming more adapted to the environment c. A trait selected for may suddenly become selected against when the environment changes d. Some traits are neither selected for nor against 1. which of the subatomic particles contributes almost no weight to an atom? a. b. c. d. Protons in electron shells Electrons in the nucleus Neutrons in the nucleus Electrons at various energy levels 1. which of the subatomic particles contributes almost no weight to an atom? a. b. c. d. Protons in electron shells Electrons in the nucleus Neutrons in the nucleus Electrons at various energy levels 2. The atomic number tells you the a. b. c. d. e. Number of neutrons in the nucleus Number of protons in the atom Atomic mass of the atom Number of its electrons if the atom is neutral Both b and d are correct 2. The atomic number tells you the a. b. c. d. e. Number of neutrons in the nucleus Number of protons in the atom Atomic mass of the atom Number of its electrons if the atom is neutral Both b and d are correct 3. an atom that has 2 electrons in the outer shell, such as magnesium, would most likely a. Share to acquire a completed outer shell b. Lose these 2 electrons and become a negatively charged ion c. Lose these two electrons and become a positively charged ion d. Bind with carbon by way of hydrogen bonds e. Bind with another calcium atom to satisfy its energy needs 3. an atom that has 2 electrons in the outer shell, such as magnesium, would most likely a. Share to acquire a completed outer shell b. Lose these 2 electrons and become a negatively charged ion c. Lose these two electrons and become a positively charged ion d. Bind with carbon by way of hydrogen bonds e. Bind with another calcium atom to satisfy its energy needs 4. Isotopes differ in their a. b. c. d. Number of protons Atomic number Number of neutrons Number of electrons 4. Isotopes differ in their a. b. c. d. Number of protons Atomic number Number of neutrons Number of electrons 5. When an atom gains electrons, it a. b. c. d. e. Forms a negatively charged ion Forms a positively charged ion Forms covalent bonds Forms ionic bonds Gains atomic mass 5. When an atom gains electrons, it a. b. c. d. e. Forms a negatively charged ion Forms a positively charged ion Forms covalent bonds Forms ionic bonds Gains atomic mass 8. In which of these are the electrons always shared unequally? a. b. c. d. e. Double covalent bond Triple covalent bond Hydrogen bond Polar covalent bond Ionic and covalent bonds 8. In which of these are the electrons always shared unequally? a. b. c. d. e. Double covalent bond Triple covalent bond Hydrogen bond Polar covalent bond Ionic and covalent bonds 12. H2CO3/NaHCO3 is a buffer system in the body. What effect will the addition of an acid have on the pH of a solution that is buffered? a. b. c. d. The pH will rise The pH will lower The pH will not change All of these are correct 12. H2CO3/NaHCO3 is a buffer system in the body. What effect will the addition of an acid have on the pH of a solution that is buffered? a. b. c. d. The pH will rise The pH will lower The pH will not change All of these are correct 13. rainwater has pH of about 5.6; therefore, rainwater is a. b. c. d. A neutral solution An acidic solution A basic solution It depends if it is buffered 13. rainwater has pH of about 5.6; therefore, rainwater is a. b. c. d. A neutral solution An acidic solution A basic solution It depends if it is buffered 15. Which type of bond results from the sharing of electrons between atoms? a. b. c. d. Covalent Ionic Hydrogen Neutral 15. Which type of bond results from the sharing of electrons between atoms? a. b. c. d. Covalent Ionic Hydrogen Neutral 17. Why is –NH2 a polar group? a. b. c. d. Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen The bonds are not symmetrical Because hydrogen bonding takes place Both a and b are correct 17. Why is –NH2 a polar group? a. b. c. d. Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen The bonds are not symmetrical Because hydrogen bonding takes place Both a and b are correct 1. Which of these is NOT a characteristic of carbon? a. b. c. d. e. Forms 4 covalent bonds Bonds with other carbon atoms Is sometimes ionic Can form long chains Sometimes shares two pairs of electrons with another atom 1. Which of these is NOT a characteristic of carbon? a. b. c. d. e. Forms 4 covalent bonds Bonds with other carbon atoms Is sometimes ionic Can form long chains Sometimes shares two pairs of electrons with another atom 3. a hydrophilic group is a. b. c. d. e. Attracted to water A polar and/or ionized group Found at the end of fatty acids The opposite of a hydrophobic group All of these are correct 3. a hydrophilic group is a. b. c. d. e. Attracted to water A polar and/or ionized group Found at the end of fatty acids The opposite of a hydrophobic group All of these are correct 4. Which of these is an example of a hydrolysis reaction? a. b. c. d. e. Amino acid + amino aciddipeptide + water Dipeptide + water amino acid + amino acid Denaturation of a polypeptide Both a and b are correct Both b and c are correct 4. Which of these is an example of a hydrolysis reaction? a. b. c. d. e. Amino acid + amino aciddipeptide + water Dipeptide + water amino acid + amino acid Denaturation of a polypeptide Both a and b are correct Both b and c are correct 6. a fatty acid is unsaturated if it a. b. c. d. e. Contains hydrogen Contains carbon-carbon double bonds Contains a carboxyl group Bonds to glycogen Bonds to a nucleotide 6. a fatty acid is unsaturated if it a. b. c. d. e. Contains hydrogen Contains carbon-carbon double bonds Contains a carboxyl group Bonds to glycogen Bonds to a nucleotide 7. Which of these is NOT a lipid? a. b. c. d. e. Steroid Fat Polysaccharide Wax phospholipid 7. Which of these is NOT a lipid? a. b. c. d. e. Steroid Fat Polysaccharide Wax phospholipid 8. The difference between one amino acid and another is found in the a. b. c. d. e. Amino group Carboxyl group R group Peptide bond Carbon atoms 8. The difference between one amino acid and another is found in the a. b. c. d. e. Amino group Carboxyl group R group Peptide bond Carbon atoms 9. The shape of a polypeptide is a. Maintained by bonding between parts of the polypeptide b. Ultimately dependent on the primary structure c. Necessary to its function d. All of these are correct 9. The shape of a polypeptide is a. Maintained by bonding between parts of the polypeptide b. Ultimately dependent on the primary structure c. Necessary to its function d. All of these are correct 11. Nucleotides a. Contain a sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group. b. Are the monomers of fats and polysaccharides. c. Join together by covalent bonding between the bases. d. Are present in both DNA and RNA e. Both a and d are correct. 11. Nucleotides a. Contain a sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group. b. Are the monomers of fats and polysaccharides. c. Join together by covalent bonding between the bases. d. Are present in both DNA and RNA e. Both a and d are correct. 12. ATP a. Is an amino acid b. Has a helical structure c. Is a high-energy molecule that can break down to ADP and phosphate d. Provides enzymes for metabolism e. Is most energetic when in the ADP state 12. ATP a. Is an amino acid b. Has a helical structure c. Is a high-energy molecule that can break down to ADP and phosphate d. Provides enzymes for metabolism e. Is most energetic when in the ADP state 14. The monomer of a carbohydrate is a. b. c. d. An amino acid A nucleic acid A monosaccharide A fatty acid 14. The monomer of a carbohydrate is a. b. c. d. An amino acid A nucleic acid A monosaccharide A fatty acid 15. The joining of two adjacent amino acids is called a. b. c. d. A peptide bond A dehydration reaction A covalent bond All of these are correct 15. The joining of two adjacent amino acids is called a. b. c. d. A peptide bond A dehydration reaction A covalent bond All of these are correct 16. The characteristic globular shape of a polypeptide is the a. b. c. d. Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure 16. The characteristic globular shape of a polypeptide is the a. b. c. d. Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure 17. The shape of a polypeptide a. Is maintained by bonding between parts of the polypeptide b. Is ultimately dependent on the primary structure c. Involves hydrogen bonding d. All of these are correct 17. The shape of a polypeptide a. Is maintained by bonding between parts of the polypeptide b. Is ultimately dependent on the primary structure c. Involves hydrogen bonding d. All of these are correct 18. Which of the following pertains to an RNA nucleotide and not to a DNA nucleotide? a. b. c. d. Contains the sugar ribose Contains a nitrogen-containing base Contains a phosphate molecule Becomes bonded to other nucleotides following a dehydration reaction 18. Which of the following pertains to an RNA nucleotide and not to a DNA nucleotide? a. b. c. d. Contains the sugar ribose Contains a nitrogen-containing base Contains a phosphate molecule Becomes bonded to other nucleotides following a dehydration reaction 19. Which is a carbohydrate? a. b. c. d. Disaccharide Amino acid Dipeptide Both a and c are correct 19. Which is a carbohydrate? a. b. c. d. Disaccharide Amino acid Dipeptide Both a and c are correct 31. Which of these does not apply to DNA? a. b. c. d. e. Sequence of nucleotides Sugar-phosphate backbone A-T and C-G Sequence of amino acids Both a and c do not apply 31. Which of these does not apply to DNA? a. b. c. d. e. Sequence of nucleotides Sugar-phosphate backbone A-T and C-G Sequence of amino acids Both a and c do not apply • 32. Which is a correct statement about carbohydrates? a. All polysaccharides serve as energy storage molecules b. Glucose is broken down for immediate energy. c. Glucose is not a carbohydrate, only polysaccharides are. d. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose have different monomers. e. Both a and c are correct. • 32. Which is a correct statement about carbohydrates? a. All polysaccharides serve as energy storage molecules b. Glucose is broken down for immediate energy. c. Glucose is not a carbohydrate, only polysaccharides are. d. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose have different monomers. e. Both a and c are correct. 33. In phospholipids, a. b. c. d. Heads are polar Tails are nonpolar Heads contain phosphate All of these are correct 33. In phospholipids, a. b. c. d. Heads are polar Tails are nonpolar Heads contain phosphate All of these are correct 1. The small size of cells best correlates with a. The fact that they are self-reproducing b. Their prokaryotic versus eukaryotic nature c. An adequate surface area for exchange of materials d. The fact that they come in multiple sizes e. All of these are correct 1. The small size of cells best correlates with a. The fact that they are self-reproducing b. Their prokaryotic versus eukaryotic nature c. An adequate surface area for exchange of materials d. The fact that they come in multiple sizes e. All of these are correct • 3. Which of these best distinguishes a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell? a. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, but eukaryotic cells never do. b. Prokaryotic cells are much larger than eukaryotic cells c. Prokaryotic cells have flagella, but eukaryotic cells do not d. Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, but eukaryotic cells do have such a nucleus. e. Prokaryotic cells have ribosomes, but eukaryotic cells do not have ribosomes. • 3. Which of these best distinguishes a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell? a. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, but eukaryotic cells never do. b. Prokaryotic cells are much larger than eukaryotic cells c. Prokaryotic cells have flagella, but eukaryotic cells do not d. Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, but eukaryotic cells do have such a nucleus. e. Prokaryotic cells have ribosomes, but eukaryotic cells do not have ribosomes. 4. Which of these is not found in the nucleus? a. b. c. d. e. Functioning ribosomes Chromatin that condenses to chromosomes Nucleolus that produces rRNA Nucleoplasm instead of cytoplasm All forms or RNA 4. Which of these is not found in the nucleus? a. b. c. d. e. Functioning ribosomes Chromatin that condenses to chromosomes Nucleolus that produces rRNA Nucleoplasm instead of cytoplasm All forms or RNA 5. Vesicles from the ER most likely are on their way to a. b. c. d. e. The The The The The rough ER lysosomes Golgi apparatus plant cell vacuole only location suitable to their size 5. Vesicles from the ER most likely are on their way to a. b. c. d. e. The The The The The rough ER lysosomes Golgi apparatus plant cell vacuole only location suitable to their size 6. Lysosomes function in a. b. c. d. e. Protein synthesis Processing and packaging Intracellular digestion Lipid synthesis Production of hydrogen peroxide 6. Lysosomes function in a. b. c. d. e. Protein synthesis Processing and packaging Intracellular digestion Lipid synthesis Production of hydrogen peroxide 7. Mitochondria a. b. c. d. e. Are involved in cellular respiration Break down ATP to release energy for cells Contain grana and cristae Are present in animal cells but not plant cells All of these are correct 7. Mitochondria a. b. c. d. e. Are involved in cellular respiration Break down ATP to release energy for cells Contain grana and cristae Are present in animal cells but not plant cells All of these are correct 12. Which of the following organelles contains its own DNA, suggesting they were once independent prokaryotes? a. b. c. d. e. Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Chloroplasts Ribosomes Both b and c are correct 12. Which of the following organelles contains its own DNA, suggesting they were once independent prokaryotes? a. b. c. d. e. Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Chloroplasts Ribosomes Both b and c are correct 13. Which organelle most likely originated by invagination of the plasma membrane? a. b. c. d. e. Mitochondria Flagella Nucleus Chloroplasts All of these are correct 13. Which organelle most likely originated by invagination of the plasma membrane? a. b. c. d. e. Mitochondria Flagella Nucleus Chloroplasts All of these are correct 14. Which structures are found in a prokaryotic cell? a. b. c. d. Cell wall, ribosomes, thylakoids, chromosome Cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, flagellum Nucleoid, ribosomes, chloroplasts, capsule Plasmid, ribosomes, enzymes, DNA, mitochondria e. Chlorophyll, enzymes, Golgi, plasmids 14. Which structures are found in a prokaryotic cell? a. b. c. d. Cell wall, ribosomes, thylakoids, chromosome Cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, flagellum Nucleoid, ribosomes, chloroplasts, capsule Plasmid, ribosomes, enzymes, DNA, mitochondria e. Chlorophyll, enzymes, Golgi, plasmids 3. A phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The tails are found a. b. c. d. e. At the surfaces of the membrane In the interior of the membrane Spanning the membrane Where the environment is hydrophilic Both a and b are correct 3. A phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The tails are found a. b. c. d. e. At the surfaces of the membrane In the interior of the membrane Spanning the membrane Where the environment is hydrophilic Both a and b are correct • 4. During diffusion, a. Solvents move from the area of higher to lower concentration, but solutes do not. b. There is a net movement of molecules from the area of higher to lower concentration. c. A cell must be present for any movement of molecules to occur. d. Molecules move against their concentration gradient if they are small and charged. e. All of these are correct. • 4. During diffusion, a. Solvents move from the area of higher to lower concentration, but solutes do not. b. There is a net movement of molecules from the area of higher to lower concentration. c. A cell must be present for any movement of molecules to occur. d. Molecules move against their concentration gradient if they are small and charged. e. All of these are correct. • 5. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, a. Solute exits the cell to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. b. Water exits the cell toward the area of lower solute concentration. c. Water enters the cell toward the area of higher solute concentration. d. Solute exits and water enters the cell. e. Both c and d are correct. • 5. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, a. Solute exits the cell to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. b. Water exits the cell toward the area of lower solute concentration. c. Water enters the cell toward the area of higher solute concentration. d. Solute exits and water enters the cell. e. Both c and d are correct. • 6. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, a. Solute exits the cell to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. b. Water exits the cell toward the area of lower solute concentration. c. Water exits the cell toward the area of higher solute concentration. d. Solute exits and water enters the cell. e. Both a and c are correct. • 6. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, a. Solute exits the cell to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. b. Water exits the cell toward the area of lower solute concentration. c. Water exits the cell toward the area of higher solute concentration. d. Solute exits and water enters the cell. e. Both a and c are correct. 7. Active transport a. Requires a carrier protein. b. Moves a molecule against its concentration gradient. c. Requires a supply of chemical energy d. Does not occur during facilitated transport. e. All of these are correct. 7. Active transport a. Requires a carrier protein. b. Moves a molecule against its concentration gradient. c. Requires a supply of chemical energy d. Does not occur during facilitated transport. e. All of these are correct. 8. The sodium-potassium pump a. Helps establish an electrochemical gradient across the membrane. b. Concentrates sodium on the outside of the membrane. c. Uses a carrier protein and chemical energy. d. Is present in the plasma membrane. e. All of these are correct. 8. The sodium-potassium pump a. Helps establish an electrochemical gradient across the membrane. b. Concentrates sodium on the outside of the membrane. c. Uses a carrier protein and chemical energy. d. Is present in the plasma membrane. e. All of these are correct. 9. Receptor-mediated endocytosis a. b. c. d. e. Is no different from phagocytosis Brings specific solutes into the cell Helps concentrate proteins in vesicles Results in high osmotic pressure All of these are correct 9. Receptor-mediated endocytosis a. b. c. d. e. Is no different from phagocytosis Brings specific solutes into the cell Helps concentrate proteins in vesicles Results in high osmotic pressure All of these are correct • 10. Plant cells a. Always have a secondary cell wall, even though the primary one may disappear b. Have channels between cells that allow strands of cytoplasm to pass from cell to cell c. Develop turgor pressure when water enters the nucleus d. Do not have cell-to-cell junctions like animal cells. e. All of these are correct • 10. Plant cells a. Always have a secondary cell wall, even though the primary one may disappear b. Have channels between cells that allow strands of cytoplasm to pass from cell to cell c. Develop turgor pressure when water enters the nucleus d. Do not have cell-to-cell junctions like animal cells. e. All of these are correct • 12. The fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure refers to a. The fluidity of proteins and the pattern of phospholipids in the membrane. b. The fluidity of phospholipids and the pattern of proteins in the membrane c. The fluidity of cholesterol and the pattern of carbohydrate chains outside the membrane d. The lack of fluidity of internal membranes compared to the plasma membrane, and the ability of proteins to move laterally in the membrane e. The fluidity of hydrophobic regions, proteins, and the mosaic pattern of hydrophilic regions. • 12. The fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure refers to a. The fluidity of proteins and the pattern of phospholipids in the membrane. b. The fluidity of phospholipids and the pattern of proteins in the membrane c. The fluidity of cholesterol and the pattern of carbohydrate chains outside the membrane d. The lack of fluidity of internal membranes compared to the plasma membrane, and the ability of proteins to move laterally in the membrane e. The fluidity of hydrophobic regions, proteins, and the mosaic pattern of hydrophilic regions. 13. Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins present in the plasma membrane? Proteins a. b. c. d. e. Assist the passage of materials into the cell Interact and recognize other cells Bind with specific hormones Carry out specific metabolic reactions Produce lipid molecules 13. Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins present in the plasma membrane? Proteins a. b. c. d. e. Assist the passage of materials into the cell Interact and recognize other cells Bind with specific hormones Carry out specific metabolic reactions Produce lipid molecules 14. The carbohydrate chains projecting from the plasma membrane are involved in a. b. c. d. Adhesion between cells Reception of molecules Cell-to-cell recognition All of these are correct 14. The carbohydrate chains projecting from the plasma membrane are involved in a. b. c. d. Adhesion between cells Reception of molecules Cell-to-cell recognition All of these are correct 15. Plants wilt on a hot summer day because of a decrease in a. b. c. d. Turgor pressure Evaporation Condensation Diffusion 15. Plants wilt on a hot summer day because of a decrease in a. b. c. d. Turgor pressure Evaporation Condensation Diffusion 16. The extracellular matrix a. Assists in the movement of substances across the plasma membrane b. Prevents the loss of water when cells are placed in a hypertonic solution c. Has numerous functions that affect the shape and activities of the cell that produced it d. Contains the junctions that sometimes occur between cells e. All of these are correct 16. The extracellular matrix a. Assists in the movement of substances across the plasma membrane b. Prevents the loss of water when cells are placed in a hypertonic solution c. Has numerous functions that affect the shape and activities of the cell that produced it d. Contains the junctions that sometimes occur between cells e. All of these are correct