* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro Chap 2n.ppt
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
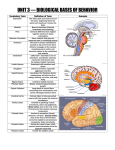
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world •Central Nervous System – consists of the brain and spinal cord •Peripheral Nervous System – consists of the autonomic and somatic systems •Autonomic System – consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems •What are all these parts made of? 100 Billion Neurons + connections Each Neuron consists of 3 structural parts 1. Soma or cell body 2. Axon 3. Dendrites Some axons are coated with myelin (for speed), and some may also be coated with neurilemma (allows for healing). 90% of nervous system cells are Glial Cells These provide structural support, nutrition, fuel, insulation and assistance with growth and development. How do these puppies interact? • It all starts with a resting potential (-70 mv) • When a signal is picked up by receptors (holes) on the dendrites we shift into an action potential (+ charge) • This new + charge travels along the axon to a knob where there is a gap – a.k.a. synapse • Off goes some neurotransmitter substance and the signal (excitatory or inhibitory) goes on • Travel speeds range from 2 to 270 mph. • Afterwards… recycling (reuptake) or clean up • A drug may act as an antagonist, or an agonist for a given neurotransmitter substance. Okay, let’s talk Spinal Cord • A long bundle of neurons (mostly axons) for data flow between the body and the brain? Sure… but wait, there’s more! • Speedy reflex reactions are possible too • Afferent neurons detect a (pain?) signal • Interneurons pass the info along to • Efferent neurons that issue instructions for actions before even getting the brain involved. The Peripheral Nervous System? • All nerves NOT in the brain/ spinal cord. • Connections allow 2 way communication between the spine and the rest o’ the body. 1. Somatic system provides sensory and motor pathways for VOLUNTARY muscles. 2. Autonomic system manages involuntary muscles, organs and glands. The Autonomic System has 2 parts • The Sympathetic System helps us deal with emergencies. Fight or flight. • The Parasympathetic System helps us get back to normal afterwards. • And then we’ve got a whole other system to consider… the Endocrine System. • These are glands that secrete hormones into the blood stream. The Pituitary is the Master Gland. It releases HGH & can stimulate the other glands • Pineal Gland – biorhythms and the sleep/wake cycle • Thyroid Gland – growth & metabolism • Pancreas – regulates blood sugar using insulin • Gonads – influence sexual behavior • Adrenal Glands – manage our stress reactions via cortisol What about BRAINS!?! • How are we gonna study them? Damage? • Can we change ‘em without breaking them? Transcranial Mag Stim or EBS? • Can we look in on them non-invasively? • EEG allows us to monitor surface activity • CAT scan using computer enhanced Xrays • MRI gives us even more structural detail • fMRI lets us watch the action as it unfolds • PET scan can see brain activity by tracking radioactive sugars. How about some brain parts? Lets start with the hind brain. • Medulla – controls things like breathing and swallowing • Pons – influences sleep, dreaming, arousal and coordination of movement • Reticular Formation (RAS) – controls our general levels of arousal and attention • Cerebellum – coordinates fine, rapid motor movement, learned reflexes, posture and muscle tone How about the Mid Brain (the limbic system) • Thalamus – sends sensory information to the proper areas of the cortex • Hypothalamus – controls hunger, thirst, sleep body temp, sex, emotions & pituitary gland • Hippocampus – helps with storing memories and remembering the location of objects • The Amygdala – manages emotions, our fear response, and memories of fearful stimuli • Cingulate Cortex – helps us with emotional and cognitve processing And finally, the Forebrain! • Is divided into two halves or hemispheres • At the back, Occipital lobes – for vision • Then the Parietal Lobes – includes the somatosensory cortex – for body processes • Temporal Lobes – primarily auditory info, language and some taste data • Frontal Lobes – planning, memory storage, emotional control, decision making + the Motor Cortex for control of body movements • Hemispheres connected by corpus callosum Anything else we should know? • Some areas that really handle very limited or specialized jobs • Broca’s Area – devoted to speech production • Wernicke’s Area – devoted to understanding the meaning of words • Some areas with an assortment of jobs… the Association Cortex filters incoming sensory data What about those hemispheres? • The left hemisphere handles things like spoken/written language, math calculations, logical thought processes, analysis of detail and controls the right side of the body. • The right hemisphere handles things like non-verbal communication, visual and spatial perception, music and art processing, emotions, pattern and facial recognition and controls the left side of the body.