* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Card review
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
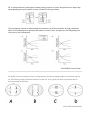
AP BIOLOGY Semester 1 Exam- 2016 NAME _________________________ 1. Mitochondria are found in most eukaryotic cells and contain their own DNA and ribosomes that are similar to those typical of many prokaryotic cells. Which of the following statements is justified by these observations? (A) The mitochondrion is the only location in which eukaryotic cells can synthesize ATP. (B) An ancestral cell most likely engulfed an aerobic prokaryote in a relationship that proved beneficial for both cells. (C) Mitochondrial membranes provide abundant surface area for reactions because of the infoldings called cristae. (D) The mitochondrion plays a role in respiration, but it also stores the cell’s extra mRNA 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Epinephrine is a protein hormone found in many animals. Epinephrine stimulates a signaling pathway that results in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver cells. Which of the following describes the initial steps in the process whereby epinephrine stimulates glycogen breakdown? (A) Epinephrine binds to a cell-surface receptor; the activated receptor stimulates production of the second messenger, cAMP. (B) Epinephrine binds to a cell-surface receptor; the activated receptor catalyzes the conversion of glycogen to glucose. (C) Epinephrine diffuses through the plasma membrane; the hormone dimerizes in the cytosol. (D) Epinephrine is taken into the cell by endocytosis; glycogen is converted to glucose in the endocytotic vesicle. 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. The transmission of information from sensory neurons to interneurons typically involves the A. exchange of electrons between specialized proteins embedded in the plasma membrane of the sensory neuron to the plasma membrane of the interneuron. B. release of chemical messengers into the space between the axon of the sensory neuron and the plasma membrane of the interneuron C. transfer of a phosphate group from ATP in the sensory neuron to a protein substrate in the interneuron. D. flow of protons down an electrochemical gradient through a gated channel between the sensory neuron and the interneuron. 2015 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. A cell is treated with a drug that prevents the formation of new lysosomes. The cell continues to transcribe the genes that code for the hydrolytic enzymes that are normally found in lysosomes and continues to translate the mRNAs for those proteins on membrane-bound ribosomes. The hydrolytic enzymes are most likely to accumulate in which of the following cellular structures? (A) Nucleus (B) Mitochondrion (C) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (D) Golgi complex 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which of the following scientific questions is most relevant to the model represented in the figure above? (A) Is ATP required for the transportation of sugars across the outer mitochondrial membrane? (B) Do the types of phospholipids in a membrane affect the rate at which molecules enter a cell by passive diffusion? (C) Which molecular substance is actively transported across the plasma membrane? (D) How does temperature affect the movement of molecules into lysosomes? 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 6. A group of students designed an experiment to determine the effect of compost on the germination and growth of plants. The students set up experimental plots by mixing different ratios of soil and compost. They planted 20 pea and 20 melon seeds in each plot and watered each plot regularly. The students recorded the number of seeds that germinated, and as the plants grew, they recorded plant length, number and size of leaves, and general health observations. The following observations were recorded. In all treatments, more pea seeds germinated than melon seeds. There was a week of rainy weather at three weeks. Melon plants developed a fungal growth at four weeks. Melon plants grew longer than pea plants, but many melon leaves showed signs of yellowing as the weeks passed. The students concluded that pea plants grew better in compost than did melon plants. Which of the following best addresses the validity of the conclusion made by the students? (A) The conclusion is valid because the independent and dependent variables in the experiment were controlled. (B) The conclusion is valid because the experimental design included a large sample size. (C) The conclusion is invalid because other variables in the experiment (both biotic and abiotic) affected the results. (D) The conclusion is invalid because the units of measurement were not given in the experimental design. 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 7. If ATP breakdown (hydrolysis) is inhibited, which of the following types of movement across cell membranes is also inhibited? A. Movement of oxygen into a cell B. Movement of water through aquaporins C. Passage of a solute against its concentration gradient D. Facilitated diffusion of a permeable substance 2013 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 8. In most freshwater fish, nitrogenous waste is primarily excreted as ammonia, which is highly soluble in water and is toxic at low concentrations. In terrestrial mammals, ammonia is converted to urea before it is excreted. Urea is also highly soluble in water but is less toxic than ammonia at low concentrations. Which of the following best explains why freshwater fish do not convert ammonia to urea for excretion? A. The metabolic pathways of fish do not normally involve nitrogen consumption. B. The dilution of ammonia by direct excretion into freshwater conserves energy. C. Ammonia is concentrated in tissues, where it is stored prior to excretion. D. The nitrogen in ammonia is recycled for use in protein and nucleotide synthesis. 2012 AP BIO Released Exam 9. Many human cells can be stimulated to divide by hormone-like growth factors that bind to receptor proteins (R) on the plasma membrane and trigger an internal signal-transduction cascade. In many cases, however, the process of contact inhibition prevents mitosis when cells are in direct contact with one another. Contact inhibition occurs when proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) interact, causing them to change shape so that the growth-factor signaling proteins that normally associate with CAMs are replaced by another protein, called M. Both pathways are depicted in the figures below. Which of the following statements accurately uses the information presented to support the hypothesis that interruption of M function in a single body cell can result in cancer? (A) (B) (C) (D) Protein 3 will be prevented from interacting with CAMs, causing the cell cycle to stop permanently. The ras protein will remain bound to DNA, blocking expression of genes required for mitosis. Growth-factor signaling can trigger mitosis in cells that are in direct contact with other cells. The receptor proteins of body cells will no longer bind to growth-factor proteins. 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Based on the figure at the left, which of these experimental treatments would increase the rate of sucrose transport into the cell? A. decreasing extracellular sucrose concentration B. decreasing extracellular pH C. decreasing cytoplasmic pH D. adding an inhibitor that blocks the regeneration of ATP 11. The graph above represents the relationship between the cadmium level in the drinking water of mice and the blood pressure of the mice. All of the following are accurate statements about the relationship shown in the graph EXCEPT: (A) Both high and low concentrations of cadmium are associated with low blood pressure. (B) An intermediate level of cadmium produces the highest blood pressure. (C) The lower the cadmium concentration in the water, the higher the blood pressure. (D) Up to a certain point, blood pressure increases as cadmium intake increases. (E) After a certain point, blood pressure decreases as cadmium intake increases. 1990 AP BIO Released Exam _______________________________________________________________________________ 12. The table below provides a comparison of nitrogenous waste production in selected organisms. Which of the following statements is most consistent with the data in the table? (A) In response to the hypotonic environment in which freshwater fish live, they excrete ammonia in concentrated urine or across their gills. (B) The kidneys of reptiles and birds are highly efficient because little water is needed to excrete uric acid. (C) Birds excrete ammonia in addition to uric acid, and the ratio of the two substances is independent of whether the birds are primarily terrestrial or aquatic species. (D) The similar regulation of extracellular fluid volume and composition in all the organisms suggests conservation of kidney structure throughout evolution. 2016 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Which of the following depicts the most probable pathways of processing and packaging a secretory protein within a eukaryotic cell? A) Secretory vesicle → rough endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi Body → cell membrane B) Rough endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi body → secretory vesicle → cell membrane C) Golgi body → secretory vesicle → rough endoplasmic reticulum → cell membrane D) Secretory vesicle → Golgi body → rough endoplasmic reticulum → cell membrane E) Golgi body → rough endoplasmic reticulum→ secretory vesicle → cell membrane 2012 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Which of the following is the correct description for starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin, and peptidoglycans? A. They are all polymers. B. They are all proteins. C. They are all polysaccharides containing α-glucose D. They can all be found in a plasma membrane E. They all contain nitrogen atoms. Cliffs AP Practice Exam 5 ________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Researchers conducted a controlled experiment to investigate the effect of diet on the health of beef cattle. The initial hypothesis was that an abrupt change in diet will benefit beef cattle by reducing the sizes of bacterial populations living in the digestive systems of the cattle. In the experiment, the researchers determined the relative abundance of two bacterial species found in the rumen of cattle. The rumen is part of the stomach that acts as a fermentation chamber in cattle and other ruminants. Shown in the table are the results from before and after an abrupt change in the cattle’s diet. Based on the results, which of the following best explains why the initial hypothesis should be revised? A. The diets were too similar, since cellulose and starch are both carbohydrates obtained from eating plants. B. The abundance of one of the bacterial species increased in response to change in diet. C. The change in the diversity of microorganisms had no observable effect on cattle physiology. D. The ability of rumen fluid to resist changes in pH counteracted the changes in microorganism diversity. 2014 AP BIO Released Exam 16. A researcher examining a root tip observes a plant cell with condensed sister chromatids, kinetochores with attached microtubules, and individual chromosomes that are aligned at the equatorial plate of the cell. Which of the following best describes what the next process will be in the cell? (A) Homologous chromosomes (each with two sister chromatids) will move toward opposite poles of the cell. (B) Paired chromatids will separate, and the new daughter chromosomes will move toward opposite poles of the cell. (C) The nuclear envelope will break down, and the spindle will begin to form. (D) The chromatin will decondense, and the daughter cell will enter interphase 2014 AP Bio Practice Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Individuals with an inherited autosomal recessive disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) often have severe respiratory problems due to defective cilia. Males with PCD are often sterile because they produce sperm with defective flagella. Which of the following most likely explains the effect of the recessive allele? A. The mitochondria are defective and do not produce sufficient proteins to synthesize microtubules in the cilia and flagella. B. The plasma membrane of the alveoli is not permeable to carbon dioxide during respiration because it is too hydrophobic. C. The Golgi bodies secrete an enzyme that destroys the proteins in the cilia and flagella. D. The cells do not produce functional motor proteins in flagella and cilia. 2014 AP Bio Practice Exam 18. A researcher examining an onion root tip observes a plant cell with condensed sister chromatids, kinetochores with attached microtubules, and individual chromosomes that are aligned at the equatorial plate of the cell. Which of the following best describes what the next process will be in the cell? A. Homologous chromosomes (each with two sister chromatids) will move toward opposite poles of the cell B. The nuclear envelope will break down and the spindle will begin to form. C. Paired chromatids will separate, and the new daughter chromosomes will move toward opposite poles of the cell. D. The chromatin will decondense and the daughter cell will enter interphase. 2014 AP BIO Practice Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 19. Antibiotics have many mechanisms of action. Some antibiotics such as azithromycin act to inhibit the small subunit of bacterial ribosomes. If a person is receiving treatment with azithromycin for a bacterial sinus infection, which of the following biologically important compounds will the bacteria be unable to produce? A. nucleic acids B. phospholipids C. carbohydrates D. proteins Lee Ferguson AP Bio Dropbox ________________________________________________________________________________ 20. Which of the following is the most direct results of the heating up of pond water during the summer? A) The water’s ability to hold oxygen decreases. B) The water’s ability to act as a buffer changes. C) The viscosity of the water increases. D) Hydrogen bonding at the surface of the water increases. E) Less light penetrates the surface of the water. 2008 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 21. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for a high rate of crossing over between two genes? A) The two genes are far apart on the same chromosome. B) The two genes are both located near the centromere C) The two genes are sex-linked D) The two genes code for the same protein. E) The two genes are on different chroosomes. 1999 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 22. The diagram at the left shows a channel protein in a membrane. Which parts of the surface of the protein would you expect to be composed of nonpolar amino acids? A. I and II only B. II and III only C. III and IV only D. I and IV only Lee Ferguson AP Bio Dropbox 23. The illustration above depicts a neuromuscular junction of a patient with an autoimmune disorder. Acetylcholine is a stimulatory neurotransmitter. Which of the following would be the most likely result of the continued presence of the antibody? A. An increase in action potentials in the motor neuron and constant nerve pain. B. A decrease in action potentials in the muscle, causing muscle weakness and fatigue. C. A decrease in the opening of sodium-gated channels in the muscle, causing less sodium to be released from the muscle. D. An increase in the opening of sodium-gated channels in the motor neuron because of the accumulation of acetylcholine in the junction. 2012 AP BIO Practice Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 24. Which of the following causes the rapid change of membrane polarity during the action potential? A) Diffusion of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine B) Diffusion of positively charged ions across the cell membrane. C) Release of electrons from inside the cell. D) Release of protons from inside the cell E) Active transport of cations by the sodium-potassium pump 2008 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 25. The tertiary structure and function of a protein is principally determined by the A) peptide bonds between amino acids B) number of nucleotides present in the polypeptide C) repeated units of glycerol making up the polypeptide D) interactions between R-group side chains E) hydrogen bonding between parts of the polypeptide backbone 2008 AP BIO Released Exam* ________________________________________________________________________________ 26. Phospholipids have both polar and non-polar ends. These macromolecules form cell membranes. Based on your knowledge of chemistry, which of the following statements is FALSE. A. Oxygen, a molecule that dissolves in water, is unable to pass through a cell membrane without the assistance of a protein. B. Water, a molecule that is polar, primarily is able to pass through a cell membrane with the assistance of a protein. C. Carbon Dioxide, a nonpolar molecule, is able to pass through a cell membrane without the assistance of proteins. D. Ethanol, a polar molecule, is able to pass through a cell membrane as it is also fat soluble ________________________________________________________________________________ 27. The figure above illustrates a eukaryotic cell. Which of the following best describes how the three structures indicated by the arrows work together? A. to synthesize lipids and modify toxic substances in order to render them harmless B. to synthesize and isolate proteins for secretion or for use in the cell C. to catabolize nutrients and produce ATP for intracellular energy storage D. to synthesize all ribosomal proteins 2014 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 28. Segregation of alleles does NOT occur in which of the following groups of organisms? (A) Flowering plants (B) Insects (C) Flatworms (D) Bacteria (E) Ferns _______________________________________________________________________________ 29. A common laboratory investigation involves putting a solution of starch and glucose into a dialysis bag and suspending the bag in a beaker of water, as shown in the figure below. The investigation is aimed at understanding how molecular size affects movement through a membrane. Which of the following best represents the amount of starch, water, and glucose in the dialysis bag over the course of the investigation? 2013 AP BIO Practice Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 30. Within a forest ecosystem, there is a large amount of diversity among members of a warbler species. Of the following stages of meiosis illustrated at the left for a typical cell, which contributes most to diversity among the warblers. AP Bio 2015 released exam Questions 31-34 refer to the following experiment, which is designed to test the effects of several chemicals on the contractility of skeletal muscle. A frog femur with the gastrocnemius muscle attached is installed in a bone clamp as indicated in the accompanying figure. The sciatic nerve leading to the muscle is attached to a battery via electrical leads. A small weight is suspended from the free end of the Achilles tendon. The entire preparation is rinsed in one of the five different solutions listed below. A brief stimulus is then applied to the sciatic nerve by closing the circuit to the battery. Three muscle responses are possible, depending on the solution with which the preparation has been rinsed: (1) the muscle will twitch once normally; (2) the muscle will go into sustained contraction until it is completely fatigued; and (3) the muscle will remain flaccid and not twitch at all. Substance Added to Ringer's Rinsing Solution None EDTA Botulin Malathion Curare Mechanism of Action Provides an isotonic saline environment for the muscle Binds free calcium ions Blocks the release of acetylcholine from presynaptic junctions Inhibits the enzyme acetylcholinesterase Binds to the acetylcholine receptor site in the synapse or myoneural junction 31. Which of the following substances allows action potentials to reach the sarcoplasmic membrane and the transverse tubule system but prevents muscle contraction? (A) Ringer's solution (B) EDTA (C) Botulin (D) Malathion (E) Curare 32. Competitors of acetylcholine include which of the following? I. Botulin II. EDTA III. Curare (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) I, II, and III 33. Which substance produces a sustained contraction (tetany) after a brief electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve? (A) Ringer's solution (B) EDTA (C) Botulin (D) Malathion (E) Curare 34. Which substance allows a single muscle twitch after a brief electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve? (A) Ringer's solution (B) EDTA (C) Botulin (D) Malathion (E) Curare 1990 AP BIO Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ 35. The figure above shows a model of a ligand precursor being cleaved to produce an active ligand that binds to a specific receptor. Which of the following is most likely to reduce the binding of the active ligand to the receptor? A. A change in the cytoskeletal attachment of transmembrane proteins. B. The presence of a large amount of the precursor form of the ligand. C. An increase in the ratio of the number of unsaturated to the number of saturated fatty acid tails of the membrane lipids. D. A mutation in the receptor gene that causes a substitution of a charged amino acid for a nonpolar amino acid in the ligand binding site of the receptor. 2013 AP BIO Practice Exam _______________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS 36-38 REFER TO THE FOLLOWING: A forest fire destroys trees in a large area. The forest rangers use the burned area to study the effect of different types of grasses on soil erosion. They choose ten plots of ground that are the same size. Each of these plots receives the same amount of sun. Each of these plots also has the same kind of soil and the same slope. The rangers plant each with a different type of grass. Measurements of soil erosion are made every week for the entire summer. 36. What is the independent variable in this study? A. the amount of soil erosion B. the type of soil in the plots C. the size of the plots D. the types of grasses 37. What is the dependent variable in this study? A. the amount of soil erosion B. the type of soil in the plots C. the size of the plots D. the types of plants 38. What hypothesis is being tested? A. If grass is planted then the amount of soil erosion will be reduced. B. If areas are burned over then they will have greater erosion than forested areas. C. If the slope of the land is changed then soil erosion will be affected. D. Certain types of grass have a greater effect on reducing soil erosion than others. 2012 AP Bio Released Exam ________________________________________________________________________________ Questions 39-45 refer to the following: A section of fresh potato was added to six beakers. One beaker was filled with distilled water, and the remaining five beakers were filled with sucrose solutions of 0.2 M, 0.4 M , 0.6 M, 0.8 M, and 1.0 M. The potato sections were removed after 15 minutes and changes in weights of the sections were recorded in the graph that follows: 39. Which of the following is true for the potato sections in the beakers with 0.6 M, 0.8 M, 1.0 M sucrose solutions? A. The value of ψ for the potato cores was greater than 0. B. The value of ψ for the solutions was greater than 0 C. The value of ψ for the solutions was equal to 0. D. The potato core was hypotonic compared to the solutions in the beakers. E. The potato core was isotonic compared to the solutions in the beakers. 40. What is the concentration of solutes inside the potato section? A. 0 B. 0.2 M C. 0.3 M D. 0.4 M E. 1.0 M Cliffs AP Practice Exam 4 GRID IN CALCULATIONS 41. A zucchini squash was peeled and cut into six identical cubes. After being weighed, each cube was soaked in a different sucrose solution for 24 hours in an open container and at a constant temperature of 21ºC. The cubes were then removed from the sucrose solutions, carefully blotted on paper towels, and weighed again. The percent change in mass (due to a net gain or loss of water) was calculated for each cube, and the results are shown in the graph below. A straight line is drawn on the graph to help in estimating results from other sucrose concentrations not tested. Using the straight line on the graph above, calculate the water potential (in bars) of the zucchini squash at 21°C. Give your answer to one decimal place. 42.