* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of manufactured fuel gases wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Separator (oil production) wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
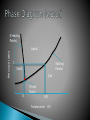
Unit 1 Properties of matter and changes of matter Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space Any substance that has a definite composition ◦ Always made of the same stuff in exactly the same proportions Examples: H2O, NaCl, C12H22O11 All around us Changes in chemicals ◦ Ex: things growing, food cooking, taking a photo (film) We use reactions to produce chemicals ◦ Ex: plastics, acids Solid, Liquid, Gas ◦ What is the difference between ice, water, steam? Solid ◦ Definite shape, definite volume Liquid ◦ No definite shape, definite volume Gas ◦ No definite shape, no definite volume 2 types of solids ◦ Crystalline solid (crystal) Arranged in an orderly, repeating pattern ◦ Amorphous solid (without form) Arranged randomly – no pattern Definite shape Definite volume Nonfluidity Definite melting point High density Incompressibility The total 3-dimensional array of points that describe the arrangement of particles in a crystal is called a crystal lattice. 1 repeating piece is a unit cell Definite volume Fluidity – able to flow Relative high density Relative incompressibility Dissolving ability Ability to diffuse Tendency to evaporate and boil Tendency to solidify Properties that can be measured or observed without changing it’s identity ◦ Length, mass, color, odor, density, boiling point, melting point Matter can change ◦ Ice melts, water fogs a mirror, bike spokes rust, red clothes fade, milk sours 2 types of changes A change in which the identity of a substance does not change ◦ Change physical properties Melting, freezing, dissolving, crushing, boiling Pressure (atm) (Freezing Points) Liquid 1 Solid (Boiling Points) . 0 Gas (Triple Point) 100 Temperature (oC) Also called a chemical reaction Things turn into something new 2 parts of a chemical reaction ◦ Reactants – things that react ◦ Products – things that are produced Reactant + Reactant Product + Product Propane + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 of 4 things must happen A gas is produced Formation of a precipitate Release of heat and light Color change All matter is made of atoms ◦ There are 115 kinds of atoms Matter is either a pure substance or a mixture 2 Types Can it be separated? ◦ Yes, it is a compound H2O, NaCl, C6H12O6, H2SO4 ◦ No, it is an element H, O, Na, Au, Pb 2 Types Is it all the same? ◦ Yes, it is a homogeneous mixture Tap water, air, apple juice ◦ No, it is a heterogeneous mixture Salt/pepper, orange juice, choc chip cookie 3 kinds of mixtures 1. Solution ◦ Soluble – will dissolve ◦ Forms a homogeneous mixture Very small particles ◦ 2 Parts of a solution Solute – stuff that dissolves Solvent – stuff that the solute dissolves in Solute Solvent Example Gas Gas Air Gas Liquid Soda Water Gas Solid - Liquid Gas Humidity Liquid Liquid Juice in water Liquid Solid - Solid Gas Sulfur in air Solid Liquid Kool Aid Solid Solid Alloy (Brass) 2. Suspensions ◦ Heterogeneous mixture that settles ◦ Large particles ◦ Muddy water, Italian salad dressing (anything that must be shaken) 3. Colloids ◦ Intermediate sized particles ◦ Particles disperse 2 parts of a colloid ◦ Tyndall Effect Seeing a beam of light (separates colloid from solution) Colloid Phase Gel solid dispersed in liquid Liquid emulsion liquid dispersed in liquid Foam gas dispersed in liquid Smoke solid dispersed in gas Fog liquid dispersed in gas Smog solid & liquid dispersed in gas Solutions Homogeneous Very small particles Does not separate No light scattering Colloids Homogeneous Intermediate sized Does not separate Tyndall effect Suspensions Heterogeneous Large particles Separates No Tyndall effect Increasing the Rate of dissolving ◦ 1.Increase the surface area of solute ◦ 2. Agitating the solution ◦ 3. Heating the solvent Electrolyte ◦ A solution that has ions in it and can conduct electricity Saturated solution Unsaturated solution ◦ Contains the maximum amount of solute ◦ Contains less than the maximum amount of solute Supersaturated solution ◦ Contains more than the maximum amount of solute (Rock candy, crystals) 1. Types of solvents and solutes ◦ Like dissolves like Refers to polarity Water is a polar molecule Oil is a nonpolar molecule If they are the same polarity, the compounds are miscible (mixable) - salt in water, vinegar in water If they are not soluble, they are immiscible (not mixable) - oil in water, salt in oil 2. Pressure ◦ Under pressure a gas will enter and dissolve in a liquid fizz in a bottle of pop ◦ If pressure is released, the liquid can’t hold as much gas Effervescence 3. Temperature ◦ Warmer liquids hold less gas Burp more from warm pop