* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap 5 Instruments
Survey
Document related concepts
Airy wave theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydraulic jumps in rectangular channels wikipedia , lookup
Hemodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Coandă effect wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Boundary layer wikipedia , lookup
Lift (force) wikipedia , lookup
Hydraulic machinery wikipedia , lookup
Wind-turbine aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Water metering wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Flow measurement wikipedia , lookup
Compressible flow wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli's principle wikipedia , lookup
Aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Reynolds number wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
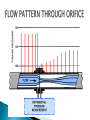
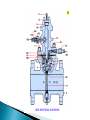
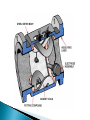
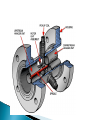
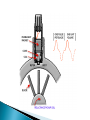
Chapter 5 INTC 1305 – 01 FLOW Vern Wilson Innage/outage Floats Interface Meniscus Density and head Chapter 5 Pipeline Meter Run #117 avi These instruments measure FLOW Fluid in motion Always from hi to lo p Molecules continually change Laminar - streamline Turbulent Obstructions mess up smooth flow Usually turbulent flow is consistent Identifies type of flow – turb or lam R=vxdxϱ/μ v = velocity d = diameter ϱ = density μ = viscosity > 4000 = turbulent > 10,000 = fully turbulent < 2,000 = laminar Between 2,000 and 4,000 = transient Positive Displacement ◦ Measures absolute volumes ◦ Uses chambers of known volume Percentage flow ◦ Based on known flow at 100% Volumetric Flow ◦ GPM ◦ MCFD Mass Flow ◦ Pounds per time Differential Pressure Bernoulli – page 109 As velocity increases the static pressure of the fluid decreases Flow devices: Orifice (differential flow meters), Venturi, Flow Nozzles, pitot tubes, Annubar tubes, rotameters, electromagnetic meters, turbine meters, mass flow meters Simple pressure drop Flat upstream – bevelled downside Set in tapped flanges Higher cost but lower op costs Smooth cone shaped As speeds increase in the throat the pressure is reduced according to Bernoulli Extended tapered inlet Can be inserted into a flange Allow higher flow then orifice plates - twice Can handle slurries Less $ than venturi but more than orifice Measures impinging pressure Disadvantage – measures flow at only one point Can’t measure laminar flow ANNUBAR or MULTI PORT Pitot with several ports Based on gravity and impinging pressure Tapered flow tube with a float Flow tube calibrated to flow Only give an estimate of flow Float can be magnetized inside steel tube Designed for specific small range Or Magmeters – no metal in body Measures electrically conductive liquids Generally water based Obstruction free – noninvasive Food and drug use Based on Faraday’s law of induction – an electrical potential is produced when a conductor moves at a right angle through a magnetic field Flow tube with free spinning turbine One blade is magnetic Induction pick up coil Each pulse indicates a rotation of the turbine Simply multiply a K factor times the number of sensor pulses CORIOLIS METER They measure density through temperature and pressure Tube vibrates and twists giving a velocity difference which is converted to flow Most common Responds to pressure Flow is proportional to square root of dp FLOW MEASURED IN: GPM POUNDS PER MINUTE An injection program requires 100 barrels of injection fluid per day. How many GPM is equal to 100 barrels per day? First: There are 42 gallons per barrel Second: Convert to GPM We are pumping mud that weighs 10.9 pounds per gallon at 4 barrels per minute. How many pounds per minute are we pumping? First: Determine how many pounds are we pumping – 4 barrels = 42 gals/barrel Second: Determine how many pounds per minute.