* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rao - CORDIS
Survey
Document related concepts
Process tracing wikipedia , lookup
Piaget's theory of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Dual process theory wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual learning wikipedia , lookup
Mental chronometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive interview wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive flexibility wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
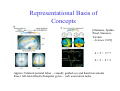
Cognitive Systems Workshop: Luxembourg, 20th March 2006 “Cognitive Systems Models & Paradigms: Key issues for FP7” Sajit Rao CSAIL, MIT The Developmental Paradigm • Cognitive Development is nature’s way of managing complexity • Development is largely Unsupervised: What babies know is overwhelmingly acquired through self learning & experimenting on the world, rather than detailed instruction by a teacher” We must build systems that cannot but help developing (1) Representational Substrate (2) Developmental Rules 3 Key Issues in Cognitive Development 1. Learning Self-Identity (at a SensoriMotor Level) 2. Representational Substrate for Concepts/Thinking 3. Developmental Rules: Mechanisms of Conceptual Change “Neuroscience and Infant psychology research have made progress on These issues – while Robotics/Computational approaches lag” (1) Body-Image: e.g. Learning a sensorimotor model of one’s arm 1. Graziano, Cooke, Taylor [Vol 290, Science Dec 2000] 2. Rao (CogVis, 2002) ps=[4, 20, 10] ps=[6, 21, 11] ps=[9, 24, 14] (2) Sensorimotor Representations not Perepheral, but Central to Cognitive Tasks Perception Representational Systems central not only to “being” in the world (perceiving and taking action) but also “thinking” about it. Common-Sense Reasoning Language Perceptual Representations & Processes Object Numerical Recognition Ability 1. Perceptual processes get re-used for inference. 2. Perceptual processes may underlie abstract concept formation Visuospatial Analysis “Is the white table in-between the two people?” “How many countries does the equator pass through in africa?” Re-used for other “non-visual” problems as well… Representational Basis of Concepts [Dehaene, Spelke, Pinel, Stanescu, Tsivkin – Science 1999] 4+5= 9?7 4+5~ 8?3 Approx: bilateral parietal lobes – visually guided eye and hand movements Exact: left-lateralized left angular gyrus – verb association tasks (3) Conceptual Change Development of the concept of “Positive Integers” [Carey 2004] • One-knowers (6 to 9 months) • Two-knowers (~2 months) • Three-knowers (~2 months) • Induce how Counting works Progression happens because different Base-Representations come into Play: Counting-Procedure Token-individuation (successor relation) Analog-Magnitude Natural-language Quantifiers Cognitive Development: specific targets for research 1. Learning to distinguish self from the world 2. Re-use of perceptual-motor mechanisms for thought – origins of concepts 3. Mechanisms of Conceptual Change