* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regulation of Gene Expression
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
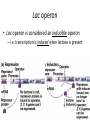
Regulation of Gene Expression Chapter 6.4 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Biology 12 (2011) Regulation of Gene Expression • Gene Regulation: refers to control of the level of gene expression – It makes sense to conserve energy and material and not synthesize proteins when not needed • Constitutive Genes: gene constantly expressed – Some genes are always active and expressed essentially at constant levels these proteins are needed for survival of the cell Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes • Operons: a cluster of genes grouped together under the control of one promoter – Remember that a promoter is where RNA polymerase binds to DNA to begin transcription – Occurs in prokaryotic genomes • Genes that are involved in the same metabolic pathway are often found in the same operon – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA Lac operon • E.coli can use lactose to grow so when surrounded by lactose, will turn on machinery to make lactose enzymes – Lac operon is responsible for coding enzymes to break down lactose • Operator: sequence in DNA to which a repressor protein binds • Repressor: a protein that binds to a particular DNA sequence to regulate transcription; – Inhibits transcription of gene(s) Lac operon • When lactose is absent: lac repressor binds to operator – Prevents RNA polymerase from binding to promoter thus transcription cannot occur = no enzyme Lac operon • When lactose is present: allolactose is produced which binds to the repressor – Repressor can no longer bind to operator – RNA polymerase is now able to bind to promoter so transcription can occur = enzyme production to break down lactose Lac operon • Lac operon is considered an inducible operon – i.e. transcription is induced when lactose is present Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes • Transcription Factors: proteins required to interact with RNA polymerase to initiate transcription • Enhancers: sequences of DNA that proteins bind to so that transcription is enhanced • RNA interference: miRNA (microRNA) and siRNA (small interefering RNA) inhibits gene expression by degrading mRNA or inhibiting translation Homework • Pg 272 #3, 4, 5