* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download e-business
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Business model wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
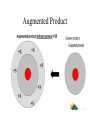
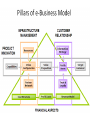
E-commerce Antoine Harfouche Session 2 From the e-business strategy to the e-business Model The Roadmap E-commerce Marketing Website Business Managerial Strategy Strategy vision Logistics e-business strategy From strategy to e-etrategy: Concepts and Overview • Strategy A broad-based formula for how a business is going to accomplish its mission, what its goals should be, and what plans and policies will be needed to carry out those goals • E-strategy (e-strategy) The formulation and execution of a vision of how a new or existing company intends to do business electronically E-Business Strategy • Strategic Planning Tools – 1. SWOT analysis A methodology that surveys external opportunities and threats and relates them to internal strengths and weaknesses – 2. Competitor analysis grid A strategic planning tool that highlights points of differentiation between competitors and the target firm • Strategic Planning Tools – 3. Scenario planning A strategic planning methodology that generates plausible alternative futures to help decision makers identify actions that can be taken today to ensure success in the future – 4. Balanced scorecard A management tool that assesses organizational progress toward strategic goals by measuring performance in a number of different areas – 5. Business plan A written document that identifies the company’s goals and outlines how the company intends to achieve those goals E-Strategy Formulation What happens when there is no e-business strategy? • Missed opportunities for additional sales on the sell-side and for more efficient purchasing on the buy-side • Fall-behind competitors in delivering online services – may become difficult to catch-up, for example, Tesco, Dell • Poor customer experience from poorly integrated channels e-Marketing strategy E-Marketing Strategy Differentiation Tier 1 tasks Tier 2 tasks Segmentation Positioning Targeting E-Marketing Strategy Offer CRM/PRM Communication Value Distribution Exhibit 3 - 1 Formulating E-Marketing Strategy in Two Tiers No Other Media has all of the Advantages of eMarketing. • • • • • • Cost effectiveness Global reach Interactive response Measurability Personalization Real-time feedback But E-marketing Suffers From • Lack of understanding of technology by marketers • Fast moving and turbulent arena • Changing technologies • Lack of trained personal • Senior management barriers • Corporate culture Augmented Product Pricing: Yield Management • There are two online pricing trends are: – Dynamic pricing—this strategy applies different price levels for different customers or situations. The Internet allows firms to price items automatically and “on the fly” while users view pages, – Online bidding—this presents a way to optimize inventory management. • E.g. Priceline.com, eBay.com Promotion: Relationship Management Strategies • E-marketing communication strategies help build relationships with a firm’s partners, supply chain members, or customers using: - Customer relationship management (CRM) software to retain customers and increase average order values and lifetime value, - Partner relationship management (PRM) software to integrate customer communication and purchase behavior into a comprehensive database, - Life time value Retail and Wholesale • Electronic retailing (e-tailing): the direct sale from business to consumer through electronic storefronts, typically designed around an electronic catalog and shopping cart model • Cybermall: a single Web site that offers many products and services at one Internet location • Manufacturing, repair, and operations (MRO) goods and services E-Marketing Strategies (cont.) There are three extra Ps as the extended marketing mix: • People: Right person, trained well, motivated • Process: Providing services to customers • Physical evidence: Case studies, testimonials PROCESS A process is the method and sequence of actions in the e-service performance. Process is a way of undertaking transaction, supplying information and providing e-services on a way which is acceptable to the e-customer and effective to the organization. E-services are rendered and experienced simultaneously, therefore it is the process through which consumers go in interaction with service provider. Types of E-Markets (cont.) • E-marketplace: An online market, usually B2B, in which buyers and sellers exchange goods or services; the three types of e-marketplaces are private, public, and consortia – Private e-marketplaces: Online markets owned by a single company; can be either sell-side or buy-side marketplaces • • Sell-side e-marketplace: A private e-market in which a company sells either standard or customized products to qualified companies Buy-side e-marketplace: A private e-market in which a company makes purchases from invited suppliers – Public e-marketplaces: B2B markets, usually owned and/or managed by an independent third party, that include many sellers and many buyers; also known as exchanges – Consortia: E-marketplaces owned by a small group of large vendors, usually in a single industry 21 The e-commerce strategy E-commerce Strategy: Creating customer value Creating Customer Value Online • Never has competition for online customer attention and dollars been more fierce. To succeed, firms must employ that result in Customer value = Benefits – Costs. Creating Customer Value Online • But what exactly is value? – The entire product experience: • Customer’s first awareness of a product, • All customer touch points (including the Web site experience and e-mail from a firm), • The actual product usage and postpurchase customer service, • The compliments a consumer gets from friends while using the product. – Value is defined wholly by the customer. – Value involves customer expectations; if the actual product experience falls short of their expectations, customers will be disappointed. – Value is applied at all price levels. Creating eBusiness Model • A Business Model A business model can best be described through nine basic building blocks that show the logic of how a company intends to make money. • The nine blocks of the following model cover the four main areas of a business: 1. Customers 2. Offer 3. Infrastructure 4. Financial viability • The business model is like a blueprint for a strategy to be implemented through organizational structures, processes, and systems. Source: Business Model Generation, Osterwalder and Pigneur 2010 Customer Segments For whom are we creating value? Who are the most important customers? Mass Market Niche Market Segmented Diversified Multi-sided platform Value Propositions Value Propositions describes what creates value for a targeted Customer Newness Segment. Cost reduction Performance Customization “Getting the job done” Brand / Status Design Risk reduction Accessibility Convenience Usability Channels Value Propositions are delivered to customers through communication, distribution and sales channels. How a company communicates with and reaches its customer segments to deliver a value proposition. Which Channels do our Customer Segments want to be reached? How are we reaching them now? Which are working best (or not working)? Enabling customers to evaluate a firm’s products Allowing customers to purchase Providing post-purchase customer support Channels Channel Phases Direct Own Channel Types Sales force Web sales Indirect Partner Own stores Partner stores Partner web sales Wholesaler 1. Awareness 2. Evaluation 3. Purchase How to raise awareness about the product? How to help customers evaluate the product's value proposition. How do we allow customers to purchase specific products and services? 4. Delivery 5. After Sales How do we How to provide deliver a Value post-purchase Proposition to customer support? Customers? Customer Relationships The types of relationships the firm establishes with its customers. What types of relationships does our customer expect and how much does this cost? How does this support the value proposition? Personal Assistance Dedicated Personal Assistance Self-service Automated Services Communities Revenue Streams For what value are our customers really willing to pay? Asset sale [product sale] Usage fee Subscription fee Lending / Renting / Leasing Licensing Brokerage fees Advertising Revenue Streams Pricing Mechanism Fixed Menu Pricing Dynamic Pricing Predefined prices are based on static variables Prices change based on market conditions List Price Product Feature Customer Segment Volume dependent Price set by product, service, or other Value Propositions Price depends on the number and quality of Value Proposition features Price depends on the type and characteristic of a Customer Segment Price as a function of quantity purchased Negotiation Price determined by bargaining skills and leverage Yield Price depends on inventory and time of Management purchase Price is determined dynamically based on Real-time-market supply and demand Auctions Price determined by outcome of competitive bidding Key Resources The most important assets required to deliver our value proposition, distribution channel, and customer relationships Physical Intellectual Human Financial Production Platform Key Activities [Capabilities] The most important activities a company must do, in order to deliver its value proposition, and makes its business model work. Marketing Engineering Managing Selling Logistics Problem solving Managing Key Partners Who are key partners in terms of suppliers and intermediaries between the firm and its end-users? Which key resources are we acquiring from partners? Which key activities do partners perform? Motivations for Partnerships Optimization and economy Reduction of risk and uncertainty Acquisition of particular resources and activities Partnerships can be motivated by needs to acquire knowledge, licenses, or access to customers. Example: Mobile phone companies that license Android, or insurance companies that rely on independent brokers. Cost Structure What are the most important costs inherent in delivering the value proposition? Which key resources are most expensive? Which key activities are most expensive? Is our business model more Cost driven or Value driven? Types of costs Fixed Variable Economies of scale Economies of scope Some business models, are more cost-driven than others. “No frills” airlines, for instance, have built business models entirely around Low Cost Structures.