* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seafloor Spreading Notes - mrs. villarreal`s orange team science
Survey
Document related concepts
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
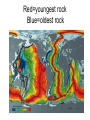
Seafloor Spreading Notes (#20) Where we’ve been w/ EQ#2… • EQ#2: What is convection and what evidence is there of convection on the surface of the Earth? • Alfred Wegener • Theory of Continental Drift • Evidence for Continental Drift (Fossils, landforms, climate) • Theory rejected in early 1900’s • In 1950’s, scientists discovered mid-ocean ridge (ocean bottom was once thought flat) Where we’re going w/ EQ#2… • Magma erupting at mid-ocean ridge creates new ocean floor & subduction at plate boundaries destroys old ocean floor • Seafloor spreading! • Caused by convection currents in mantle • We now know HOW the continents can move • Theory of Continental Drift revisited! Wegener was a brilliant, brilliant man after all! Video Introduction to Sea Floor Spreading #20- Seafloor Spreading • WHO: Discovered by Harry Hess- U.S. Geologist at Princeton, Navy Reservist • WHEN: 1950’s • WHERE: Pacific Ocean • WHAT: – The process by which new ocean crust is formed by the upwelling of magma at mid-ocean ridges. – Cause: Convection currents in the mantle. – Result: Existing/older ocean crust is pushed to the side to make room for the new crust. Seafloor spreading OLDER NEW OLDER EQUAL DISTANCE FROM RIDGE = SAME AGE CONVEYOR BELT ANIMATION Red=youngest rock Blue=oldest rock What happens to the OLD crust? • Subduction: When the edge of one crustal plate is pushed underneath another. • This happens at the edge of oceans, where denser ocean crust is pushed underneath less dense continental crust. The rock returns to the mantle. How can this move continents? • If NEW ocean floor is produced FASTER than old floor is subducted, the ocean floor GROWS, which would push continents APART. • If OLD ocean floor is subducted FASTER than new ocean floor is produced, the ocean floor SHRINKS, which would “pull” continents TOGETHER. Please add the following to your EQ#2 Vocabulary List (#19) • 7. Seafloor Spreading: The process by which new ocean crust is formed by the upwelling of magma at mid-ocean ridges • 8. Harry Hess: an American Geologist who used SONAR to map the ocean floor in the 1950’s and discovered seafloor spreading • 9. mid-ocean ridge• 10. Subduction: process by which ocean crust sinks beneath a deep ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary • Magnetization of the Ocean Floor Animation • http://www.absorblearning.com/media/atta chment.action?quick=12n&att=2771