* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1st Semester Final Exam Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
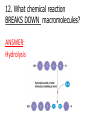
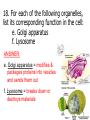
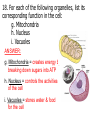
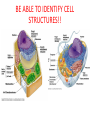
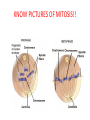
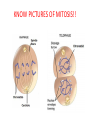
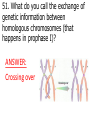
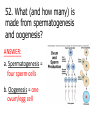
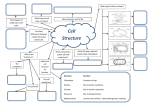
1st Semester Final Exam Study Guide Answers to Questions #1-55 (Intro. To Science, Biochemistry, Microscopes & Cells, Cell Transport, Photosynthesis & Respiration, Mitosis & Meiosis) 1) Play the slide show 2) Read the question, answer on your own and then click to show the correct answer 3) Click to go to the next question INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE 1. When making a title for a data table of graph, what three items must be included? ANSWER: a) SUBJECT (what you work with) b) PURPOSE (why you’re doing the experiment) c) INDEP./DEP. VARIABLES 2. When making a scientific data table… ANSWER: a. The first column is the INDEPENDENT variable (what the experimenter controls) b. Starting in the 2nd column is the DEPENDENT variable (what is measured/observed) c. All columns should include UNITS in parentheses to show what you measured in. 3. When making a scientific graph… ANSWER: a. The independent variable (what the experimenter controls) goes on the X axis. b. The dependent variable (what is measured/observed) goes on the Y axis. c. Data points should not be connected; a BESTFIT STRAIGHT line should be drawn instead. 4. An explanation based on observations that is tested with an experiment is called a ____. ANSWER: HYPOTHESIS 5. Define the term homeostasis. (Look at your notes on the characteristics of life) ANSWER: Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a stable internal environment. For example, humans maintain their own body temperature, breathing rate, heartbeat, etc. BIOCHEMISTRY (CHAPTER 2) 6. Name the 3 subatomic particles. Which two are in the nucleus of an atom? Answer: a) Protons (found in the nucleus) b) Neutrons (found in the nucleus) c) Electrons 7. For energy levels for the first twenty elements of the Periodic Table, how many electrons fit into the… Answer: a. First Level = 2 b. Second Level = 8 c. Third Level = 8 d. Fourth Level = 2 8. A substance that forms hydrogen ions (H+) is called a(n) ____. A substance that forms hydroxide ions (OH-) is called a(n) ____. ANSWER: A substance that forms hydrogen ions (H+) is called a(n) ACID. A substance that forms hydroxide ions (OH-) is called a(n) BASE. 9. Draw the pH scale and label 1)strong acids, 2)weak acids, 3)neutral, 4)weak bases and 5)strong bases. ANSWER: 10. What do you call a protein that speeds up chemical reactions? ANSWER: ENZYMES! 11. What chemical reaction FORMS macromolecules? ANSWER: Condensation 12. What chemical reaction BREAKS DOWN macromolecules? ANSWER: Hydrolysis 13. For each of the macromolecules of life, name its monomer (building block). ANSWER: a. Carbohydrates = Monosaccharide b. Protein = Amino acid c. Lipid = Carboxyl/glycerol + fatty acid tails d. Nucleid acid = Nucleotide 14. For each function below, identify the correct macromolecule. ANSWER: a. It stores hereditary information for an organism = Nucleic acid b. It gives immediate energy and gives some structure = Carbohydrate 14. For each function below, identify the correct macromolecule. ANSWER: c. It stores energy in the form of fat = Lipids d. It gives structure, helps build muscle, speeds up chemical reactions = Proteins MICROSCOPES & THE CELL (SECTIONS 7-1 TO 7-3) 15. What is the formula for total magnification on a microscope? ANSWER: Eyepiece magnification x objective lens 16. What part of the microscope should never be moved on high power? Answer: The coarse adjustment knob (which controls the stage) 17. The smallest unit of life is called a ___. ANSWER: The smallest unit of life is called a CELL. 18. For each of the following organelles, list its corresponding function in the cell: a. cell membrane b. cell wall ANSWER: a. Cell membrane = lets certain materials go in or out of the cell b. Cell wall = provides protection for the cell, structure and support 18. For each of the following organelles, list its corresponding function in the cell: c. Chloroplast d. Endoplasmic Reticulum ANSWER: c. Chloroplast = makes energy by converting sunlight into chemical energy (sugars) d. Endoplasmic Reticulum = transports materials within the cell; Rough ER transports proteins and Smooth ER transports lipids 18. For each of the following organelles, list its corresponding function in the cell: e. Golgi apparatus f. Lysosome ANSWER: e. Golgi apparatus = modifies & packages proteins into vesicles and sends them out f. Lysosome = breaks down or destroys materials 18. For each of the following organelles, list its corresponding function in the cell: g. Mitochondria h. Nucleus i. Vacuoles ANSWER: g. Mitochondria = creates energy by breaking down sugars into ATP h. Nucleus = controls the activities of the cell i. Vacuoles = stores water & food for the cell 19. What two structures are found only in plant cells? ANSWER: Cell wall & Chloroplasts! BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY CELL STRUCTURES!! 20. What molecule is the cell membrane made of? ANSWER: Phospholipids (2 layers) 21. What phrase is used to describe how the cell membrane only allows some materials to go in or out of the cell? Answer: SELECTIVE PERMEABILITY CELL TRANSPORT (SECTION 7-3) 22. The type of cell transport that does not use energy is ___ transport. The type of cell transport that uses energy is ___ transport. Answer: The type of cell transport that does not use energy is PASSIVE transport. The type of cell transport that uses energy is ACTIVE transport. 23. Name the three types of PASSIVE transport. Answer: 1) Diffusion (Simple Diffusion) 2) Facilitated Diffusion 3) Osmosis 24. The movement of small & nonpolar molecules through the cell membrane from high concentration to low concentration is called ____. ANSWER: DIFFUSION 25. The movement of large & polar molecules through the cell membrane using carrier proteins from high concentration to low concentration is called ____. ANSWER: FACILITATED DIFFUSION 26. What is equilibrium? Answer: Equilibrium is when you have the same number of molecules everywhere. 27. The movement of water from areas of high concentration to low concentration is called ____. Answer: OSMOSIS 28. For each solution below, a)identify the direction water moves and b)what happens to the size of the cell. Answer: Hypertonic Solution = a) water moves OUT b) the cell shrinks in size 28. For each solution below, a)identify the direction water moves and b)what happens to the size of the cell. Answer: Isotonic Solution = a) water moves IN & OUT b) the cell remains normal size 28. For each solution below, a)identify the direction water moves and b)what happens to the size of the cell. Answer: Hypotonic Solution = a) water moves IN b) the cell GROWS/ENLARGES 29. What term describes the amount of force the vacuole has on the cell membrane and cell wall? ANSWER: Turgor Pressure 30. What happens to a plant under high turgor pressure? Under low turgor pressure? Answer: • Under high turgor pressure, the vacuole is very full of water & the plant stands upright & tall. • Under low turgor pressure, the vacuole is nearly empty & the plant will start to wilt or not stand upright. 31. What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis? ANSWER: Endocytosis moves a large amount of material INTO the cell by forming vesicles. Exocytosis moves a large amount of material OUT OF the cell by packaging it into vesicles & forcing them out. PHOTOSYNTHESIS & RESPIRATION (CHAPTERS 8 & 9) 32. What does ATP stand for? ANSWER: ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate 33. How is energy released from ATP? ANSWER: Break the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate (by hydrolysis) 34. Define photosynthesis. ANSWER: Photosynthesis makes glucose/sugars using light energy/sunlight. 35. Write out the complete chemical equation for photosynthesis. ANSWER: Sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O --------- C6H12O6 + 6O2 36. What is chlorophyll? ANSWER: Chlorophyll is a pigment that captures sunlight. 37. Describe why plants appear green. ANSWER: Chlorophyll reflects the green light wavelengths – green is not absorbed. 38. Define cellular respiration. ANSWER: Cellular respiration breaks down glucose/sugar to make ATP 39. Write out the complete chemical equation for cellular respiration. ANSWER: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 +6H2O + ATP 40. What is the total amount of ATP made from one glucose in cellular (aerobic) respiration? ANSWER: 36 ATP 41. What does the term “aerobic” mean? What does the term “anaerobic” mean? ANSWER: Aerobic means it uses/requires oxygen Anaerobic means it does not use or need oxygen. 42. Define fermentation. Is it aerobic or anaerobic? ANSWER: Fermentation is when you break down sugars for energy but without using oxygen. It is an anaerobic process. 43. Which one is more effective the production of energy – aerobic cellular respiration or fermentation? ANSWER: Aerobic respiration because it makes 36 ATP. (fermentation only makes 2 ATP) MITOSIS & MEIOSIS (SECTIONS 10-2, 10-3 & 11-4) 44. What is the longest phase of the cell cycle? ANSWER: Interphase 45. What is made at the end of mitosis? ANSWER: Two cells that are identical 46. Identify the correct phase of mitosis for each description. ANSWER: a. The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell = METAPHASE b. The nuclear membrane reappears when centrioles & spindle fibers disappear = TELOPHASE 46. Identify the correct phase of mitosis for each description. ANSWER: c. Chromosomes form, centrioles & spindle fibers appear as the nuclear membrane disappears = PROPHASE d. The chromosomes split into single chromatids = ANAPHASE KNOW PICTURES OF MITOSIS!! KNOW PICTURES OF MITOSIS!! 47. What is the splitting of the cytoplasm called? ANSWER: Cytokinesis 48. Describe two ways mitosis is different in animal and plant cells. ANSWER: Animal cells Plant cells a. uses centrioles a. no centrioles b. forms a cleavage b. forms a cell plate in furrow in cytokinesis cytokinesis 49. What is made at the end of meiosis? ANSWER: 4 gamete cells that are non-identical 50. Identify the correct phase of meiosis I for each description. ANSWER: a. Homologous chromosome pairs split into single chromosomes, moving to opposite ends of the cell = ANAPHASE I b. Chromosomes form into pairs and crossing over takes place = PROPHASE I 50. Identify the correct phase of meiosis I for each description. ANSWER: c. Centrioles & spindle fibers disappear while nuclear membrane forms around single chromosomes = TELOPHASE I d. Homologous chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell = METAPHASE I 51. What do you call the exchange of genetic information between homologous chromosomes (that happens in prophase I)? ANSWER: Crossing over 52. What (and how many) is made from spermatogenesis and oogenesis? ANSWER: a. Spermatogenesis = four sperm cells b. Oogenesis = one ovum/egg cell 53. What is the difference between asexual & sexual reproduction? ANSWER: Asexual reproduction only requires one parent to make offspring. Sexual reproduction requires two parents to make offspring. 54. The name of the process that combines sperm & egg together is called ___. ANSWER: FERTILIZATION 55. The first cell that is made after sperm cell and egg cell combine is called ___. ANSWER: ZYGOTE