* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aberration File
Survey
Document related concepts
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting telescope wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
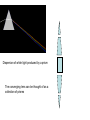
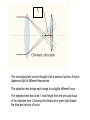
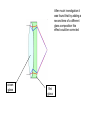
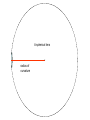
Chromatic Aberration An image of the planet Jupiter showing strong chromatic aberration An example of chromatic aberration in an image produced by a telescope with a simple converging lens The image on the left shows strong chromatic aberration compared to the image of the same star field at the same magnification on the right Stong chromatic aberration shown around the broght blue stars in the foreground of the image Dispersion of white light produced by a prism The converging lens can be thought of as a collection of prisms Fe The converging lens can be thought of as a series of prisms. A prism disperses light of different frequencies The objective lens brings each image to a slightly different focus. The eyepiece lens has to be 1 focal length from the principal focus of the objective lens. Choosing this distance for green light leaves the blue and red out of focus. After much investigation it was found that by adding a second lens of a different glass composition this effect could be corrected crown glass flint glass Spherical Aberration Spherical aberration in lenses is an effect which produces an imperfection in the image. It happens when light being refracted from the edge of a lens is brought to a focus slightly before light from the centre of the lens. This is due to the fact that the surfaces of simple converging lenses are lenses are spherical. (That is they form part of the surface of a sphere) circle of confusion A spherical lens though simple to make is not the ideal shape for a lens A spherical lens radius of curvature Spherical Aberration In Lenses The effect is minimised with telescopes of long focal legnth In lens systems, the effect can be minimized using special combinations of convex and concave lenses, as well as using asymmetric lenses With different radii of curvature at each side The amount of spherical abberation is proportional to 1/f3 and is therefore greatly reduced with objective lenses of long focal lengths. Other Problems With Refracting Telescopes • Faint light must pass through the lens so it must be totally free of optical defects such as tiny bubbles. Therefore lenses are very expensive. • Glass is opaque to certain frequencies of light. Especially UV. • Even visible light is substantially absorbed as it passes through the lens. • It is impossible to produce a large lens free of chromatic aberration • It is difficult to support large lenses without blocking a great deal of light. Therefore mirrors are preferred Spherical Aberration In Mirrors spherical mirror Spherical mirrors are easier to grind and polish but have an appreciable degree of spherical aberration parabolic mirrors do not suffere from spherical aberration but do not have a wide field of view like spherical mirrors. (they suffer from “coma”. Bernhart Schmitt (1930,s) introduced a thin correcting lens to correct the image in a spherical mirror. Many large telescopes are Scmitt reflectors