* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain - cloudfront.net
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
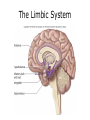
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
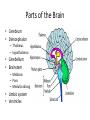
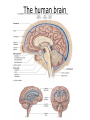
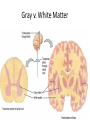
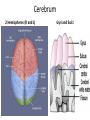
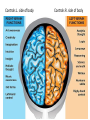
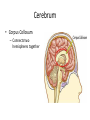
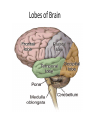
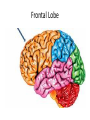
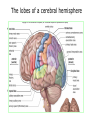
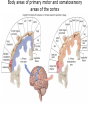
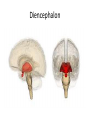
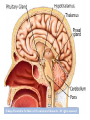
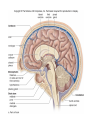
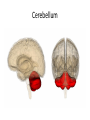
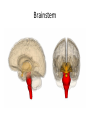
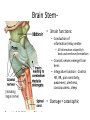
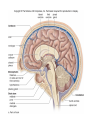
The Brain Parts of the Brain • Cerebrum • Diencephalon – Thalamus – hypothalamus • Cerebellum • Brainstem – Midbrain – Pons – Medulla oblongata • Limbic system • Ventricles The human brain Cerebrum • Largest part of the brain • Most highly developed part of the human brain • Outer portion: cerebral cortex – Cell bodies and unmyelinated axons • Inner portion: central white matter – Myelinated axons – How parts of cerebrum communicate with each other and other parts of brain. Gray v. White Matter Cerebrum 2 Hemispheres (R and L) Gyri and Sulci Controls L. side of body Controls R. side of body Cerebrum • Corpus Collosum – Connects two hemispheres together Lobes of Brain Frontal Lobe Frontal Lobe Function • Function: – Higher Level Cognitive Function /Executive Function • Judgment and reasoning – Control of voluntary muscle movement (MOTOR FUNCTION) • Including speech and swallowing Frontal Lobe- Important Areas • Primary Motor Cortex – Anterior to Central Sulcus – Controls voluntary movements of skeletal mm. – More area dedicated to muscles of mouth and fingers (use more) • Premotor Cortex – Programming of motor movements (except for speech) • Prefrontal Cortex – Complex cognitive process (reason and judgement) • Broca’s Area – Coordination of motor movement for production of speech sounds. Creates motor plan which is then sent to primary motor cortex The lobes of a cerebral hemisphere Parietal Lobe • Posterior to central sulcus • Function: – Associated with Sensation • Touch, kinesthesia, perception of warmth and cold and vibration • Important Parts: – Primary sensory area • Receives sensory information from the joints and tendons in body , organized similar to motor area – Somatosensory Association Area: • Detailed discrimination and analysis of 1 Sensory area • ***angular gyrus: recognition of sensory symbols Temporal Lobe • Function: – Auditory processing and olfaction (smelling) – Involved in semantics / word meaning • Important areas: – Primary auditory area – Wernicke’s Association Area: dominant hem. • Understand and produce meaningful speech Occipital Lobe • Function: Vision • Important parts: – Primary Visual Area: receives input from the optic tract. – Secondary visual area: integrates visual information, give meaning to what is seen,visual memories. Body areas of primary motor and somatosensory areas of the cortex Basal nuclei a.Masses of gray matter deep in the cerebrum b.Integrate motor commands c.Huntington disease and Parkinson’s disease – uncontrollable movements believed to be from neurotransmitter imbalances in the basal nuclei Diencephalon Thalamus – “the router” • Function: – Relays sensory, spatial sense and motor signals to cerebral cortex • Receives auditory, somatosensory and visual sensory signals, sorts data and relays it to proper area in brain – Regulation of consciousness • Controls sleep and awake states of consciousness • Sides of third ventricle Hypothalamus • Function: – Maintaining homeostasis • Integrating center involved in maintaining homeostasis • Regulates hunger, sleep, thirst, temperature and water balance – Autonomic control – Link between nervous system and endocrine system – Involved in emotional responses The Limbic System Limbic System: “Emotional Brain” • Deals with – Emotions- fear, anger, happiness, pleasure – Memories/ learning – Arousal (stimulation) • Several parts above brainstem and within cerebrum • Important parts: – Amygdala: responsible for memory of emotion (especially fear) – Hippocampus: responsible for processing of long term memory and emotional responses • Short term to long term memory and learning Cerebellum Cerebellum • Function: – Responsible for balance and coordination of muscles in the body – Important in • • • • preforming voluntary tasks (walking, writing) Maintaining balance and posture Muscle memory Learning new muscle skills • Remember: separated from brain by 4th ventricle Brainstem Brain Stem• 3main functions: – Conduction of information/relay center: • All information relayed b/n body and cerebrum/cerebellum – Cranials nerves emerge from here: – Integrative function: Control HR, RR, pain sensitivity, awareness, alertness, consciousness, sleep • Damage = catastophic Brain Stem • Midbrain: – Response to sight, eye movements, pupil dilation, hearing • Pons – Communication/coordination center between the two hemispheres – Important in arousal and sleep • Medulla Oblongata – Controls autonomic functions • RR, HR, Blood vessel function, swallowing, sneezing