* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
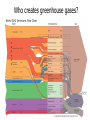
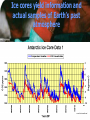
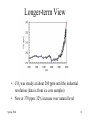
CLIMATE is the average of many years of weather observation. CLIMATE IS: • Long term • Wide area • Seasonal changes • Measured over long spans of time Climate is affected by many factors ABIOTIC FACTORS: BIOTIC FACTORS: Latitude Transpiration Altitude Respiration Ocean Currents Photosynthesis Topography Decomposition Solar Radiation Digestion Evaporation Orbital Variations Volcanic Activity Greenhouse Gases are essential to our climate http://www.larryjzimmerman.com/wproblems/warming/greenhouse.gif A number of greenhouse gases occur naturally in the Earth’s atmosphere •Water vapor •Carbon dioxide •Methane •Nitrous oxide The greenhouse gas content of the atmosphere is being altered by human activity. The result of this change is global warming. Who creates greenhouse gases? Evidence of Climate Change comes from many different sources. Glaciers are melting away worldwide Agassiz Glacier, Montana, in 1913… …and in 2005 Pasterze Glacier, Austria, in 1875… …and in 2004 Ice cores yield information and actual samples of Earth’s past atmosphere www.daviesand.com/ Animal and plant life is changing 2/3 of European butterfly species studied have shifted their ranges northward by as much as 150 miles. (Parmesan, 1996; Parmesan et al., 1999) An analysis of the distributions of British birds found that many species have moved north by an average of 18.9 km. (Thomas et al, 1999) At Boston's Arnold Arboretum, plants are flowering eight days earlier on average than they did from 1900 to 1920. (Primack et al,2004) Climate change seems to accelerating Each of the 48 continental states experienced above-normal annual temperatures in 2006. For the majority of states, 2006 ranked among the 10 hottest years since 1895. ( NOAA) Carbon Dioxide In the distant past, the Earth was much warmer. High levels of Carbon Dioxide in the atmosphere fueled lush growth, some of which was stored in the form of fossil fuels. Carbon Dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere has risen by about 30% since the beginning of the industrial revolution. Most of the increase is due to the combustion of fossil fuels, which releases the longstored CO2 back into the atmosphere. www.epa.gov/climatechange The CO2 Problem Spring 2004 15 Longer-term View • CO2 was steady at about 280 ppm until the industrial revolution (data is from ice core samples) • Now at 370 ppm: 32% increase over natural level Spring 2004 16 Predicted Temperature Changes • The IPCC predicts an increase of 1.4ºC to 5.8ºC from 1990 to 2100 depending on scenario • Earth can be slow to respond, due to thermal sink of oceans, and this lag means the temperature will continue to rise even if we ceased burning fossil fuels today! • CO2 hangs around long enough that we would likely not see the end of changes until ~2300 – this is under scenario that we STOP fossil fuels tomorrow – sea-level rise is the gift that keeps on giving Spring 2004 17 Spring 2004 18 Sea-level rise • Thermal expansion of water plus polar ice-cap melting raise the sea level • The oceans are predicted to rise something like half-a-meter by 2100, maybe as much as 1 meter – goodbye to much of Bangladesh, much of the Nile valley, Louisiana • Doesn’t stop there: it won’t stabilize until maybe 2300, by which time the rise could be several meters – this is even if we stop the CO2 production today Spring 2004 19 IPCC Estimates on Sea Level Spring 2004 20 What can be done? First we must admit that climate change is everyone’s problem. No agency, government, or scientist can “fix it” for us. We are all in this together. We got here because of our lifestyle. So our lifestyle has to change. There’s no place like home… …and there may never be again