* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06 - The Creativity Process
Survey
Document related concepts
Problem of universals wikipedia , lookup
Eliminative materialism wikipedia , lookup
Situated cognition wikipedia , lookup
Exact cover wikipedia , lookup
Mental image wikipedia , lookup
Anomalous monism wikipedia , lookup
Empirical theory of perception wikipedia , lookup
Genetic algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Conduit metaphor wikipedia , lookup
Hard problem of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Computational creativity wikipedia , lookup
Plato's Problem wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Multi-armed bandit wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Eureka effect wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
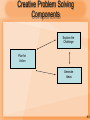
What is Creativity? 9-1 Creativity is… Person Process Produce Press 9-2 Creative Problem Solving Components Explore the Challenge Plan for Action Generate Ideas 9-3 Creative Problem Solving: The Six Stages Building Blocks Explore the Challenge Generate Ideas * * * * Stages Identify Goal, Wish or Challenge Gather Data Clarify the Problem * Generate Ideas Prepare for Action * * Select &Strengthen Solutions Plan for action 9-4 Theoretical Assumptions The creative process involves a set of mental operations; These mental operations can be described; The creative process is a natural process; People possess preferences for different mental operations (i.e., cognitive styles); and Therefore, people possess different preferences for the mental operations associated with creative problem solving. 9-5 Creative Problem Solving Styles Clarifier Collector Ideator Developer Implementer 9-6 Clarifier Enjoys exploring the problem space; Likes to examine the details associated with the challenge; Likes to make sure he or she has a clear understanding of the problem; Prefers a methodical approach to problem solving; Likes to gather information; and May suffer from ‘analysis paralysis’. 9-7 Collector Likes to gather information; Enjoys researching ideas; Likes to focus on the details; Tends to think and solve problems in a structures way; and May over analyze a situation. 9-8 Ideator Likes to look at the big pictures; Enjoys toying with ideas and possibilities; Likes to stretch his or her imagination; Enjoys thinking in more global and abstract terms; May take a more intuitive approach to problem solving; and May overlook the details. 9-9 Developer Enjoys putting together workable solutions; Likes to examine the pluses and minuses of an idea; Likes to compare competing solutions; Enjoys thinking about, and planning, the steps to implement an idea; Enjoys analyzing potential solutions; and Can get stuck in developing the perfect soluition. 9-10 Implementer Likes to see things happen; Enjoys giving structure to ideas so that they can become a reality; Enjoys seeing ideas come to fruition; Likes to focus on ideas and solutions that he or she feels are workable; Likes the ‘Nike’ approach to problem solving (i.e., ‘Just do it’); and May leap to action too quickly. 9-11 Interpreting Results Strength of scores (I.e., how do your scores compare to others?) Leading and least preferred style (i.e., looking across your scores, what stands out as the most and least preferred operations within the creative problem solving process?) 9-12 Divergent Thinking Guidelines Rule Out Judgment (Suspend Evaluation) Seek Quantity (Quantity Breeds Quality) Build on Options (Mental Hitch-hiking) Seek Novel Associations (Freewheel) 9-13

















![Name: [Child 2] Date: 15 September 2014](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008467771_1-7ec1d608bbaeb50f71b6339e3a145ce9-150x150.png)