* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Reverse osmosis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Water testing wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Properties of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Strengthening mechanisms of materials wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
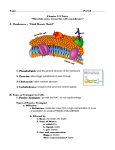
Solutions and Properties of Water Do Now Is chlorine a reactive element? Explain why or why not. Go Over Assignment • Practice problems #2, 3, & 9 (p. 14) • Practice Problems #9-12 (p. 17-23) • 1.2 Questions: Pg. 23-24 #1-5 • Diagrams of Atoms Summative Assignment–Due Monday, February 8th. The Plan • Learn about chemical change, solutions, solvents & solutes. • Discuss why water is an excellent solvent. • I can explain how dissolving substances in water is often required for chemical reactions. Chemical Change • The way to tell if a chemical change is occurring or has occurred is if there is a new substance produced, accompanied by a change in colour, odour, state, or energy. • Changes in state usually involve formation of gas or solid. Chemical Change • Chemical changes show that bonds between atoms in the original substance have been broken and new bonds have been formed to create new substances. • Weird Chem RXN Solutions • Often, substances are dissolved in water in order for chemical changes and reactions to occur. When matter is dissolved in water this forms something called an aqueous solution. • Examples: Sea water, urine, crystal light Alka Seltzer in Stomach Reaction • NaHCO3 + HCl => NaCl + CO2 + H20 Solutions • Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of substances composed of at least one solvent and one solute • Solvents are the substances in which the solutes dissolve. • Water is the most common solvent and forms aqueous solutions. • Solutes are the substances dissolving into the solute. • (e.g. in salt water, salt is the solute and water is the solvent.) Crystal Light • What is our solvent? • What is our solute? Structure of Water • Triatomic molecule • Meaning it has 3 atoms • Held together by covalent bonds • Oxygen and the 2 hydrogens share the electrons Structure of Water • Oxygen has a stronger pull on the electron than hydrogen. • it is considered to be a polar molecule, because one end (the oxygen) has a more negative charge than the other end (the hydrogen). • Polarity DEMO Polarity of Water • polar molecules attract one another water molecules tend to “stick together” more strongly than other molecular compounds that are non-polar • polar substances act as good solutes for other polar molecules and for all ionic compounds. Aqueous Solutions • Aqueous solutions are by far the most common and versatile type of solutions • All aqueous solutions are clear or transparent Solvation • The process of a solute dissolving in a solvent • Solute is added to solvent solvent particles attract solute particles bonds holding solute together break down solute becomes surrounded by solvent molecules • if the attraction between particles of the solute is stronger than those with water, the particles of the solute will not solvate very much (e.g. oil in water) Assignment • Read pgs. 24-31 • 1.3 Questions pg. 33 #1,2,4, 5