* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chambers Valves, Conduction System, Coronary Circulation
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
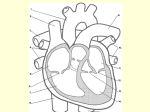
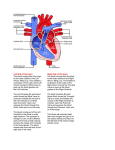
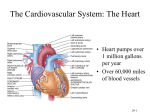
Cardio 2a – Chambers, Valves, Conduction System, Coronary Circulation Anil Chopra 1. Understand the circulatory pathway through the heart. Vessels that enter the heart and vessels that leave the heart. Lungs Pulmonary Vein Pulmonary Trunk Right Atrium Left Atrium Right Ventricle Left ventricle Vena Cava Aorta Body 2. a) Understand the Chambers of the heart Right Atrium: - Appendage and venous components. - Appendage is large - Venous component receives blood from vena cavae and coronary arteries. - Leads to tricuspid valve Left Atrium: - Appendage and venous components. - Appendage is small and finger-like - Venous component receives blood from the pulmonary veins. - Leads to mitral valve Right Ventricle - Elliptical in shape. - Inlet is tricuspid valve - Output is infundibulum that supports pulmonary valve. - Supraventricular crest separates pulmonary and tricuspid valve. - Trabecular portion (inside connective tissue and framework) is rough, project into the cavity and are made from irregular muscle bundles. Left Ventricle: - Conical in shape with rounded cross-section. - Thicker walled than right ventricle. - Inlet is mitral valve. - Aortic and mitral valve and are adjacent. - Output is aortic valve and is in between ventricular septum and mitral valve. - Trabecular portion in apex. It comprises of criss-crossing bundle fibres. b) Understand the components of the septum. Atrial septum: between left and right atria. It contains the oval fossa where the septum is thin. It is noticeable on the right atrium. Ventricular septum: runs obliquely between left and right ventricles. It is mainly muscular but also contains Purkinje Fibres. A small part of the ventricular septum is membranous. c) Understand the components of heart valves. Atrioventricular Valves: between atria and ventricles. prevent backflow of blood in ventricular systole. have hinge like attachments which attach tendons to papillary muscles. Tricuspid Valves: has 3 cusps (leaflets), antero-superior, mural, septal. between right atria and ventricles. Mitral (bicuspid) Valves: has 2 cusps between left atria and ventricles, anterior and posterior. Arterial Valves (semilunar) prevent reflux from arteries into ventricles oven when ventricles contract in systole. 3 semilunar leaflets not attached to chords. have nodules in the middle of each of the leaflets. fills with blood in diastole as the valve closes. Pulmonary Valves: right infundibulum Aortic Valve: Left side of heart in junction between aorta LV. d) Understand the conduction system. (1) Sinus Node (SAN) – initiates the conduction of impulses. (2) Atrioventricular Node (AVN) – amplifies current down septum through the bundle branches of the Purkinje network. e) Coronary Circulation. Consists of: Right: Right coronary artery Left: Anterior descending, posterior descending, circumflex arteries. NB: If the right coronary artery supplies the posterior descending coronary artery than it is RIGHT CORONARY DOMINANCE (90%) If the left coronary artery supplies the posterior descending artery it is LEFT CORONARY DOMINANCE. Venous return consists of great, middle and small cardiac veins which all drain into the coronary sinus which returns blood to the right atrium. Thebesian veins also drain directly into chambers.