* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download permanent magnet synchronous motor
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
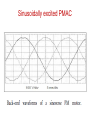
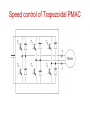
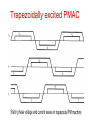
PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR DRIVES (PMSM) PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR • The notation for PMSM is PMAC • In PMSM the D.C field winding of the rotor is replaced by Permanent Magnets • Permanent Magnet Materials: Alnico, Cobalt-Samarium, Ferrite. Advantages: • Elimination of field copper loss. • Higher power density. • Lower rotor inertia. • More robust construction of motor. • Higher efficiency. Disadvantages : Loss of flexibility of field flux control. Remagnetization effect. Higher costs. Application: Low power range motors are widely used in industries. Types Permanent Magnet Synchronous motors 1.Surface Mounted-PMSM Projecting type Inset type 2.Interioror Buried-PMSM Types of Permanent Magnet Synchronous motors 1.Surface Mounted-PMSM Projecting type Inset type 2.Interioror Buried-PMSM Types of Permanent Magnet Synchronous motors Based on nature of voltage induced in the stator classified as Sinusoid ally excited PMAC: • Stator has distributed winding. • Stator induced voltage has sinusoidal waveform. Trapezoid ally excited PMAC: • Stator has concentrated winding. • Stator induced voltage has trapezoidal waveform. Speed control of sinusoidal PMAC • The speed of the PMAC motor is controlled by feeding them from variable frequency ,voltage and current. • They are operated in self controlled mode. • In closed loop control ,current regulated VSI is used. • The inverter is operated to supply motor three phase currents of the magnitude and phase commanded by reference currents isa,isb and isc which generated by a reference current generator. • The stator current templates for the three phases are generated by the rotor position sensors in such a way that δ = π/2 Speed control of sinusoidal PMAC Sinusoidally excited PMAC Trapezoid ally excited PMAC Speed control of Trapezoidal PMAC • According to the torque equation torque is proportional to Id. • Regenerative braking mode operation is obtained by reversing phase currents. • This will also reverse the source current Id. • Now power flow from the machine to inverter and from inverter to dc source. Speed control of Trapezoidal PMAC Trapezoidally excited PMAC