* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Module Macromolecules, Cell Theory, Organelles, Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
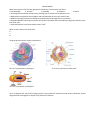
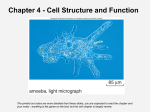
Review Module Match the scientist to the role they played in the discovery of cells and the cell theory. A. Leeuwenhoek b. Virchow C. Schleiden D. Schwann E. Hooke 1. Physiologist that looked at animal tissues, deciding that all animals are composed of cells. 2. Botanist that surveyed the plant kingdom and concluded that all plants are made of cells. 3. Made his own high powered microscope and viewed microscopic organisms in pond water. 4. Hypothesized after examining a collection of scientific information that cells made up living things and they came from other cells. 5. Examined pieces of cork and termed the word “cells” What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? 6. 7. 8. Using the pictures below, answer the questions. 9. Is this a plant or animal cell? 10. Is this a prokaryote or eukaryote? 11. Is this a plant or animal cell? 12. Is this a prokaryote or eukaryote? 13. Is this a prokaryote or eukaryote? 14. In a eukaryotic cell, the job of creating a protein is very important. Describe how the nucleus, ribosomes, ER and Golgi would all work together to help the cell perform this function. 15. Complete the table below to demonstrate your understanding of similarities and differences in cell types. Write “yes” or “no” in each box. Cell Structure Cell membrane Cell wall Cytoplasm Ribosomes DNA Mitochondria Chloroplasts Centrioles Vacuole All Cells Prokaryotes Animal Cells Plant Cells 16. Why is the cell membrane called a lipid bilayer? Sketch a diagram below. 17. What is the purpose of cell membrane proteins? 18. What does it mean for a membrane to be “selectively permeable”? 19. Explain the differences between passive and active transport. Cell Transport True or False 20. Plasmolysis is seen in animal cells when they take on too much water and burst. 21. Crenation is caused by the movement of water out of a cell by osmosis. 22. Isotonic solutions on either side of the membrane are equal and cells show no net change. 23. A dialysis tube is filled with water and sugar. It is placed in distilled water. Water will move out of the bag. 24. If you sprinkle salt on a slug, it will be harmed by the loss of too much water. 25. Water tends to diffuse from where the solute is less concentrated to where the solute is highly concentrated. 26. Endocytosis is the process of taking materials into the cell by means of infolding of the cell membrane. 27. Active transport does not require the use of energy by the cell. 28. Diffusion is affected by temperature. 29. Hypertonic solutions cause cells to swell due to water rushing into the cells. 30. Sodium-potassium pumps a form of active transport. Match the macromolecule to its function or monomer. A. Carbohydrate b. Protein C. Lipid D. Nucleic Acids 31. Used by the cell as an immediate energy source 32. Used to store energy and consist of mostly carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 33. Made up of nucleotides (5 carbon sugar, phosphate and nitrogen base) 34. Control the rate of reactions. 35. An example would be saturated fats 36. Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus 37. Examples of this macromolecule would be glucose, fructose, lactose, and maltose 38. Made up of amino acids 39. Examples are DNA and RNA 40. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen atoms