* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fronts - Lincoln High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Australian contribution to the Allied Intervention in Russia 1918–1919 wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
List of World War I memorials and cemeteries in Artois wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
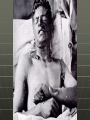
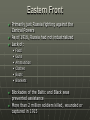
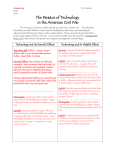
The “Fronts” Western, Eastern and Home Fronts of WWI Western Front Characterized by trench warfare Generals were used to fighting by movement War of Attrition: Attempting to wear down the other side by constant attacks and heavy losses Airplanes, tanks and chemical warfare (Mustard gas) used for the first time in war “Going Over The Top” Rifle Bayonet Grenades 170 rounds of ammunition Gas Mask Shovel Wire cutters Full water bottle Food rations Extra clothing Medical supplies Cooking stove/fuel Eastern Front Primarily just Russia fighting against the Central Powers As of 1916, Russia had not industrialized Lack of: • • • • • • Food Guns Ammunition Clothes Boots Blankets Blockades of the Baltic and Black seas prevented assistance More than 2 million soldiers killed, wounded or captured in 1915 Home Front Wounded soldiers were brought home late at night to not draw attention to the amount of soldiers being hurt Inflation: Food prices rose Government implemented rationing • sugar, meat, butter, cheese, margarine Bombing raids by the Germans Round the clock factories Influence of Industrial Revolution on War Railroads were able to supply the troops more quickly than before Railroads could replace worn out/wounded soldiers Factories were able to produce munitions in large amounts Soldiers were maimed and disfigured due to the new way of fighting Major Battles Battle of the Marne 1 (1914): • First major battle of WWI ending in Allied victory • Destroyed the Schlieffen Plan Battle of Tannenburg (1914): • German victory over Russia • Regained East Prussia Battle of the Somme (1916): • Allied Victory in France Battle of the Marne 2 (1918): • Fresh American troops • Victory for the Allied leading to end of war The Entry of the U.S. United States tried to remain neutral Britain and Germany set up naval blockades to prevent war materials and other goods from getting to their enemies Germany enforced their blockade by sinking passenger liners 1915: British ship Lusitania was sunk by German forces. Over 100 Americans were aboard that ship Zimmermann Note: Message from Germany to Mexico, 1917 United States officially entered the war in April 1917 and was a major source of money and war goods U.S. Home Front College students joined student Army training corps Curriculum emphasized America’s superiority over Germany Children were taught to sing patriotic songs Women volunteered with the Army Nursing Corps Worked in factories, on Navy ships, and in charitable organizations such as the Red Cross