* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IB Biology Topic 2 - Cells Revision Sheet What is understood by the
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
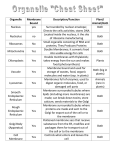
IB Biology What is understood by the term “cell theory”? All living things are made of cells, All cells come from pre-existing cells, The smallest unit of life is the cell. Explain why striated muscle, giant algae, fungal hyphae don’t quite fit. Striated muscle is multinucleate, extra large Giant algae are too big, have super low SA:V ratio Fungal Hyphae are multinucleate and super large Is this enough evidence to falsify cell theory? No Briefly explain each of the following: Specialized tissues can develop by cell differentiation Topic 2 - Cells Revision Sheet Explain why a small surface area to volume ratio limits cell size. Materials that are essential to life have to be transported in via passive transport. (due to the fact that they are needed all of the time, it is not energy efficient to transport them via active transport) For passive transport, you want lots of surface area (membrane area) to passively transport things through. As you increase in size, your SA:V ratio goes down, because volume goes up faster than area. This leads to inefficiencies in passive transport as you increase the distance materials have to travel via passive xport, and it ultimately means there is a maximum cell size. Name organelles A & B. Calculate the size of each. Cells start out as stem cells, and are induced by chemical signals into specific cell types by chemical signals. Describe an example of an emergent property. The living cells that make up your body are, in themselves, not special. However, when they work together, they can have extra properties. It works through the idea that cells - tissues Organs Organ Systems Organisms At each of the levels, when they are combined, they create the next level, and gain new abilities/properties. Based on the fact that these new properties “emerge” at each subsequent level, we call them “emergent properties” Draw a simple labelled diagram of a Prokaryotic cell. Draw a simple diagram of a Eukaryotic cell. Stem cells can divide and differentiate along different pathways Each stem cell can differentiate in to a wide variety of types of cells from a single precursor A Lysosome – 1 um B – Vacuole – 0.5 um Use of stem cells to treat one named disease Leukemia – Harvest healthy Adult stem cells, chemotherapy kills off cancerous tissue, reintroduce healthy stem cells back in to the body. Explain how phospholipids form bilayers due to the amphipathic properties Describe three locations & five functions of membrane proteins. The head of a phospholipid is polar, while the tail is non polar. This means that the heads of the molecules are attracted to each other and the tails are attracted to each other. This contributes to the ability to form a bilayer. The other factor in their ability to form a bilayer is how much they like water. The polar parts will be outward facing the water environment, while the tails will be facing inwards, away from the water. Location Function Outside of the membrane Signalling, receptors Integrated through both membranes Integrated through one layer Channels, Active transport proteins Contributing to integrity of cell membrane Describe how molecules move across membranes by simple diffusion, High concentration to low concentration, through the plasma membrane facilitated diffusion, High concentration to low concentration, through channel proteins osmosis High concentration to low concentration, through aquaporins Active transport. Pay no attention to conc. Gradient, using active transport proteins Explain how vesicles are used to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus and plasma membrane. Vesicles are formed from the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum around newly synthesized proteins. Vesicles then carry the proteins to the golgi apparatus, which determines the end goal for the proteins. The golgi then creates a new vesicle that moves the proteins to the end destination. The plasma membrane allows all of this transport to happen, due to the fact that it is resealable, and can allow vesicles to fuse with it. List the stages in cell division by mitosis? Give a detail about each stage. Mitosis phase Detail(s) Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Regular cell processes, DNA Synthesis, Cell gets bigger Nuclear membrane goes away, DNA condenses Chromosomes line up in middle of cell, spindle fibers reach out towards them Chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell New nuclear membrane begins to form, cells begin dividing cytoplasm What causes the cell cycle & division to go wrong and cause 1° and 2° tumors in cancer? Use the terms cyclins, mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis Cancer is caused by cells losing control of the cell cycle. Cyclins, which normally can halt the cell cycle, can no longer do so, and for this reason, the cell cycle proceeds when it shouldn’t. This occurs when oncogenes stop allowing the cell to create p53. A primary tumor is a small formation of cells that have divided from one cancerous cell. A secondary tumor is a tumor that has recruited blood vessels because of its size. This leads to metastasis often.