* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name the terms - St John Brebeuf
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
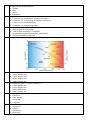
Astronomy_Practice_Test http://chss.sd57.bc.ca/~spearce/Science_9/Practice%20Tests/AstronomyPractiseTest.htm True/false. Same story. 1. Revolution is the spinning of an object around an axis. _______________________ 2. The equinoxes occur in March and September. __ 3. The same side of the moon is always facing us. __ 4. Meteorites are large lumps of trapped rock or metal that actually reach the Earth’s surface.__________ 5. The gas giants are mainly composed of hydrogen and nitrogen. _________________________ 6. In a geocentric model of the universe, the Sun is at the centre. _________________________ 7. The moon revolves around the Earth every 31 days. 8. The neap tides are the weaker type of tide. ___ 9. Venus, Mercury, Earth, and Mars are all considered terrestrial planets. ______________ 10.Mars has an atmosphere composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen. _________________________ 11.Ptolemy devised the heliocentric model. ________ 12.Kepler first proposed that the Earth revolves around the Sun. _________________________ 13.It takes Mars longer than Earth to orbit around the Sun. _________________________ 14.The moon is brightest when it is in its first quarter phase. _________________________ 15.The neap tides occur during the new and full moon phases. _________________________ 16.Light from a source moving toward an observer would have a shift toward the red end of the spectrum. 1. 2. 4. 17.Triangulation is the apparent motion of a nearby star against the background of more distant, nonmoving stars. ___ 18. The outer layer of the Sun is the corona.________ 19. Dark spots on the Earth’s surface caused by disturbances in the Sun’s magnetic field are called sunspots.______ 20. Supernovas produce either a neutron star or a black hole. _________________________ 21. Spiral galaxies are full of new and young stars. ____ 22. Our Earth is located in an elliptical galaxy. _______ 23. Hotter stars are typically blue in colour. _________ 24. Globular clusters usually contain only a few hundred stars. _________________________ 25. The Very Large Array (VLA) located in New Mexico consists of several microwave telescopes. ______ 26. A space probe is an unpiloted spacecraft that leaves the Earth’s orbit. _________________________ 27. Both Spirit and Opportunity were two robotic rovers sent to the Moon to study its geology. _________ 28. An object in geosynchronous orbit will stay in the same position above Earth. ________________ 29. A possible way of bringing people, energy, and other cargo to and from space would be to build a space elevator. __ The study of the objects and events beyond the Earth is called A. Astrology B. Physics C. Astronomy D. Biology The seasons occur due to A. the Earth’s elliptical orbit B. the tilt of the Earth’s axis C. the Earth’s rotation D. the Earth’s revolution Which of the following is the correct order of the initial phases of the moon? A. new moon, waxing gibbous, full moon, waxing crescent, first crescent B. new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon C. full moon, waxing crescent, first crescent, waxing gibbous, new moon D. new moon, first crescent, waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, full moon 5. Which of the following phenomena is directly caused by the Earth’s rotation? A. the seasons B. the changing photoperiod C. the solstices D. day and night 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. The picture above represents a A. waxing crescent B. first quarter C. waxing gibbous D. third quarter When the Earth casts its shadow on the surface of the Moon, a(n) __________ can occur. A. partial solar eclipse B. lunar eclipse C. equinox D. total solar eclipse Spring tides are A. rare B. common C. very high D. especially low Chunks of frozen matter that orbit the Sun in long elliptical paths are called A. comets B. meteors C. asteroids D. supernovas Which of the following planets is not classified as terrestrial? A. Mars B. Venus C. Earth D. Neptune 11. Scientific evidence suggests that the Earth formed __________ billion years ago. A. 12.5 B. 4.6 C. 3.2 D. 6.8 12. Which of the following best describes the term “constellation”? A. a group of stars that travel through space together B. a group of stars that form a shape or pattern C. a group of stars that is seen in the same part of the sky D. a group of stars that are located near each other in space 13 The average surface temperature on this planet ranges from –88C to 58C. A. Mercury B. Venus C. Earth D. Uranus 14 Which of the following planets has a rotation that is in the opposite direction to other planets? A. Mercury B. Earth C. Venus D. Mars 15. Which of the following is not considered a true planet? A. Jupiter B. Venus C. Pluto D. Neptune 17. An astronomical unit is defined as A. the distance between the Earth and the Moon B. the distance between the Sun and the Moon C. the distance between the Earth and the Sun D. the distance between any two planets 18. Which one of the following scientists first devised a geocentric model of the universe? A. Nicholas Copernicus B. Claudius Ptolemy C. Nicholas Copernicus D. Galileo Galilei 19. In a heliocentric model of the solar system, choose the statement that would be true. A. The Earth is at the centre. B. The planets and stars orbit the Earth. C. The planets orbit the Sun. D. The planets and stars orbit the Sun. 20. For a(n) __________ to occur, the new moon must be positioned between the Earth and Sun at a node. A. lunar eclipse B. solar eclipse C. equinox D. solstice 21. On Earth, there are __________ tide cycles each day. A. 2 B. 3 C. 5 D. 6 23. It is a scientifically-accepted theory that the origin of the universe occurred approximately: A. 4.6 billion years ago B. 10.3 billion years ago C. 13.7 billion years ago D. 22.4 billion years ago 25. Which of the following is not useful for measuring distances in space? A. B. C. D. 26. star map parallax radar red shift When astronomers use a baseline to measure objects by parallax, the longest possible baseline they can use is: A. the distance from the Earth to the Sun B. the diameter of the Moon’s orbit C. the diameter of the Earth’s orbit D. the distance from the Earth to the Moon 27. 28. 32. 34. 35. 36. 37. A light year is a measurement of: A. distance B. time C. speed D. brightness Triangulation is A. a direct way of measuring the distance to an object B. an indirect way of measuring the distance to an object C. a direct way of measuring angles D. an indirect way of measuring angles Solar wind is best described as: A. dark spots on the solar surface B. wind on Earth caused by UV radiation C. an ionized gas emitted from the Sun continuously D. the outer atmosphere of the Sun Figure 1 Hertzsprung-Russell diagram According to Figure 1, blue giants are typically: A. cooler, dimmer stars B. cooler, brighter stars C. hotter, dimmer stars D. hotter, brighter stars According to Figure 1, Proxima Centauri is a A. cooler, dimmer star B. cooler, brighter star C. hotter, dimmer star D. hotter, brighter star Using Figure 1, determine which type of stars have the hottest surface temperatures. A. red dwarfs B. white dwarfs C. blue giants D. red giants What object is most likely to be the birthplace of stars? A. Supernova B. Nebula C. neutron star D. black hole 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 45. 46. Which of the following stars is a type of neutron star? A. Supernovas B. white dwarfs C. Pulsars D. black holes Which of the following is not a property of a supernova? A. it can release large amounts of energy B. it can turn into a black hole C. it occurs near the end of a star’s life D. it is the same as stellar birth The colour of a star depends on its: A. temperature B. size C. distance D. Position Choose the correct order for the life cycle of a Sun-like star. A. nebula, white dwarf, red giant B. nebula, supergiant, black hole C. nebula, red giant, white dwarf D. nebula, supergiant, neutron star Which type of galaxy is the Milky Way? A. elliptical B. spiral barred spiral C. spiral D. irregular What is the difference between a reflecting and refracting telescope? A. only one type contains an eyepiece lens B. only one gathers and focuses visible light C. only one type produces clear images D. only one type contains mirrors in its body tube Select the space probe that discovered the rings of Jupiter. A. Luna 1 B. Voyager 2 C. Magellan D. Spirit 50. The Canadarm2 is: A. used as a high-powered telescope B. a probe that is orbiting the Earth C. used to assist astronauts on the ISS D. a anti-gravity machine 52. The process of changing a planetary body to support human life is called A. terraforming B. geosynchronizing C. colonizing D. cloning Match each item to the word listed below. A. comets E. asteroids B. outer planets F. nebula C. protoplanets G. supernova D. meteorites H. meteors small chunks of material that burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere also known as gas giants, and consist mainly of hydrogen and helium chunks of frozen matter that orbit the sun small clumps of matter, forced together by gravity that condense to form planets a collection of dust and gases consisting mainly of hydrogen and helium lumps of material travelling through space that reach the Earth’s surface small, rocky, metallic objects that rotate around the sun a star in its final phases of life 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Match each planet to the corresponding description below. A. Mercury E. Jupiter B. Venus F. Saturn C. Earth G. Uranus D. Mars H. Neptune 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. about 70% of this planet’s surface is covered by water this planet spins on its side and has winds of up to 500 km/h this is the planet closest to the Sun this is the largest planet in our solar system this planet has a moon named Triton that revolves around it in the opposite direction to the planet’s rotation this gas giant is the least dense of all the planets and currently has over 50 moons this planet’s atmosphere is composed primarily of carbon dioxide gas this planet is dry and barren with many craters and reddish soil Name the terms a groups of stars, bound together by gravity, that travel together through space a star that releases enormous amounts of energy and, depending on its mass, will produce a neutron star or black hole a type of neutron star that beams out light and very high-energy radio waves a star-like object that emits powerful radio waves a collection of dust and gases, mainly hydrogen and helium, that results in the formation of new stars the end stage of a supernova that contains such a dense core, that even light cannot escape a massive grouping of gas, dust, and stars that can be elliptical, spiral, or irregular. 1. The patterns in the sky that are not official constellations are called ____________________. 2. The Aquila, Cassiopeia, and Orion are all examples of ____________________. 3. A ______ is a star in its final phases of life, when it explodes to many times its original size. 4. Objects that are located beyond the eighth planet are referred to as ___________________. 5. Impact craters on Earth are caused by _________. 6. The common name for the aurora borealis is the __. 7. The outer planets are also known as the _______ due to their mass and composition. 8. The _____________ theory is the most widely accepted theory of the origin of the universe. 9. A mathematical method used to measure interstellar distances by using the apparent motion of a nearby star against the background of a more distant, non-moving star is called _________. 10. Light can travel a distance of _____ in one second. 11. When all of the hydrogen of the Sun is used up, it will turn into a ____________________.










![SolarsystemPP[2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081776_2-3f379d3255cd7d8ae2efa11c9f8449dc-150x150.png)
















