* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Subject:
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Statistical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Detailed balance wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme catalysis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Reaction progress kinetic analysis wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
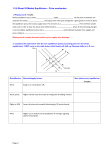
Subject: Chemistry Timeframe Needed for Completion: 5 days Grade Level/Course: 10-12 Unit Title: Collision Theory and Chemical Equilibrium Grading Period: 3rd six weeks Big Idea/Theme: Understanding how effective collisions encourage chemical reactions and how pressure, temperature and concentration affects the progression of equilibrium in a reversible reaction Learning Targets: (“I can” or “I will” statements) I will understand the factors that affect the rate of reactions I will be able to define catalyst and understand their role in the rate of chemical reactions. I will be able to interpret information from graphs that represent catalyzed and uncatalyzed endergonic and exergonic reactions. I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach equilibrium. Essential Questions: (3-5 questions per unit) – This is not a yes or no question; it must be broad, debatable, and thought-provoking. Curriculum Goals/Objectives: (Common Core or Essential Standards) Do you think Fritz Haber should have been awarded a Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his contributions to the field? Explain your answer. If you could create a catalyst to speed up any chemical reaction, which reaction would it be and describe the shape of your catalyst. Chem 2.2.1Explain the energy content of chemical reactions. Chem 3.1.1 Explain the factors that affect the rate of a reaction Chem 3.1.2 Explain the conditions of a system at equkibrium Chem 3.1.3 Infer the shift in equilibrium when a stress is applied to a system. Essential Concepts: Assessment Tasks: (examples of summative and/or formative assessments) 1-Identifying factors that affect rate ( temperature, concentration, particle size and the presence of a catalyst) 2-Use an energy graph to determine the following for a forward and reverse catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction - ∆H, activation energy, potential energy of the products and reactants 3- Understand the concept of chemical equilibrium and calculate equilibrium values using keq. 4- Compare keq and Q values to determine the direction a reaction will proceed if it is not at equilibrium. Graphs of reactions both catalyzed and uncatalyzed Worksheets Quizzes Tests Red, green, yellow cards Thinking maps Project on Haber processing plants and their importance to the world economy Two 15 minute videos on chemical kinetics and catalysts Readings from Current Science Other Integration Opportunities: (literacy anchor standards, Information and Technology Essential Standards, 21st century content and skills, other disciplines) Literacy Determine central idea or conclusions of a text Follow precisely a complex, multistep procedure when carrying out experiments. Determine the meaning of symbols and key terms. Write informative/explanatory texts. ITES Evaluate resources for reliability. Evaluate content for relevance to the assigned task. Analyze ethical issues and practices related to copyright, not plagiarizing, and netiquette. 21st Century Skills Students can determine the verifiability of evidence in print and electronic resources to evaluate scientific claims. Students can provide of examples of how scientists use technology to expand their research. Students apply their scientific knowledge to a variety of situations. Students have a variety of opportunities to read/review and interpret scientific information through popular and professional media in areas that interest them, and are able to discuss their thoughts and questions on these topics informally with peers. Resources: Worksheets and paper handouts 30% peroxide manganese dioxide videos Current Science magazine










![[A, 8-9]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006655537_1-7e8069f13791f08c2f696cc5adb95462-150x150.png)