* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IIT Paper 2010 - auroraclasses.org
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
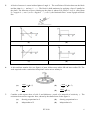
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of mass wikipedia , lookup
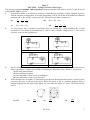
1. 2. 3. IIT-2010 PART-I Physics Paper-1 SECTION – I (Single Correct Choice Type) This Section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x-axis. It is at rest and from t = 0 onwards it is subjected to a time-dependent force F(t) in the x direction. The force F(t) varies with t as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is (a) 4.50 J (b) 7.50 J (c) 5.06 J (d) 14.06 J A uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R carries uniform surface charge density of σ per unit area. It is made of two hemispherical shells, held together by pressing them with force F (see figure). F is proportional to (a) 1 2 2 σR ε0 (b) 1 2 σR ε0 (c) 1σ 2 ε0 R (d) 1σ 2 ε0R 2 A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field of strength 4. 5. 6. 81π 7 ×105 Vm -1 . When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 × 10−3 ms−1. Given g = 9.8 ms−2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10−5 Ns −2 m and the density of oil = 900 kg m−3, the magnitude of q is (a) 1.6 × 10−19C (b) 3.2 × 10−19 C (c) 4.8 × 10−19 C (d) 8.0 × 10−19 C A Vernier calipers has 1 mm marks on the main scale. It has 20 equal divisions on the Vernier scale which match with 16 main scale divisions. For this Vernier calipers, the least count is (a) 0.02 mm (b) 0.05 mm (c) 0.1 mm (d) 0.2 mm A biconvex lens of focal length 15 cm is in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the lens and the mirror is 10 cm. A small object is kept at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. The final image is (a) virtual and at a distance of 16 cm from the mirror (b) real and at a distance of 16 cm from the mirror (c) virtual and at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror (d) real and at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror A hollow pipe of length 0.8 m is closed at one end. At its open end a 0.5 m long uniform string is vibrating in its second harmonic and it resonates with the fundamental frequency of the pipe. If the tension in the wire is 50 N and the speed of sound is 320 ms−1, the mass of the string is (a) 5 grams (b) 10 grams (c) 20 grams (d) 40 grams IIT-2010 1 SECTION –II (Integer Type) This Section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question no. in the ORS is to be bubbled. 7. A large glass slab (μ = 5/3) of thickness 8 cm is placed over a point source of light on a plane surface. It is seen that light emerges out of the top surface of the slab from a circular area of radius R cm. What is the value of R? [Ans.6] 8. Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 m along its optical axis is observed to move from 25 3 m to 50 7 m in 30 seconds. What is the speed of the object in km per hour ? 9. [Ans.3] To determine the half life of a radioactive element, a student plots a graph of n dN(t) versus t. Here dt dN(t) is the rate of radioactive decay at time t. If dt the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16 years, the value of p is [Ans.8] 10. A diatomic ideal gas is compressed adiabatically to 1 32 11. of its initial volume. If the initial temperature of the gas is Ti (in elvin) and the final temperature is aTi the value of a is [Ans.4] At time t = 0, a battery of 10 V is connected across points A and B in the given circuit. If the capacitors have no charge initially, at what time (in seconds) does the voltage across them becomes 4 volt? [Ans.2] [take n 5 = 1.6, n 3 = 1.1] SECTION –III (Paragraph Type) This Section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Paragraphs for Question 50 To 52 When liquid medicine of density ρ is to be put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop. We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When the force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper. 12. If the radius of the opening of the dropper is r, the vertical force due to the surface tension on the drop of radius R (assuming r < R) is IIT-2010 2 (a) 13. 14. 2 (b) 2RT (c) 2 r 2 T R (d) 2 R 2 T r If r = 5×10-4 m, ρ= 103 kg m-3, g = 10 m/s2, T = 0.11 Nm-1, the radius of the drop when it detaches from the dropper is approximately (a) 1.4 × 10-3 m (b) 3.3 × 10-3 m (c) 2.0 × 10-3 m (d) 4.1 × 10-3 m After the drop detaches, its surface energy is (a) 1.4 ×10-6J (b) 2.7 ×10-6J (c) 5.4 ×10-6J (d) 8.1 × 10-6J Paragraph for questions 53 to 55. The key feature of Bohr’s theory of spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantization of angular momentum when an electron is revolving around a proton. We will extend this to a general rotational motion to find quantized rotational energy of a diatomic molecule assuming it to be rigid. The rule to be applied is Bohr’s quantization condition. 15. A diatomic molecule has moment of inertia I. By Bohr’s quantization condition its rotational energy in the nth level (n = 0 is not allowed) is (a) 16. 1 h2 n 2 8 I (c) h2 2 8 I n (d) h2 2 8 I n2 It is found that the excitation frequency from ground to the first excited state of rotation for the CO 4 10-34 Hz . Then the moment of inertia of CO molecule about its centre of mass is close to (Take h = 2π × 10-34 Js) (a) 2.76 × 10−46 kg m2 (b) 1.87 × 10−46 kg m2 −47 2 (c) 4. 67 × 10 kg m (d) 1.17 × 10−47 kg m2 In a CO molecule, the distance between C (mass = 12 a.m.u) and O (mass = 16 a.m.u.), where 1 molecule is close to 17. 1 h2 n 8 2 I (b) a.m.u. 5 10-27 kg , 3 (a) 1. 6. 16. is close to 2.4 × 10-10m (c) (b) (b) 1.9 ×10-10m (b) (c) 2. ANSWER-SHEET IIT- JEE-2010 PAPER - 1 (a) 3. (d) 12. 17. (c) (c) 13. (a) 1.3 ×10-10m (d) 4.4 ×10-10m 4. (d) 5. (b) 14. (b) 15. (d) SECTION – IV (Matrix Type) This Section contains 2 questions. Each question has four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with one or more statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question, statement B matches with the statements given in q and r, then for that particular question, against statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS. 18. Two transparent media of refractive indices 1 and 3 have a solid lens shaped transparent material of refractive index 2 between them as shown in figures in Column II. A ray traversing these media is also shown in the figures. In Column I different relationships between 1, 2 and 3are given. Match them to the ray diagram shown in Column II. IIT-2010 3 (a) Column I 1 < 2 (p) Column II (b) 1 > 2 (q) (c) 2 = 3 (r) (d) 2 > 3 (s) (t) Ans. 19. A : p and r B: q anf s and t C: p and r and t D: q and s You are given many resistances, capacitors and inductors. These are connected to a variable DC voltage source (the first two circuits) or an AC voltage source of 50 Hz frequency (the next three circuits) in different ways as shown in Column II. When a current I (steady state for DC or rms for AC) flows through the circuit, the corresponding voltage V1 and V2.(indicated in circuits) are related as shown in Column I. (a) Column I I ≠ 0, V1 is proportiona l to I (b) I ≠ 0, V2 > V1 (c) V1 = 0, V2 =V (d) I ≠ 0, V2 is proportiona l to I Column II ( p ) ( q ) ( r ) ( s ) ( t ) Ans. A: C: r and s and t, p and q B: D: q and r and s and t q and r and s and t PHYSICS IIT-2010 4 Paper-2 SECTION – I (Single Correct Choice Type) This Section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. 1. Incandescent bulbs are designed by keeping in mind that the resistance of their filament increases with the increase in temperature. If at room temperature, 100 W, 60 W and 40 W bulbs have filament resistances R100, R60 and R40, respectively, the relation between these resistances is (a) (c) 2. 1 R100 1 R40 1 (b) R60 R100 > R60 > R40 R100 = R40 + R60 (d) 4. R100 1 R60 1 R40 To verify Ohm's law, a student is provided with a test resistor RT, a high resistance R1, a small resistance R2, two identical galvanometers G1 and G2, and a variable voltage source V. The correct circuit to carry out the experiment is (a) 3. 1 (b) (c) (d) An AC voltage source of variable angular frequency ω and fixed amplitude V0 is connected in series with a capacitance C and an electric bulb of resistance R (inductance zero). When ω is increased (a) the bulb glows dimmer (b) the bulb glows brighter (c) total impedance of the circuit is unchanged (d) total impedance of the circuit increases. A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed points and carries a current I in the clockwise direction, as shown in the figure. When the system is put in a uniform magnetic field of strength B going into the plane of the paper, the wire takes the shape of a circle. The tension in the wire is (a) IBL (b) IBL (c) IBL IIT-2010 2 (d) IBL 4 5 5. 6. A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle θ. The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is μ and tan θ > μ. The block is held stationary by applying a force P parallel to the plane. The direction of force pointing up the plane is taken to be positive. As P is varied from P1 = mg(sinθ−μcosθ) to P2 = mg(sinθ + μcosθ), the frictional force f versus P graph will look like (b) (c) (d) A thin uniform annular disc (see figure) of mass M has outer radius 4R and inner radius 3R. The work required to take a unit mass from point P on its axis to infinity is (a) (c) 7. (a) 2GM 7R GM (4 2 5) (b) (d) 4R 2GM 7R 2GM 5R (4 2 5) ( 2 1) Consider a thin square sheet of side L and thickness t, made of a material of resistivity ρ. The resistance between two opposite faces, shown by the shaded areas In the figure is (a) directly proportional to L (b) directly proportional to t (c) independent of L (d) independent of t IIT-2010 6 8. A real gas behaves like an ideal gas if its (a) pressure and temperature are both high (b) pressure and temperature are both low (c) pressure is high and temperature is low (d) pressure is low and temperature is high SECTION – II (Multiple Correct Choice Type) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of which ONE OR MORE may be correct. 9. 10. 11. 12. A point mass of 1 kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass of 5 kg. After their collision, the 1 kg mass reverses its direction and moves with a speed of 2 ms-1. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct for the system of these two masses? (a) Total momentum of the system is 3 kg ms-1 (b) Momentum of 5 kg mass after collision is 4 kg ms-1 (c) Kinetic energy of the centre of mass is 0.75 J (d) Total kinetic energy of the system is 4J One mole of an ideal gas in initial state A undergoes a cyclic process ABCA, as shown in the figure. Its pressure at A is P0. Choose the correct option(s) from the following (a) Internal energies at A and B are the same (b) Work done by the gas in process AB is P0V0n 4 (c) Pressure at C is P0 4 (d) Temperature at C is T0 4 A student uses a simple pendulum of exactly 1m length to determine g, the acceleration due to gravity. He uses a stop watch with the least count of 1 sec for this and records 40 seconds for 20 oscillations. For this observation, which of the following statement(s) is (are) true? (a) Error ΔT in measuring T, the time period, is 0.05 seconds (b) Error ΔT in measuring T, the time period, is 1 second (c) Percentage error in the determination of g is 5% (d) Percentage error in the determination of g is 2.5% A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q1 and Q2 fixed at two different points on the x–axis are shown in the figure. These lines suggest that IIT-2010 7 13. (a) |Q1| > |Q2| (b) |Q1| < |Q2| (c) at a finite distance to the left of Q1 the electric field is zero (d) at a finite distance to the right of Q2 the electric field is zero. A ray OP of monochromatic light is incident on the face AB of prism ABCD near vertex B at an incident angle of 60 (see fig.) If the refractive index of the material of the prism is 3 , which of the following is (are) correct? (a) (b) (c) (d) The ray gets totally internally reflected at face CD The ray comes out through face AD The angle between the incident rays and the emergent ray is 90 The angle between the incident rays and the emergent ray is 120 SECTION –III (Paragraph Type) This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon the first paragraph 2 multiple choice questions and based upon the second paragraph 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of WHICH ONLY ONE CORRECT. Paragraph for Questions 14 to 15 Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature Tc(0). An interesting property of superconductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than Tc(0) if they are placed in a magnetic field, i.e., the critical temperature Tc (B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of Tc(B) on B is shown in the figure. 14. In the graphs below, the resistance R of a superconductor is shown as a function of its temperature T for two different magnetic fields B1 (solid line) and B2 (dashed line). If B2 is larger than B1 which of the following graphs shows the correct variation of R with T in these fields? (a) (b) IIT-2010 8 (c) 15. (d) A superconductor has TC (0) = 100 K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 Tesla is applied, its Tc decreases to 75 K. For this material one can definitely say that when (a) B = 5 Tesla, Tc (B)= 80 K (b) B = 5 Tesla, 75 K < Tc (B) < 100 K (c) B = 10 Tesla, 75K < Tc < 100 K (d) B = 10 Tesla, Tc = 70K Paragraph for Questions 16 to 18 When a particle of mass m moves on the x-axis in a potential of the form V(x) = kx2 it performs m simple harmonic motion. The corresponding time period is proportional to as can be seen k , easily using dimensional analysis. However, the motion of a particle can be periodic even when its potential energy increases on both sides of x = 0 in a way different from kx 2 and its total energy is such that the particle does not escape to infinity. Consider a particle of mass m moving on the x-axis. Its potential energy is V(x) = αx4 (α > 0) for |x| near the origin and becomes a constant equal to V0 for |x| ≥ X0 (see figure). 16 17. If the total energy of the particle is E, it will perform periodic motion only if (a) E<0 (b) E>0 (c) V0 > E > 0 (d) E > V0 For periodic motion of small amplitude A, the time period T of this particle is proportional to (a) 18. A m (b) 1 m A (c) A (b) proportional to (d) zero m (d) 1 A m The acceleration of this particle for |x| > X0 is (a) proportional to V0 (c) proportional to A V0 mX 0 ANSWER-SHEET IIT- JEE-2010 PAPER - 2 IIT-2010 V0 mX 0 9 1. 6. 11. 16. (d) (a) (a,c) (c) 2. 7. 12. 17. (c) (c) (a,d) (b) 3. 8. 13. 18. (b) (d) (a,b,c) (d) 4. 9. 14. (c) (a,c) (a) 5. 10. 15. (a) (a,b) (b) SECTION –IV (Integer Type) This section contains TEN questions. The answer to each question is a single digit integer ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question number in the ORS is to be bubbled. 19. 20. 21. 22. 6 g , where g is the gravitational 11 2 acceleration on the surface of the earth. The average mass density of the planet is times that of the 3 -1 earth. If the escape speed on the surface of the earth is taken to be 11 kms , the escape speed on the surface of the planet in kms-1 will be [Ans. 3 km/s] -1 ° -1 -1 A piece of ice (heat capacity = 2100 J kg C and latent heat = 3.36 ×105J kg ) of mass m grams is at -5°C at atmospheric pressure. It is given 420 J of heat so that the ice starts melting. Finally when the ice-water mixture is in equilibrium, it is found that 1 gm of ice has melted. Assuming there is no other heat exchange in the process, the value of m is [Ans. 8] A stationary source is emitting sound at a fixed frequency f0, which is reflected by two cars approaching the source. The difference between the frequencies of sound reflected from the cars is 1.2% of f0. What is the difference in the speeds of the cars (in km per hour) to the nearest integer ? The cars are moving at constant speeds much smaller than the speed of sound which is 330 ms-1. [Ans. 7] The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20 cm. When an object is moved from a distance of 25 cm m in front of it to 50 cm, the magnification of its image changes from m25 to m50. The ratio 25 is m50 Gravitational acceleration on the surface of a planet is [Ans. 6] 23. An α- particle and a proton are accelerated from rest by a potential difference of 100 V. After this, p their de Broglie wavelengths are λα and λp respectively. The ratio to the nearest integer, is p [Ans.3] 24. When two identical batteries of internal resistance 1 each are connected in series across a resistor R, the rate of heat produced in R is J1. When the same batteries are connected in parallel across R, the rate is J2. If J1 = 2.25 J2 then the value of R in is [Ans. 4] 25. Two spherical bodies A (radius 6 cm) and B(radius 18 cm) are at temperature T1 and T2, respectively. The maximum intensity in the emission spectrum of A is at 500 nm and in that of B is at 1500 nm. Considering them to be black bodies, what will be the ratio of the rate of total energy radiated by A to that of B? [Ans. 9] 26. 27. When two progressive waves y1 4sin(2 x 6t ) and y2 3sin 2 x 6t are superimposed, the 2 amplitude of the resultant wave is [Ans. 5] A 0.1 kg mass is suspended from a wire of negligible mass. The length of the wire is 1m and its crosssectional area is 4.9 × 10-7 m2. If the mass is pulled a little in the vertically downward IIT-2010 10 direction and released, it performs simple harmonic motion of angular frequency 140 rad s-1. If the Young’s modulus of the material of the wire is n × 109 Nm-2, the value of n is [Ans. 4] 28. A binary star consists of two stars A (mass 2.2Ms) and B (mass 11Ms), where Ms is the mass of the sun. They are separated by distance d and are rotating about their centre of mass, which is stationary. The ratio of the total angular momentum of the binary star to the angular momentum of star B about the centre of mass is [Ans. 6] IIT-2010 11