* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parametric Equations
Survey
Document related concepts
Homogeneous coordinates wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Vector space wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean vector wikipedia , lookup
Basis (linear algebra) wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Covariance and contravariance of vectors wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
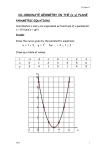
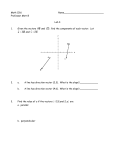
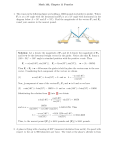
Review Parametric Equations x f (t) parametric equations of a curve with parameter y g(t) ex. Graph the following parametric equations and find the Cartesian equation of the curve that the equations trace. x t 3 2, y 2t 2 , 0 t 3 t. ex. x 2cos2 sin t, y sin sin t , 0 t 2 Polar Coordinates x 2 y2 r 2 x r cos y r sin y tan x Convert between polar and Cartesian 7 r, 5, ex. 6 ex. x, y 3 3, 3 ex. The Cartesian equation for ex. is: : ex. Plot the curve r 2 16cos(2 ) Complex Numbers z x iy z re i Cartesian form Polar form ex. 2i z 4 2i ex. z 1 i 12 ex. z 12 1 i Basic Vectors 1. Find a vector between points A(3, 4) and B(-5, 1). 2. Find point C which is equally distant from point A as point B in the direction of vector <-4, -3>. 3. Is vector AC orthogonal to AB? parallel? What is the angle between AC and AB? Understand dot and cross products. Lines and Planes The parametric equations of a line are: x a v1t y b v2 t z c v 3t The equation of a plane is is the normal vector and ex. n1 x n2 y n3 z n p where n p is the vector formed by the point. Vector-valued Functions Be able to differentiate and integrate vector-valued functions. y 0 Projectiles: maximum height y 0 maximum range If non constant gravity, be able to integrate from acceleration at 0,g to find velocity and position. Formulas v T Unit tangent vector; v s t v dt t2 Arclength: 1 Unit normal vector: Curvature: T N T T v v t at v t or at aT T aN N Components of acceleration: aT dv dt va v 3 2 aN v va v














![Homework on FTC [pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008882242_1-853c705082430dffcc7cf83bfec09e1a-150x150.png)